Aphelion - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth's orbit affects our distance from the Sun
What is Aphelion?
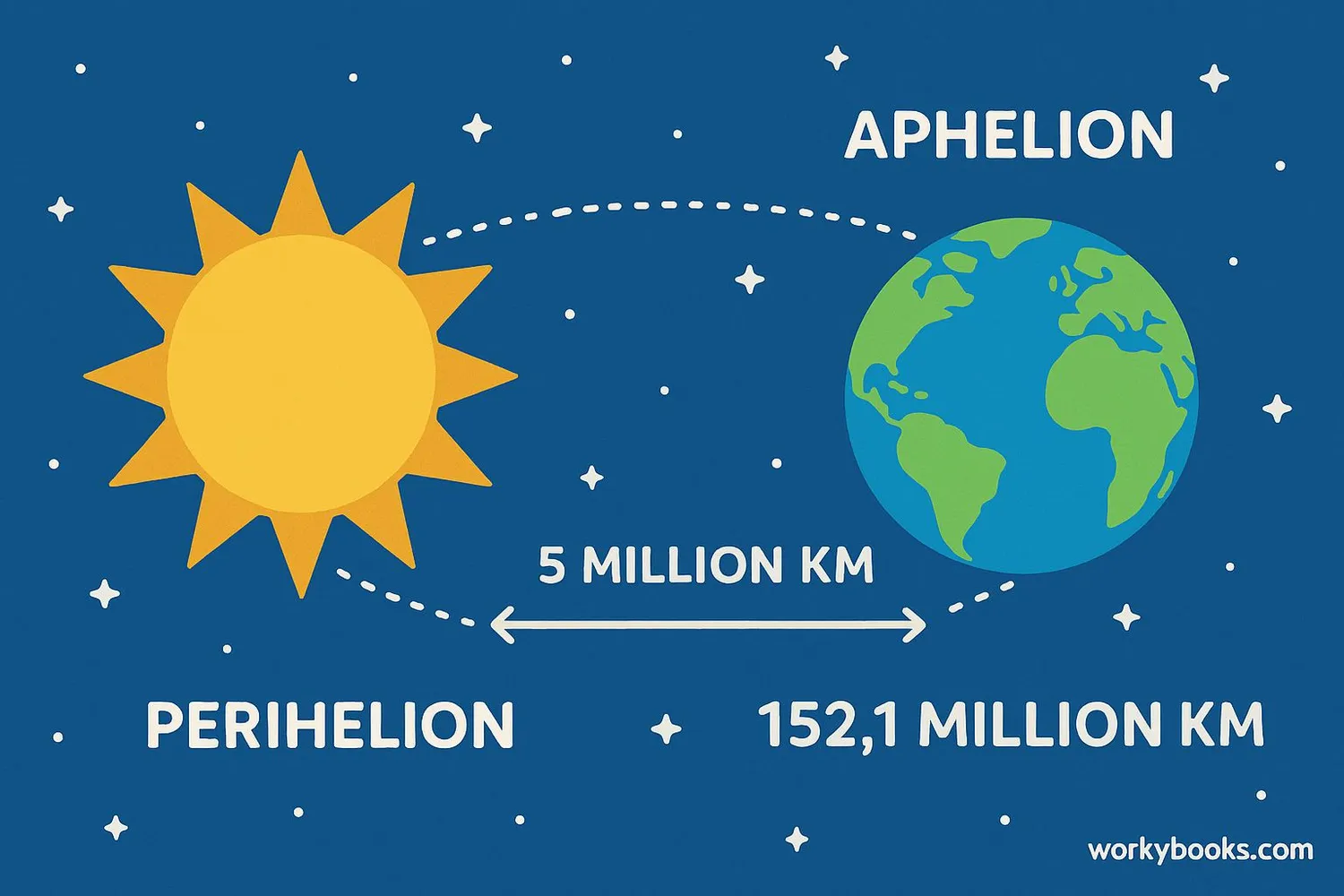
Aphelion (pronounced uh-FEE-lee-un) is the point in Earth's orbit when it's farthest from the Sun. This happens every year around July 4th. The word comes from Greek: "apo" meaning away, and "helios" meaning Sun.
Earth doesn't orbit in a perfect circle but follows an elliptical path. This means our distance from the Sun changes throughout the year. At aphelion, Earth is about 152 million kilometers (94.5 million miles) from the Sun. That's about 5 million km farther than at its closest point!
Space Fact!
Even though Earth is farthest from the Sun in July, it's summer in the Northern Hemisphere because seasons are caused by Earth's tilt, not distance!
How Aphelion Works
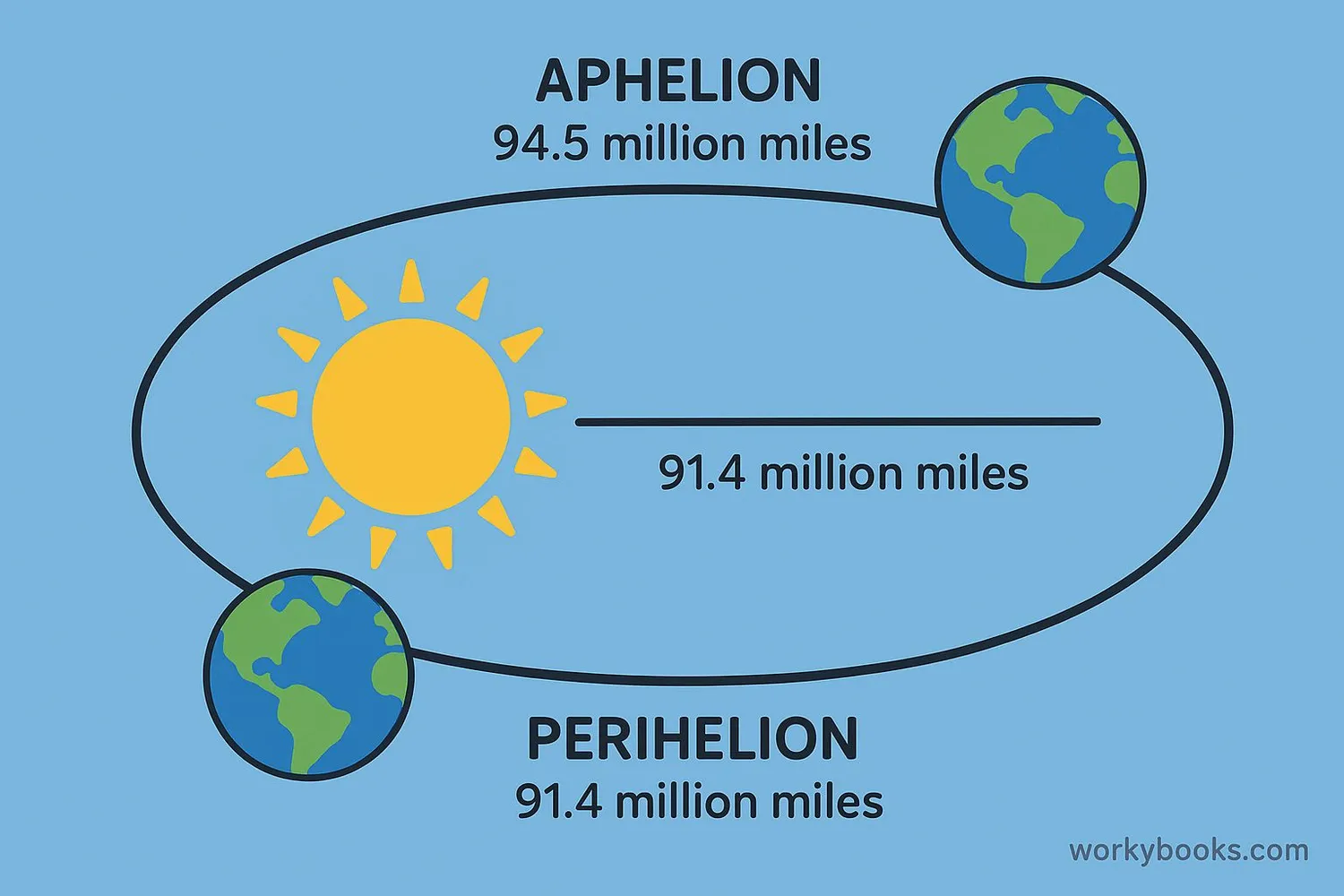
Earth's orbit is an ellipse - like a slightly flattened circle. Johannes Kepler discovered in the 1600s that planets orbit in ellipses with the Sun at one focus point. This is called Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion.
Here's how orbital mechanics work:
Elliptical Path
Earth follows an oval-shaped orbit around the Sun
Two Key Points
Aphelion (farthest) and perihelion (closest)
Orbital Speed
Earth moves slowest at aphelion (Kepler's Second Law)
Distance Difference
Earth is about 3.3% farther at aphelion
Annual Cycle
We reach aphelion once every year in July
The difference between aphelion and perihelion distances is about 5 million kilometers. That might seem like a lot, but it's only about 3.3% of Earth's average distance from the Sun.
Orbital Fact!
Earth travels about 107,000 km/h (67,000 mph) in its orbit, but moves slightly slower at aphelion than at perihelion.
Why Aphelion Matters
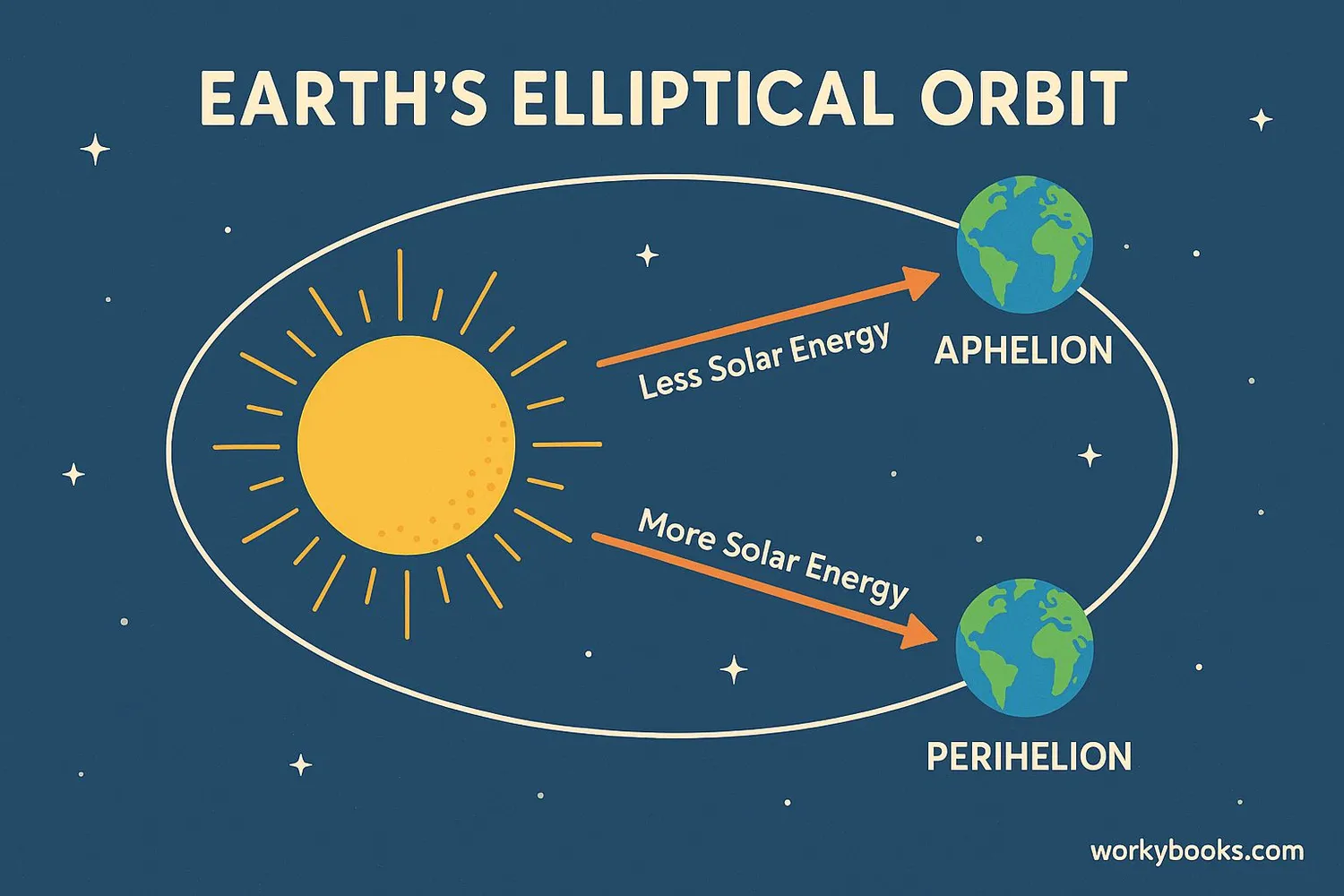
Understanding aphelion helps us learn important concepts about our planet and solar system:
Seasonal Effects
Shows that seasons aren't caused by distance from Sun
Solar Energy
Earth receives 7% less solar energy at aphelion
Space Missions
Affects planning for spacecraft trajectories
Key reasons why aphelion is important:
• Helps us understand Earth's orbital mechanics
• Explains why summers aren't hotter when closer to the Sun
• Affects the length of seasons (Northern Hemisphere summer is longer)
• Important for astronomical observations and calculations
The difference in solar energy between aphelion and perihelion is about 7%, but Earth's tilt has a much greater effect on seasons than this distance difference.
Aphelion Quiz
Test your space knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned about aphelion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about aphelion:
Space Trivia
Discover amazing facts about Earth's orbit and aphelion:
Speedy Earth
Earth moves about 1,000 km/h (620 mph) slower at aphelion than at perihelion due to Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion.
Longer Summers
Northern Hemisphere summers are about 5 days longer than winters because Earth moves slower during aphelion when it's summer in the north.
Solar Difference
Earth receives about 6.5% less solar energy at aphelion than at perihelion. That's equivalent to the energy used by all humans in 10 years!
Changing Orbit
Earth's orbit becomes slightly more circular and then more elliptical in a 100,000-year cycle. This affects ice ages and long-term climate patterns.




