Speed of Light - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how light travels faster than anything else in the universe!
What is the Speed of Light?
The speed of light is how fast light travels through space. In a vacuum (empty space with no air or other matter), light travels at an incredible 299,792,458 meters per second! That's about 186,282 miles per second.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that our eyes can detect. It travels in straight lines called rays and behaves both like a particle and a wave. The speed of light is constant in a vacuum, meaning it never changes and is the same for all observers.
Light Fact!
Light travels so fast that it could circle Earth 7.5 times in just one second!
How Fast is Light?
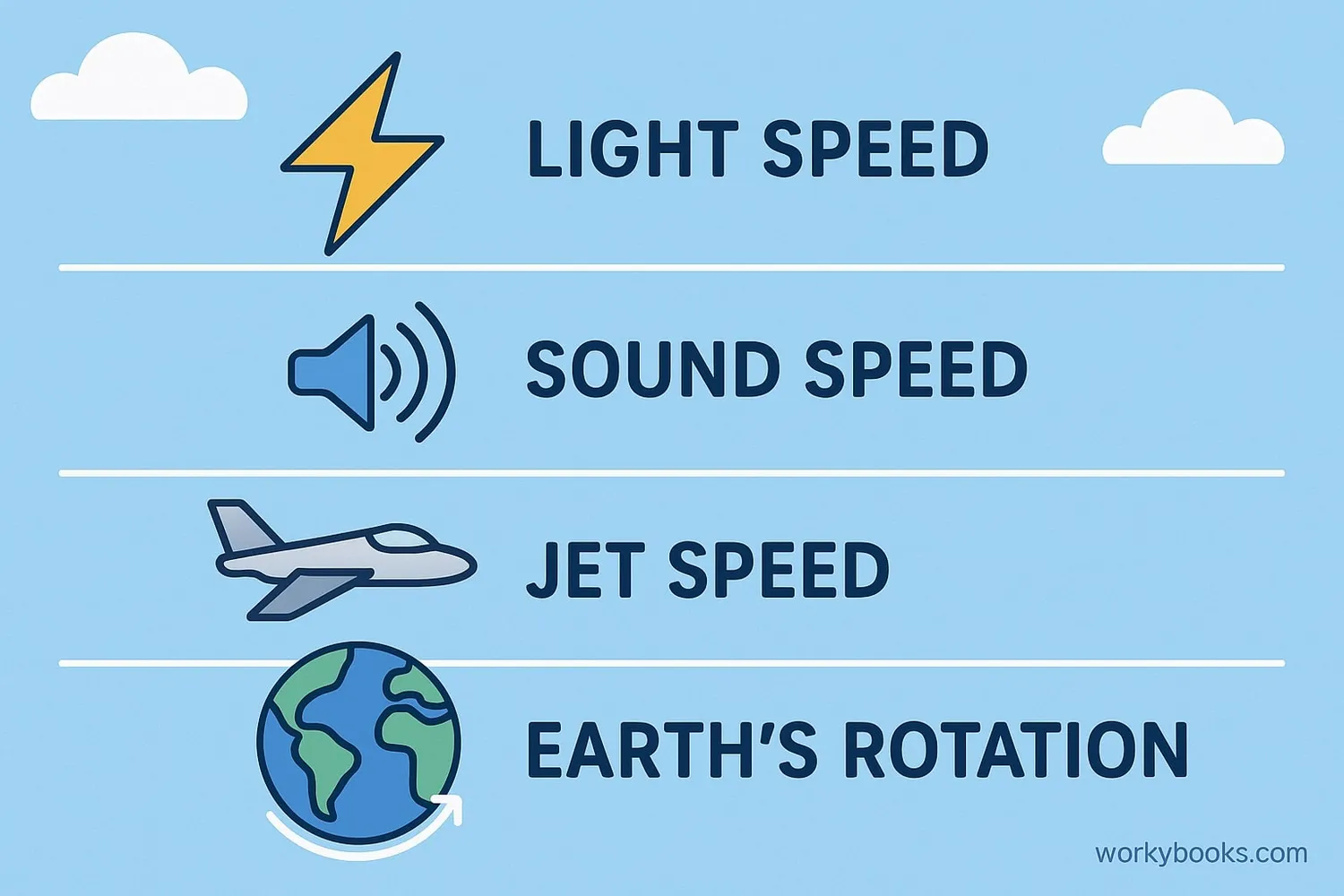
The speed of light is the fastest possible speed in the universe! Nothing travels faster than light. To understand just how fast light travels:
Earth to Moon
Light travels to the Moon in about 1.3 seconds
Earth to Sun
Light takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach Earth from the Sun
Across Our Galaxy
Light takes 100,000 years to cross the Milky Way galaxy
To Nearby Star
Light from Proxima Centauri takes 4.24 years to reach us
Scientists measure very large distances in space using light-years. One light-year is the distance light travels in one year - about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers)! This helps us understand the vast scale of the universe.
History of Measuring Light Speed

For centuries, scientists wondered if light had a finite speed or traveled instantly. Here's how we discovered and measured the speed of light:
Galileo's Attempt
In the 1600s, Galileo tried to measure light speed with lanterns on hills but concluded it was too fast to measure
Ole Roemer (1676)
By observing Jupiter's moon Io, Roemer first proved light has a finite speed and calculated 220,000 km/s
Michelson (1926)
Using rotating mirrors, Michelson measured light speed as 299,796 km/s - very close to today's value
Today, we use lasers and precise electronics to measure light speed with incredible accuracy. Since 1983, the meter has been defined as the distance light travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second!
Einstein and the Speed of Light
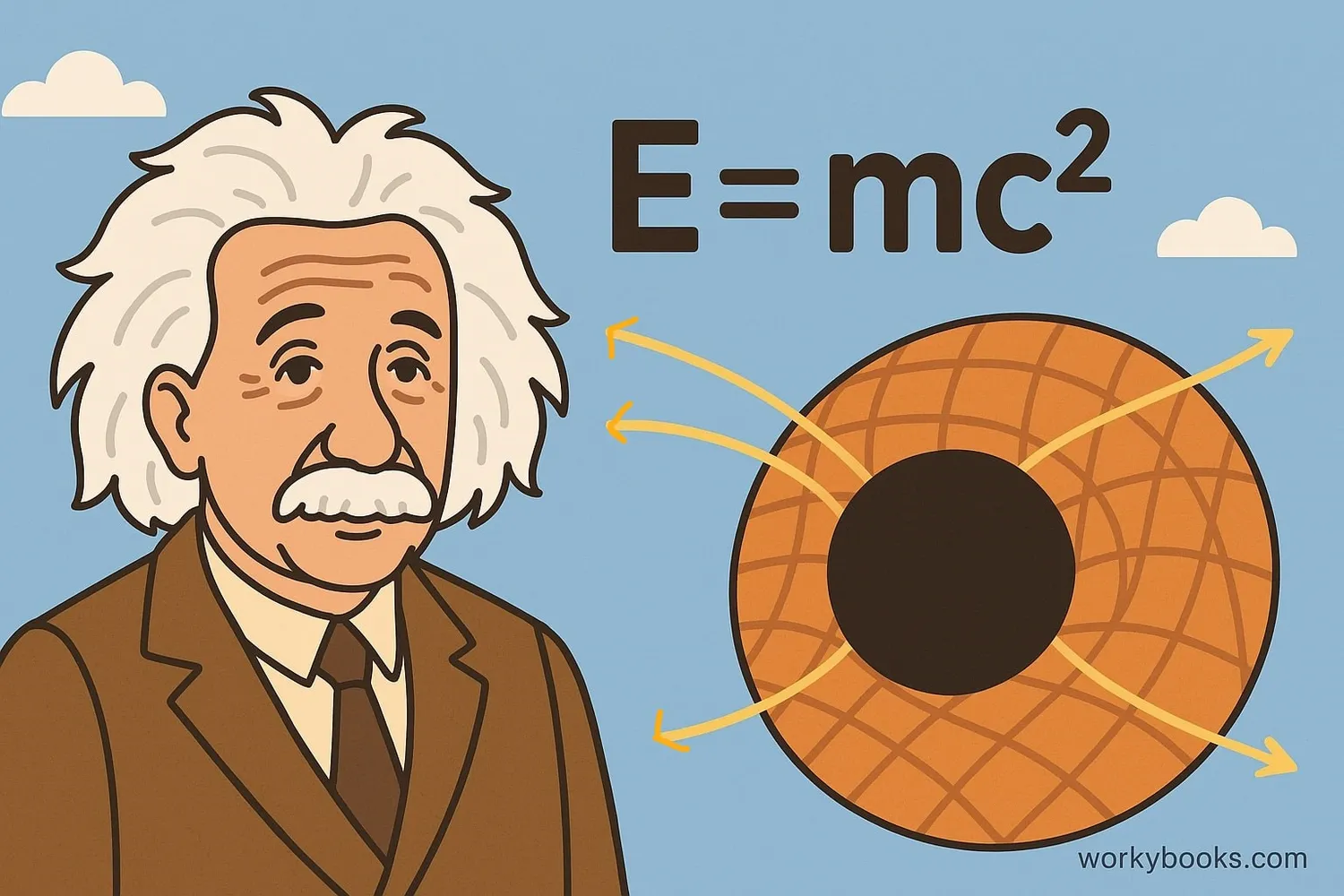
Albert Einstein's theory of relativity changed how we understand light, space, and time. His work showed that:
Constant Speed
Light speed is constant for all observers, no matter how fast they're moving
Cosmic Speed Limit
Nothing can travel faster than light in a vacuum
E=mc²
Energy and mass are related by the speed of light squared
Einstein discovered that time and space aren't fixed - they change depending on how fast you're moving. This is why astronauts on the International Space Station age slightly slower than people on Earth!
The equation E=mc² shows that a small amount of mass can be converted into a huge amount of energy because the speed of light is so enormous (c² = 89,875,517,873,681,764 m²/s²).
Speed of Light Quiz
Test your knowledge about the speed of light with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the speed of light:
Fascinating Light Speed Facts
Discover some amazing facts about the speed of light:
Looking Back in Time
When you look at stars, you're seeing them as they were in the past! The light from the nearest star (Proxima Centauri) takes 4 years to reach us, so we see it as it was 4 years ago.
Defining the Meter
Since 1983, the meter has been defined as the distance light travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second. The speed of light is now the standard for measuring distance!
Space Communication Delay
When NASA communicates with Mars rovers, there's a delay of 4-24 minutes each way due to light speed. Mission controllers have to plan commands in advance!
Massless Particles
Only massless particles like photons (light particles) can travel at light speed. Any particle with mass would require infinite energy to reach light speed.





