Polar Amplification - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover why the Arctic is warming faster than anywhere else on Earth!
What is Polar Amplification?

Polar amplification is a scientific term that describes how the Arctic and Antarctic are warming much faster than the rest of our planet. While the whole Earth is getting warmer due to climate change, the polar regions are heating up 2-4 times faster than other places!
Think of it like wearing a dark shirt on a sunny day - it gets hotter faster than a light-colored shirt. The polar regions act like Earth's "dark shirt," absorbing more heat and warming up quicker than other areas. This faster warming has big effects on ice, animals, and weather patterns all around the world.
Did You Know?
Since the 1970s, the Arctic has warmed about 3 times faster than the rest of the world! That's like going from a chilly day to a warm day much quicker at the poles than where you live.
Why Does Polar Amplification Happen?
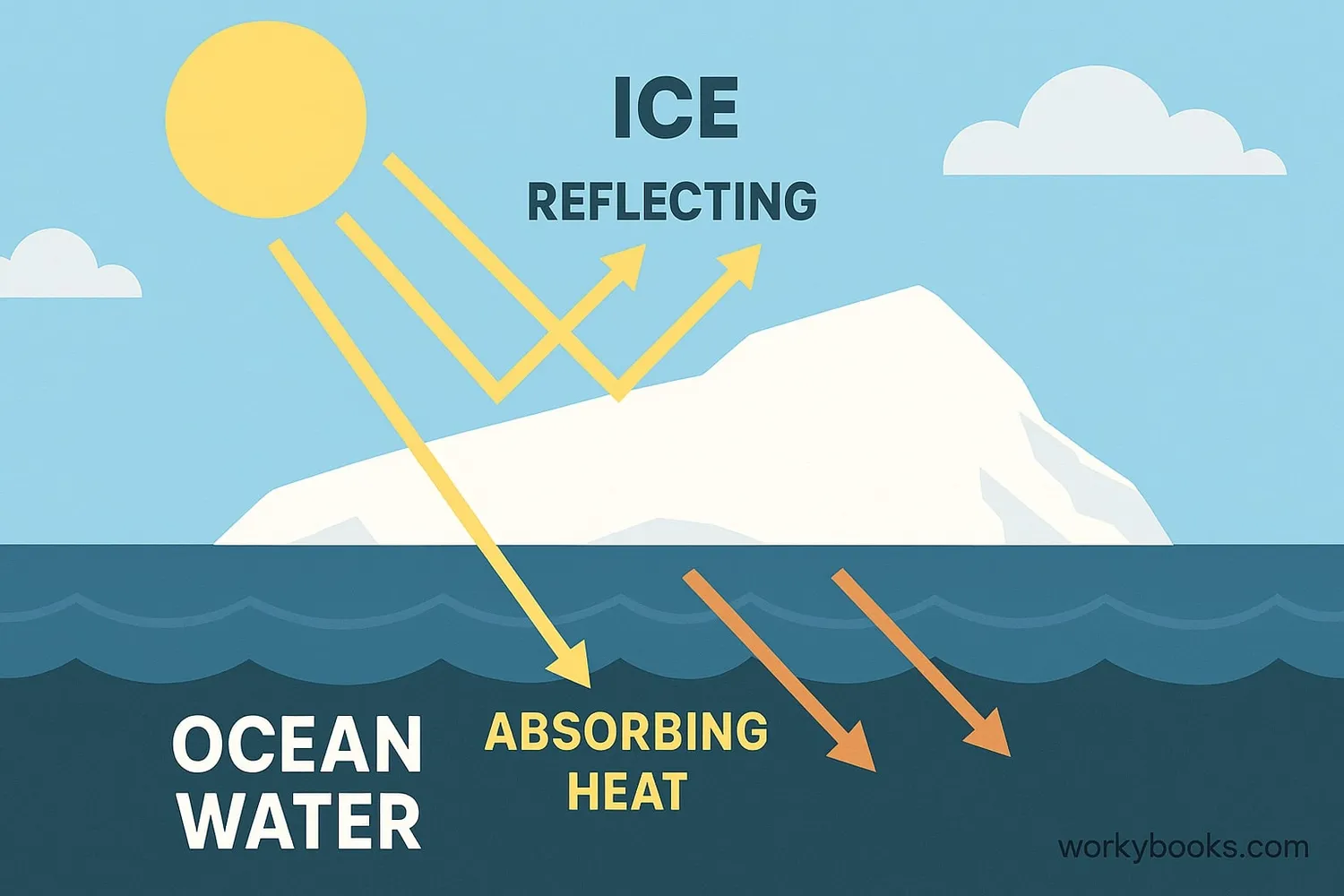
Polar amplification happens because of special processes that only occur at the poles. The main reason is called the ice-albedo feedback:
Ice Reflects
Bright white ice and snow reflect sunlight back to space
Ice Melts
As Earth warms, ice begins to melt
Dark Water
Dark ocean water is exposed where ice used to be
Heat Absorbed
Dark water absorbs more heat from the sun
More Melting
More ice melts, creating a warming cycle
This creates a "feedback loop" where warming leads to more warming. Other factors include:
• Ocean currents bringing warmer water to polar regions
• Atmospheric changes that trap more heat at the poles
• Cloud patterns that change with warming temperatures
Albedo Effect
Fresh snow can reflect up to 90% of sunlight, while ocean water absorbs about 90%! This huge difference explains why losing ice makes such a big impact.
Effects of Polar Amplification
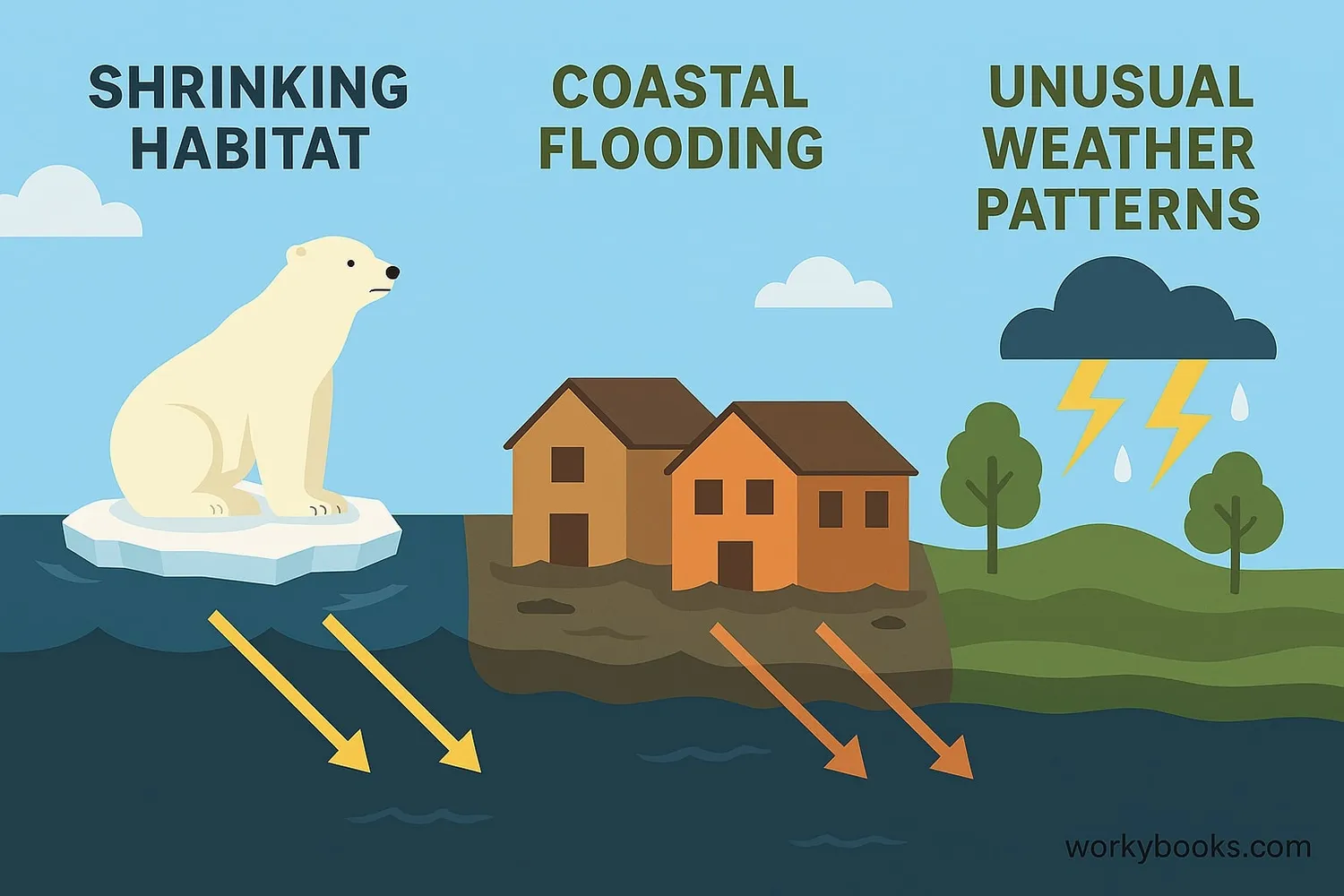
The faster warming at the poles affects our whole planet in important ways:
Sea Level Rise
Melting ice sheets add water to oceans, causing coastal flooding
Habitat Loss
Animals like polar bears lose their ice hunting grounds
Weather Changes
Jet stream patterns shift, causing extreme weather worldwide
Other important effects include:
• Thawing permafrost releases greenhouse gases
• Ocean currents may slow down, changing climate patterns
• Indigenous communities face challenges to their traditional ways of life
• Global temperatures increase faster as ice disappears
What happens at the poles doesn't stay at the poles - it affects weather, coastlines, and ecosystems all around the world!
Polar Amplification Quiz
Test what you've learned about polar amplification with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about polar amplification:
Polar Science Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about polar regions and climate science!
Massive Ice Sheets
Antarctica's ice sheet contains about 70% of Earth's fresh water! If it all melted, sea levels would rise about 60 meters (200 feet).
Record Temperature
In 2020, Siberia reached 38°C (100°F) - the hottest temperature ever recorded north of the Arctic Circle!
Underwater Forests
As sea ice retreats, sunlight reaches Arctic sea floors, allowing kelp forests to grow where they couldn't before - creating new ecosystems!
Ancient Air
Scientists study air bubbles trapped in polar ice that are hundreds of thousands of years old, helping us understand Earth's climate history.





