Carbon Dioxide - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the invisible gas that powers life and affects our planet
What is Carbon Dioxide?
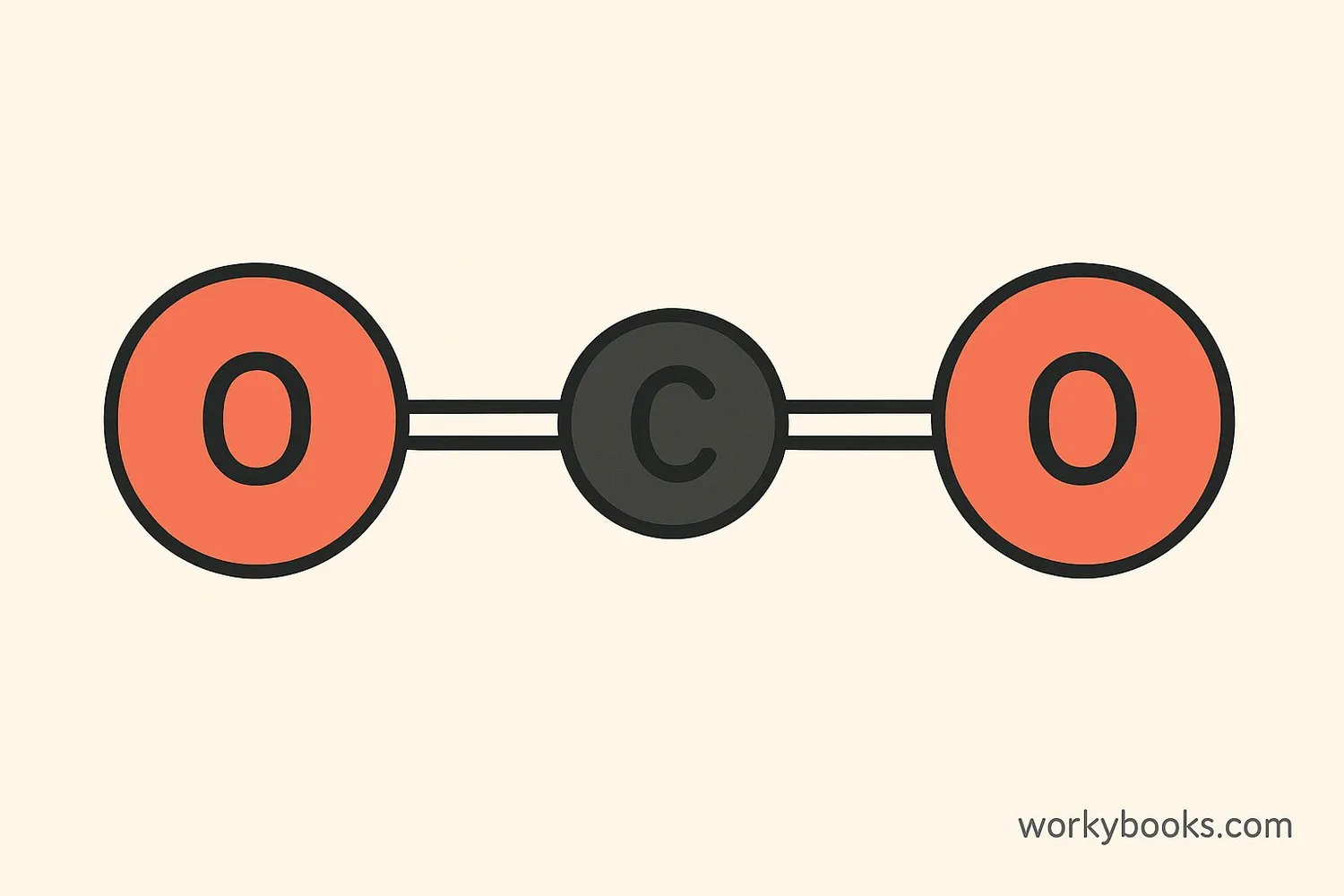
Carbon dioxide, often written as CO₂, is a colorless, odorless gas that exists naturally in Earth's atmosphere. It's made up of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms—that's what the "C" and "O₂" stand for in its name.
Even though you can't see or smell it, carbon dioxide is all around us and plays important roles in many natural processes. It's what we exhale when we breathe, what plants use to make their food, and what makes soda drinks fizzy!
Did You Know?
Carbon dioxide makes up only about 0.04% of Earth's atmosphere, but it has a huge impact on our planet's temperature!
Natural Gas
CO₂ exists naturally in Earth's atmosphere
Chemical Formula
One carbon atom bonded to two oxygen atoms
Essential for Life
Plants use CO₂ to create food through photosynthesis
The Carbon Cycle
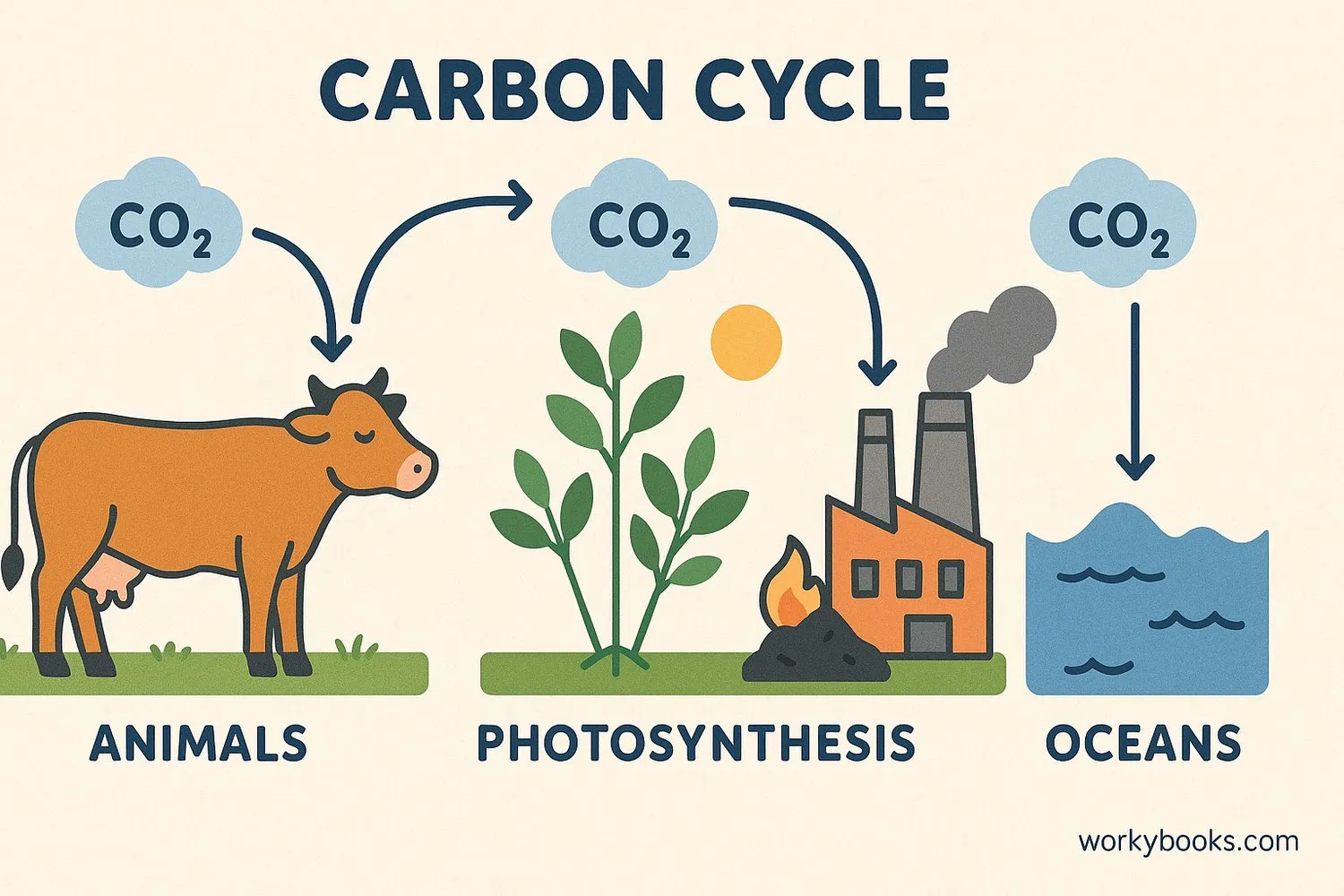
Carbon dioxide doesn't stay in one place—it constantly moves between the air, water, land, and living things in what scientists call the carbon cycle. This natural recycling process helps maintain balance in Earth's atmosphere.
Photosynthesis
Plants absorb CO₂ from the air and use sunlight to convert it into food
Respiration
Animals and humans breathe in oxygen and exhale CO₂
Ocean Exchange
Oceans absorb and release CO₂, helping regulate atmospheric levels
The carbon cycle is a delicate balance that has worked for millions of years. Human activities like burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and gas) are adding extra carbon dioxide to the atmosphere faster than natural processes can remove it, which is changing Earth's climate.
Carbon Dioxide and Climate Change
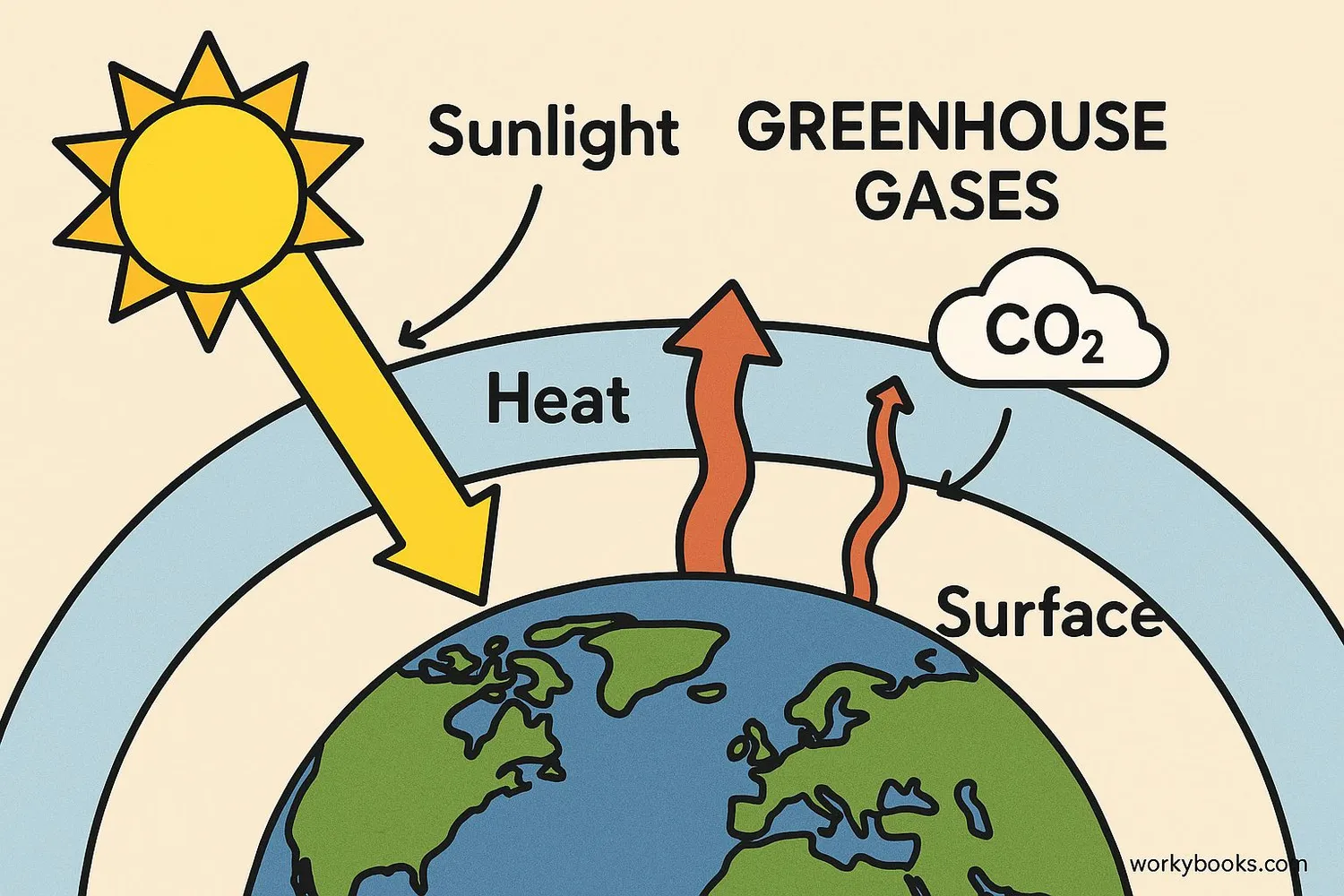
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, which means it helps trap heat in Earth's atmosphere. This natural greenhouse effect is what keeps our planet warm enough for life to exist. Without any greenhouse gases, Earth would be too cold for most living things.
However, human activities—especially burning fossil fuels for energy—have significantly increased the amount of CO₂ in the atmosphere. This enhanced greenhouse effect is causing Earth's average temperature to rise, leading to climate change.
Natural Greenhouse Effect
CO₂ and other gases naturally trap heat, keeping Earth warm
Human Activities
Burning fossil fuels releases extra CO₂ into the atmosphere
Enhanced Effect
Extra CO₂ traps more heat, causing global warming
Making a Difference
Reducing our carbon footprint by using less energy, choosing renewable resources, and planting trees can help balance the carbon cycle and slow climate change.
Carbon Dioxide Knowledge Quiz
Test what you've learned about carbon dioxide with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to check your understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about carbon dioxide:
Interesting Carbon Dioxide Facts
Discover some amazing facts about carbon dioxide!
Historical Discovery
Carbon dioxide was first identified in the 1750s by Scottish chemist Joseph Black. He called it "fixed air" and discovered it through experiments with limestone and other materials.
Dry Ice
Solid carbon dioxide is called dry ice because it doesn't melt into a liquid—it turns directly from solid to gas in a process called sublimation. It's extremely cold at -109.3°F (-78.5°C)!
Martian Atmosphere
The atmosphere on Mars is about 95% carbon dioxide! But the atmosphere is so thin that even with all that CO₂, Mars doesn't have a strong greenhouse effect like Earth.
Plant Food
In some greenhouses, growers increase CO₂ levels to 3-4 times normal atmospheric concentration. This "CO₂ enrichment" helps plants grow faster and produce higher yields!





