Adiabatic Cooling - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how cooling happens when air expands without losing heat!
What is Adiabatic Cooling?
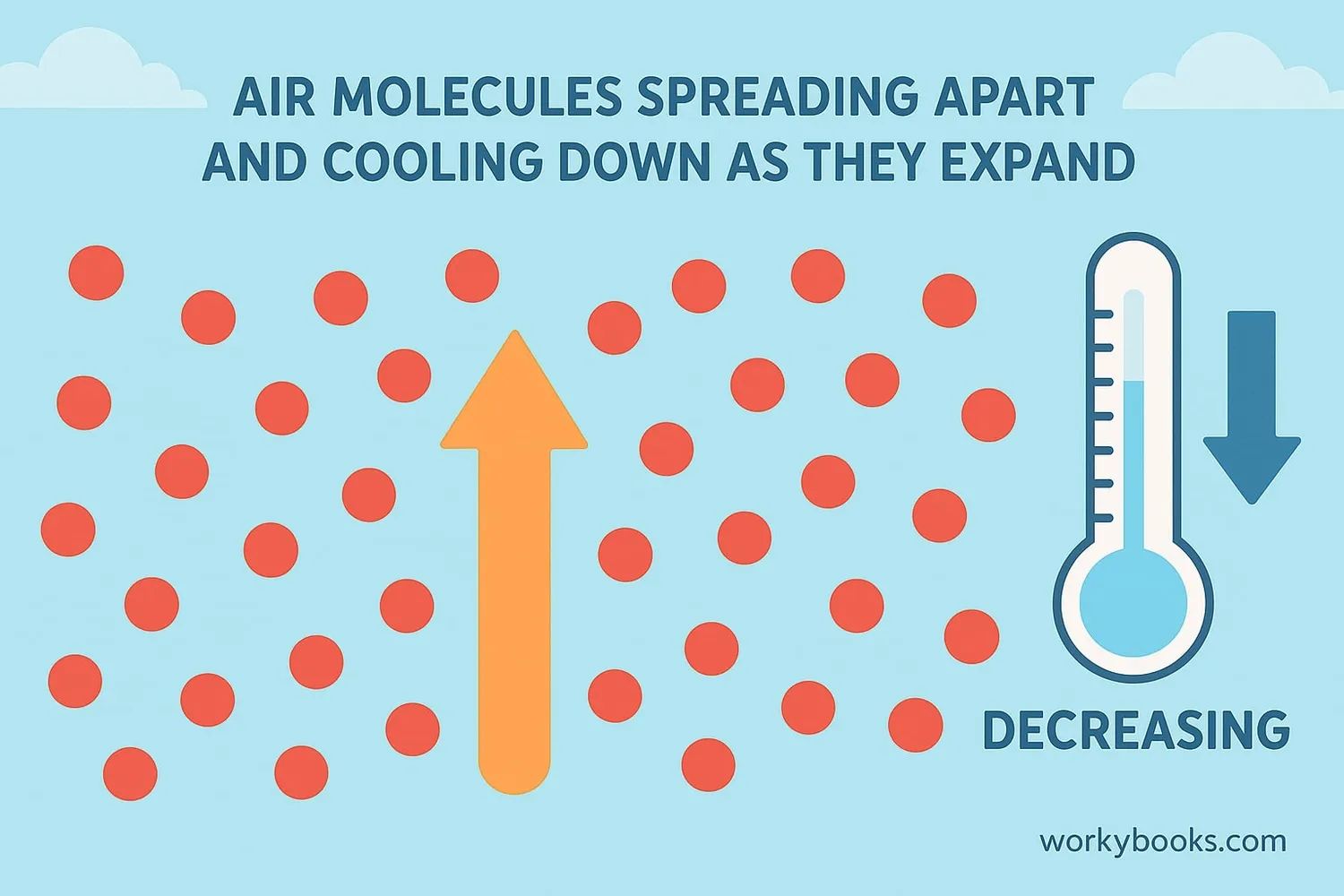
Adiabatic cooling is a natural process where air cools down as it expands without losing heat to its surroundings. The word "adiabatic" means "without heat transfer."
Think of it like this: When air expands, its molecules spread out and move slower, which makes the air cooler. No heat is added or removed from the environment - the cooling happens because the air is expanding.
This process is different from regular cooling because it doesn't require adding cold air or removing heat. It's all about the air expanding on its own!
Real-World Example
When you use a spray can, it gets cold because the gas inside expands quickly when released. That's adiabatic cooling in action!
How Adiabatic Cooling Works
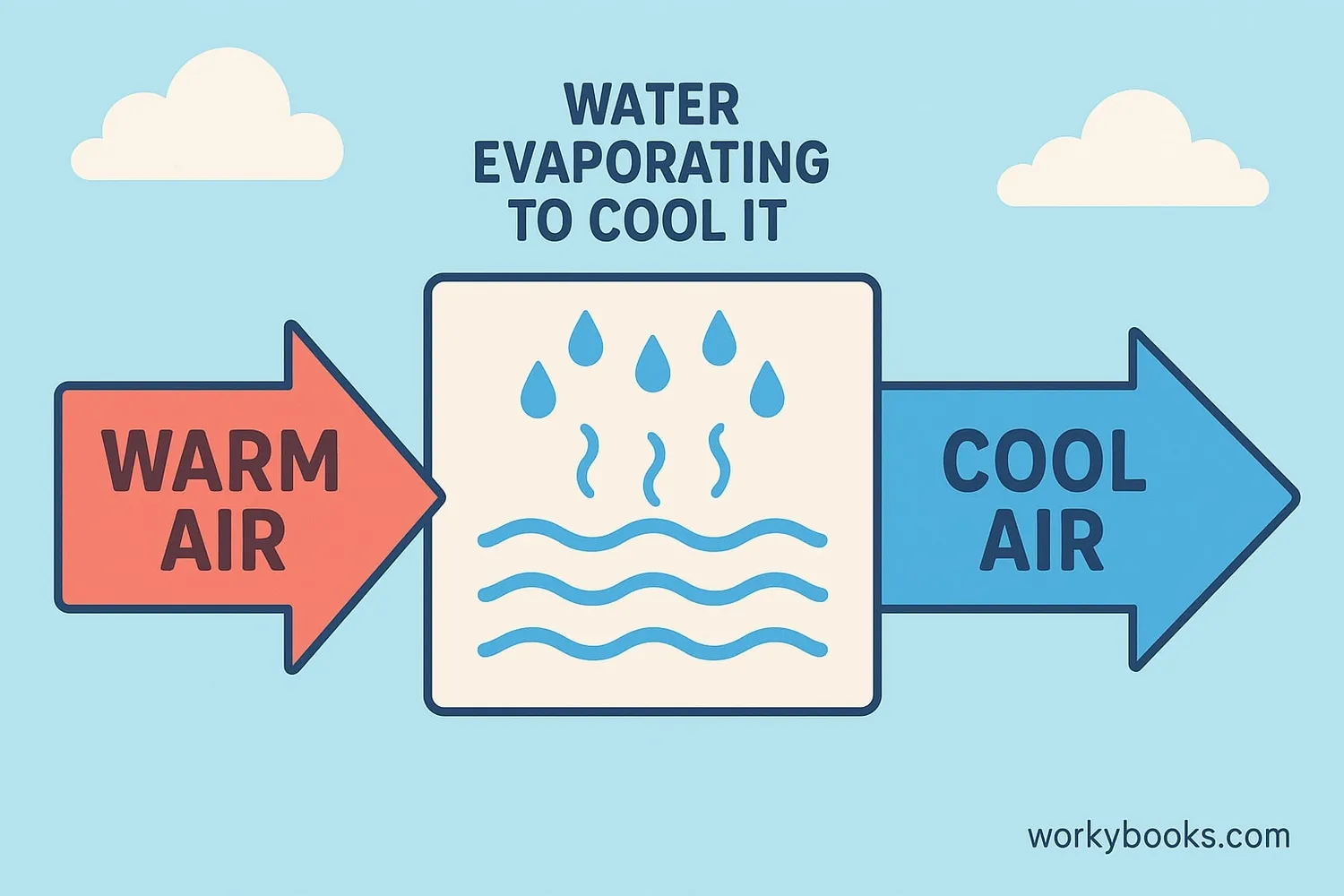
Adiabatic cooling systems use the natural process of evaporation to cool air efficiently. Here's how these systems work:
Warm Air Enters
Hot air from outside enters the cooling system
Water Evaporates
A fine mist of water is sprayed into the air
Heat Absorption
Water absorbs heat as it evaporates
Air Cools Down
The air temperature drops significantly
Cool Air Exits
Cooled air is distributed where needed
The key scientific principle is that when water evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding air. This causes the air temperature to drop without using much energy. Adiabatic cooling systems are much more efficient than traditional air conditioning!
Efficiency Fact
Adiabatic coolers can use up to 90% less electricity than traditional air conditioning systems!
Why Adiabatic Cooling is Important
Adiabatic cooling is becoming increasingly important in our world for several reasons:
Energy Efficiency
Uses much less electricity than traditional cooling methods
Water Conservation
Uses minimal water compared to other cooling systems
Environmentally Friendly
Reduces carbon footprint and uses natural refrigerants
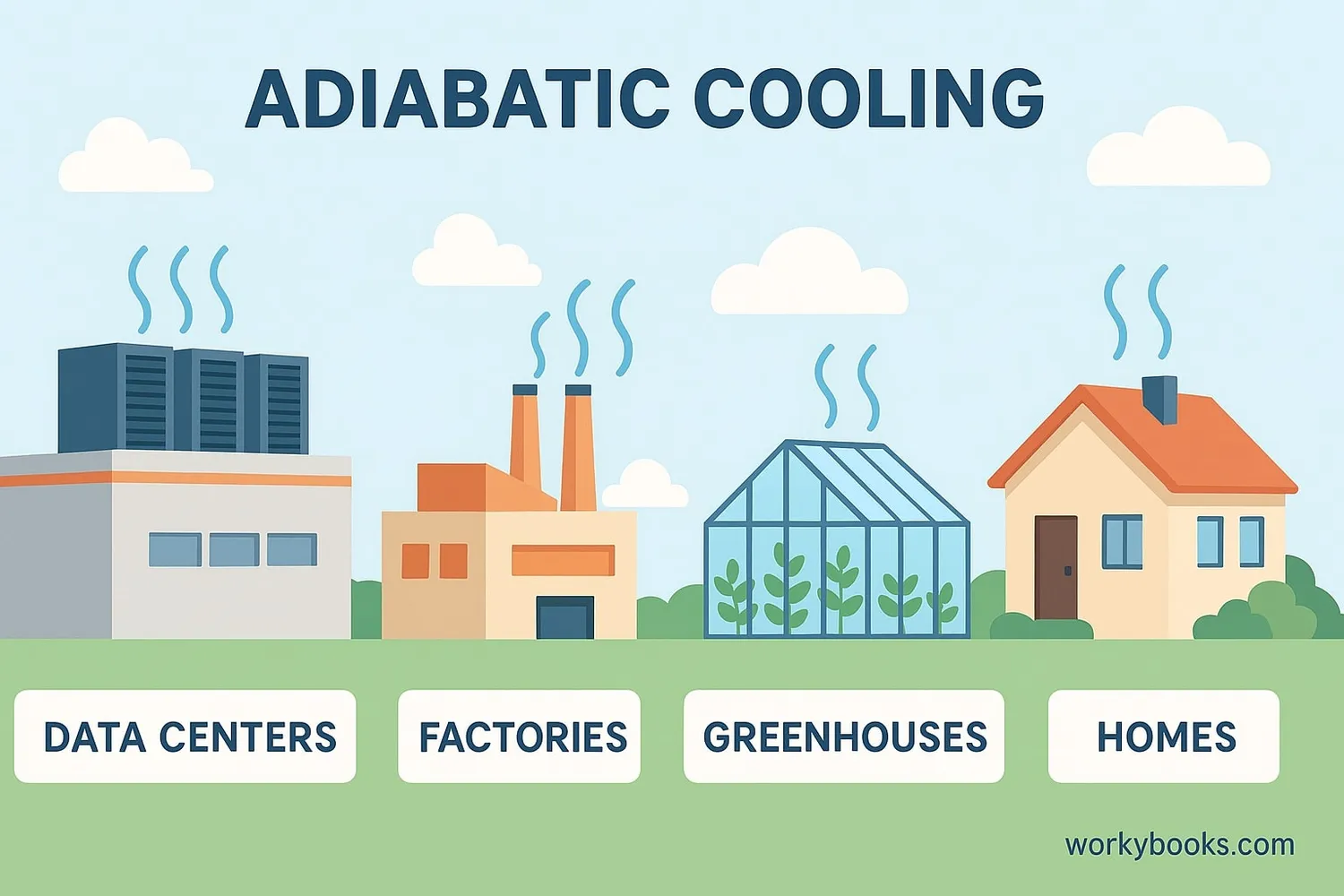
Adiabatic cooling is used in many important places:
• Data centers to keep computers cool
• Industrial processes in factories
• Large commercial buildings
• Greenhouses for plant growth
• Power plants for efficient operations
As our world gets warmer and energy costs rise, these efficient cooling systems help us stay comfortable while protecting our planet.
Adiabatic Cooling Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz on adiabatic cooling! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about adiabatic cooling:
Adiabatic Cooling Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about adiabatic cooling!
Nature's Cooling
Adiabatic cooling is why mountaintops are colder than valleys. As air rises and expands at higher altitudes, it cools naturally through adiabatic processes.
Water Savers
Some data centers using adiabatic cooling save over 20 million gallons of water annually compared to traditional cooling methods!
Industrial Impact
Factories using adiabatic cooling can reduce their energy consumption for cooling by up to 90%, making manufacturing more sustainable.
Ancient Technology
People have used evaporative cooling for thousands of years! Ancient Egyptians hung wet reeds in windows, and Romans circulated water through walls to cool buildings.





