Biosphere - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover Earth's life-supporting layer where all living things interact
What is the Biosphere?
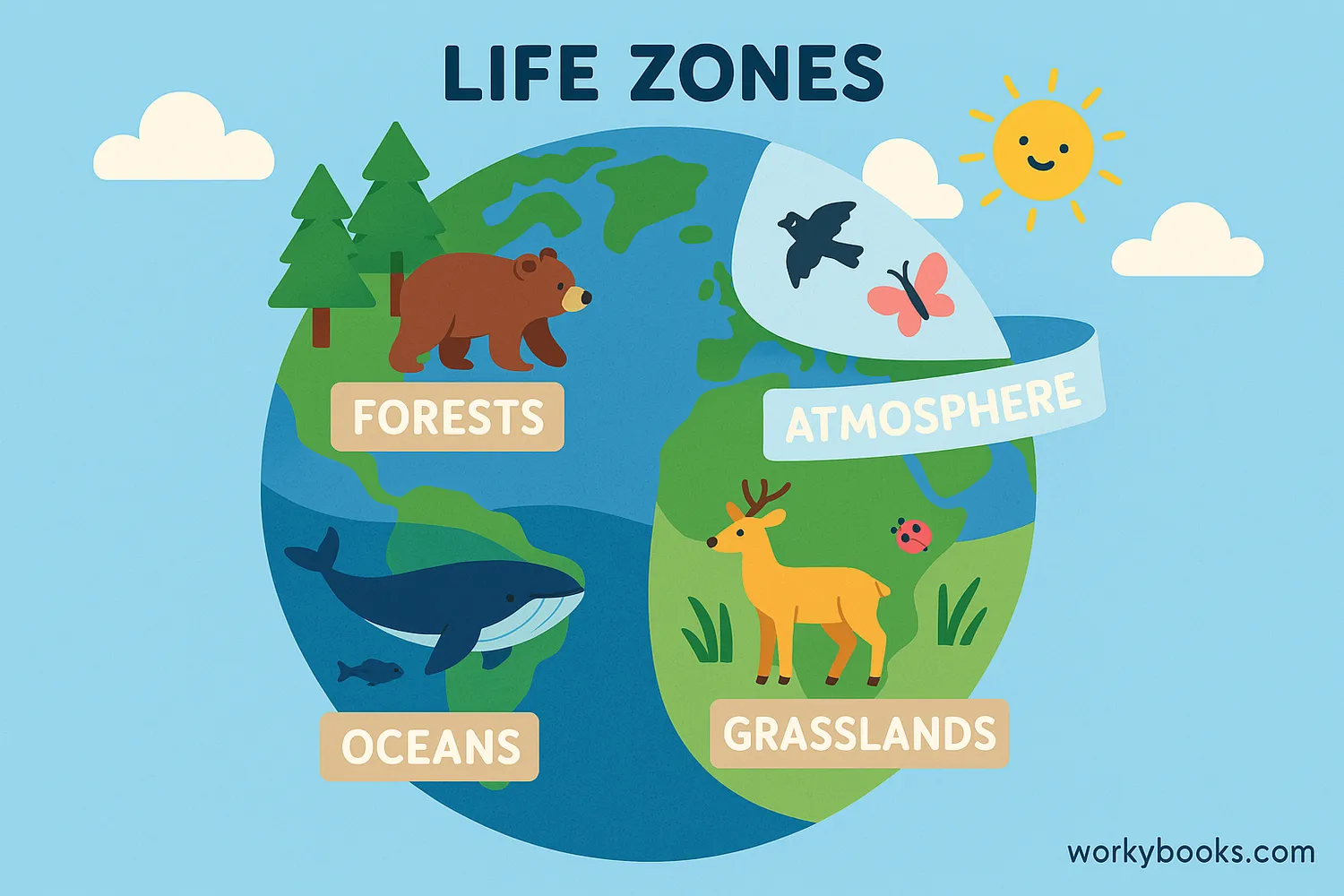
The biosphere is the part of Earth where life exists! It includes all living things and the environments they live in. The biosphere extends from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountains where life can survive - about 20 kilometers from the bottom of the ocean to the top of the atmosphere.
Think of the biosphere as Earth's "life zone" - a thin, precious layer where air, water, and land come together to support life. It includes all ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to desert environments, and all the plants, animals, and microorganisms that call these places home.
Did You Know?
The biosphere is about 20 kilometers thick, but most life exists in a much thinner layer - just a few hundred meters above and below Earth's surface!
Ecosystems & Biodiversity
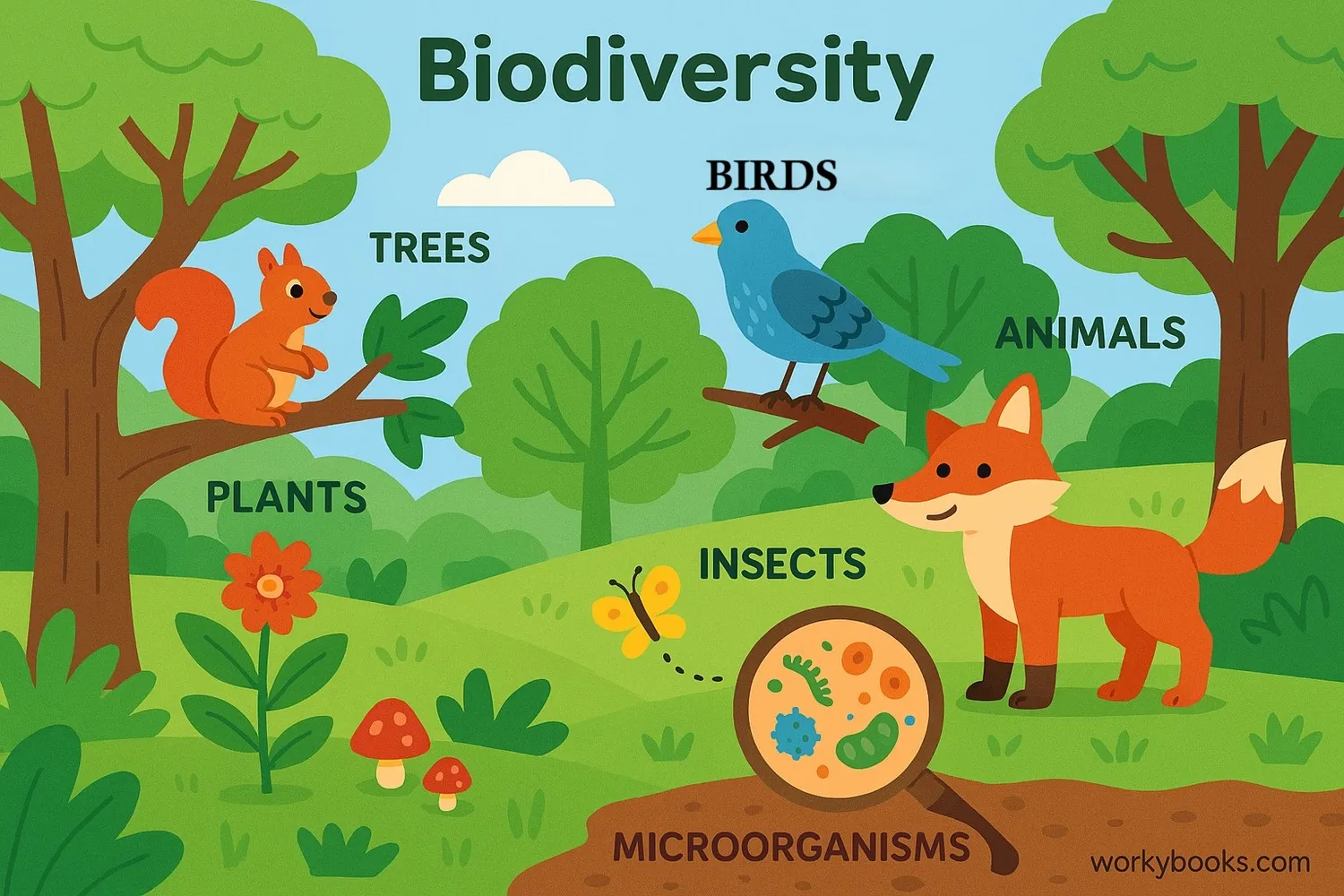
An ecosystem is a community of living things that interact with each other and their non-living environment. Ecosystems can be as large as an ocean or as small as a pond. Biodiversity refers to the variety of living things in an ecosystem - the more species, the greater the biodiversity!
Each species has a special role in its ecosystem, and this ecological balance helps keep the environment healthy. When biodiversity is high, ecosystems are more resilient to changes and can better provide important services like clean air, water, and soil.
Habitats
The natural home or environment where a plant or animal lives
Communities
Different populations living together in an area
Ecosystems
Communities interacting with their physical environment
Biomes
Large areas with similar climate and ecosystems
Biodiversity Hotspot!
Tropical rainforests cover less than 2% of Earth's surface but contain about 50% of the world's plant and animal species!
Food Chains & Food Webs
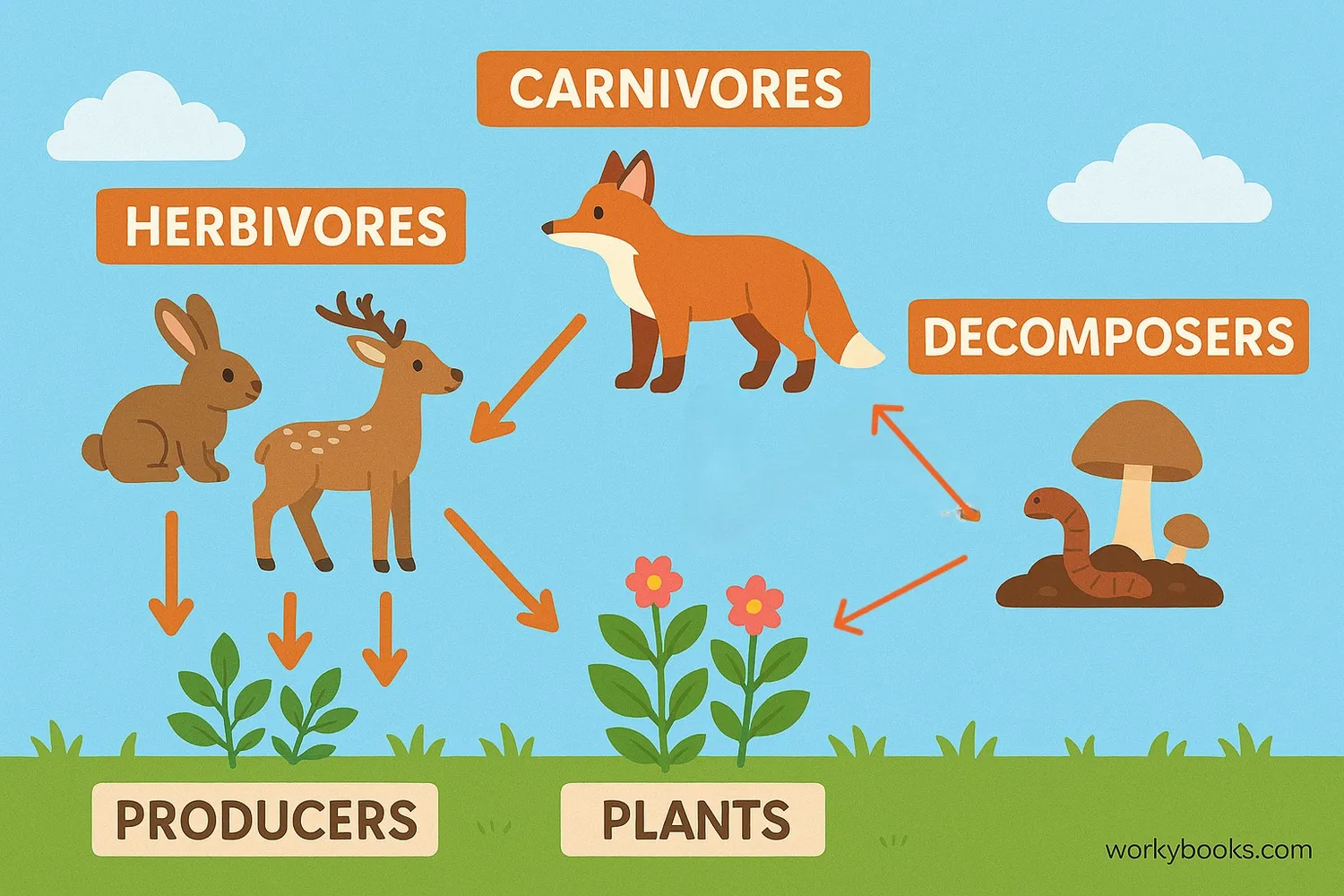
Food chains and food webs show how energy moves through an ecosystem. They always start with primary producers (usually plants) that make their own food through photosynthesis.
Herbivores eat the plants, carnivores eat the herbivores, and so on up the food chain. Decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down dead plants and animals, returning nutrients to the soil for new plants to use. This creates a continuous cycle of energy and nutrients!
Producers
Plants that make food using sunlight (photosynthesis)
Consumers
Animals that eat plants or other animals for energy
Decomposers
Organisms that break down dead material and waste
A simple food chain example:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Hawk
In reality, most feeding relationships form complex food webs rather than simple chains because most animals eat more than one type of food.
Natural Cycles in the Biosphere
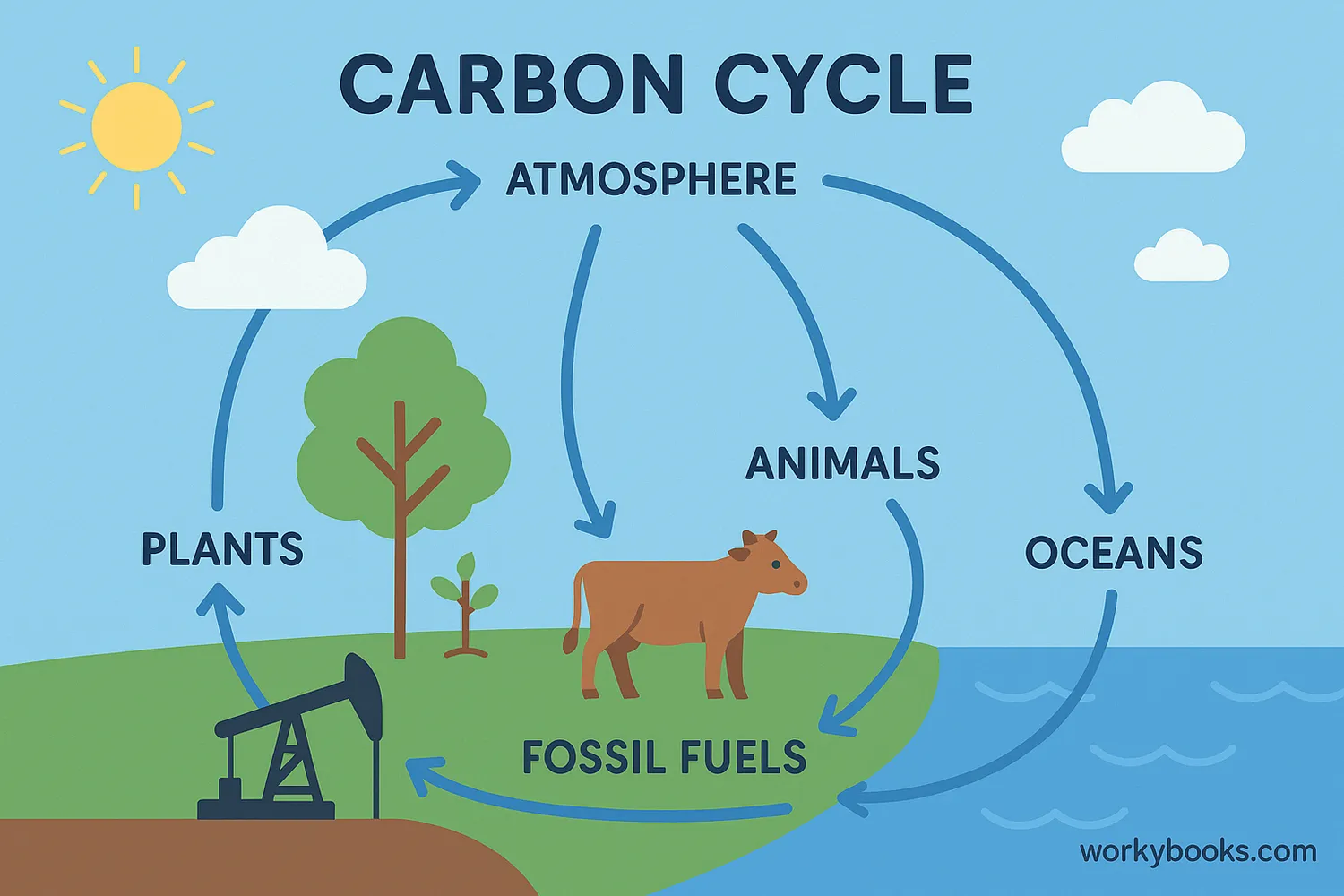
The biosphere depends on important biogeochemical cycles that move essential elements through living and non-living parts of Earth. Two of the most important are the carbon cycle and the nitrogen cycle.
These cycles ensure that nutrients are continuously recycled and available to support life. Without these cycles, nutrients would get used up and life couldn't continue!
Carbon Cycle
Carbon moves between the atmosphere, organisms, oceans, and Earth
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen moves from the air to soil, to plants and animals, then back
Water Cycle
Water evaporates, forms clouds, falls as rain, and flows back to oceans
In the carbon cycle:
• Plants take in CO₂ during photosynthesis
• Animals eat plants and incorporate carbon into their bodies
• Both plants and animals release CO₂ back to the atmosphere through respiration
• Decomposers release carbon when breaking down dead organisms
• Some carbon becomes stored in fossil fuels over millions of years
Cycle Connections!
These natural cycles are all connected! For example, the water cycle helps move nutrients through ecosystems, and photosynthesis in the carbon cycle produces oxygen that animals need.
Biosphere Quiz
Test your knowledge about the biosphere with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the biosphere:
Biosphere Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about Earth's biosphere!
Microbial Majority
Microorganisms like bacteria make up most of the biomass in the biosphere! There are more microbes in a teaspoon of soil than there are people on Earth.
Ocean Life
The oceans contain 99% of the living space on Earth! Yet we've explored less than 5% of the world's oceans, meaning most marine species remain undiscovered.
Tree Communication
Trees in forests communicate through an underground network of fungi! This "Wood Wide Web" allows them to share nutrients and warn each other of dangers.
Extreme Life
Some life forms called extremophiles thrive in places once thought uninhabitable—boiling hot springs, acidic lakes, and even deep inside rocks!




