Continental Drift - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how Earth's continents have moved over millions of years!
What is Continental Drift?
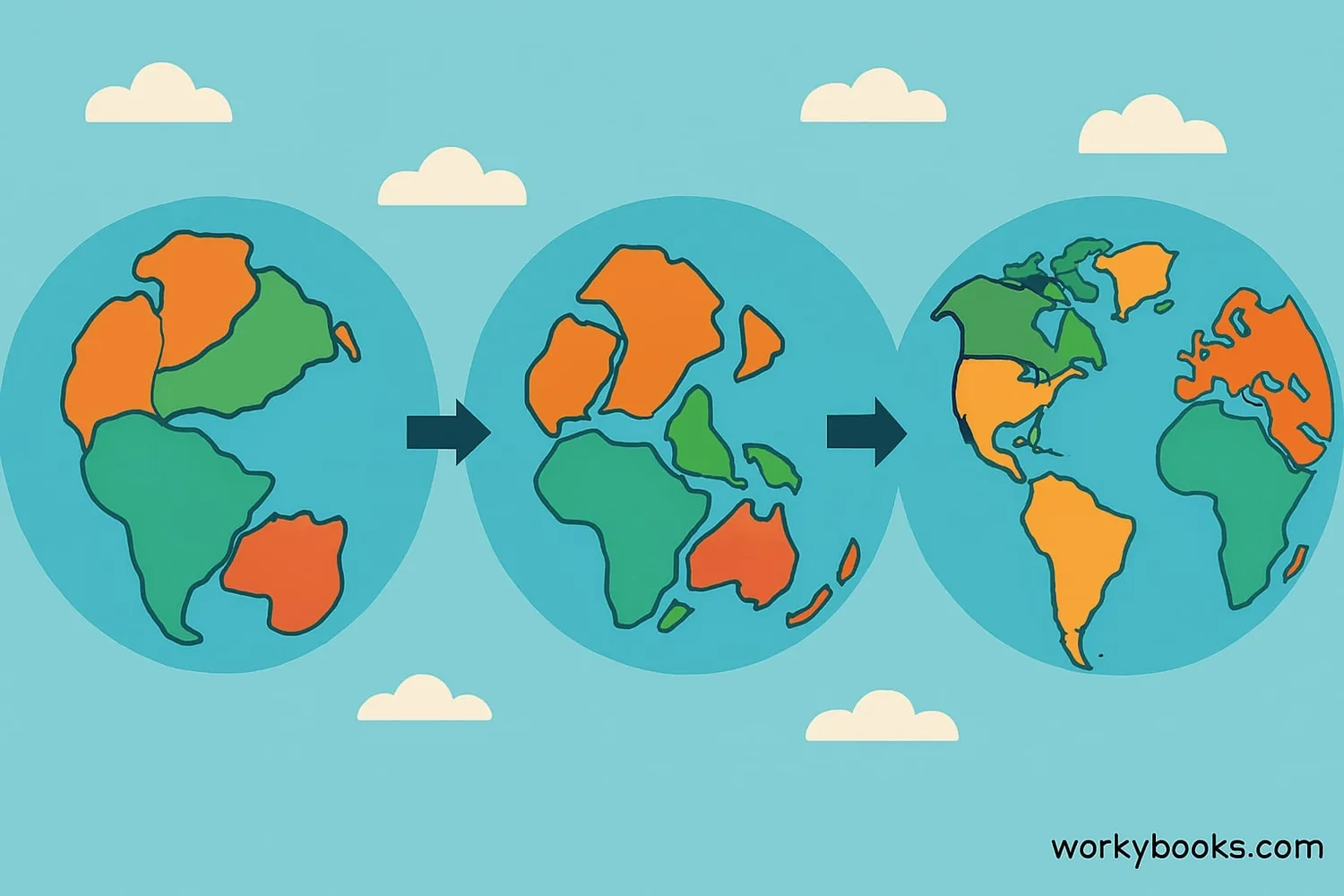
Continental drift is the theory that Earth's continents have moved over geological time and continue to move today! Imagine Earth as a giant jigsaw puzzle where the pieces slowly move around.
About 300 million years ago, all the continents were joined together in one supercontinent called Pangaea (which means "all lands" in Greek). Over millions of years, these landmasses broke apart and drifted to their current positions. This movement happens because Earth's crust is made up of giant pieces called tectonic plates that float on the planet's molten interior.
Movement Fact!
Continents move about as fast as your fingernails grow - 2-5 centimeters per year!
How Continental Drift Works
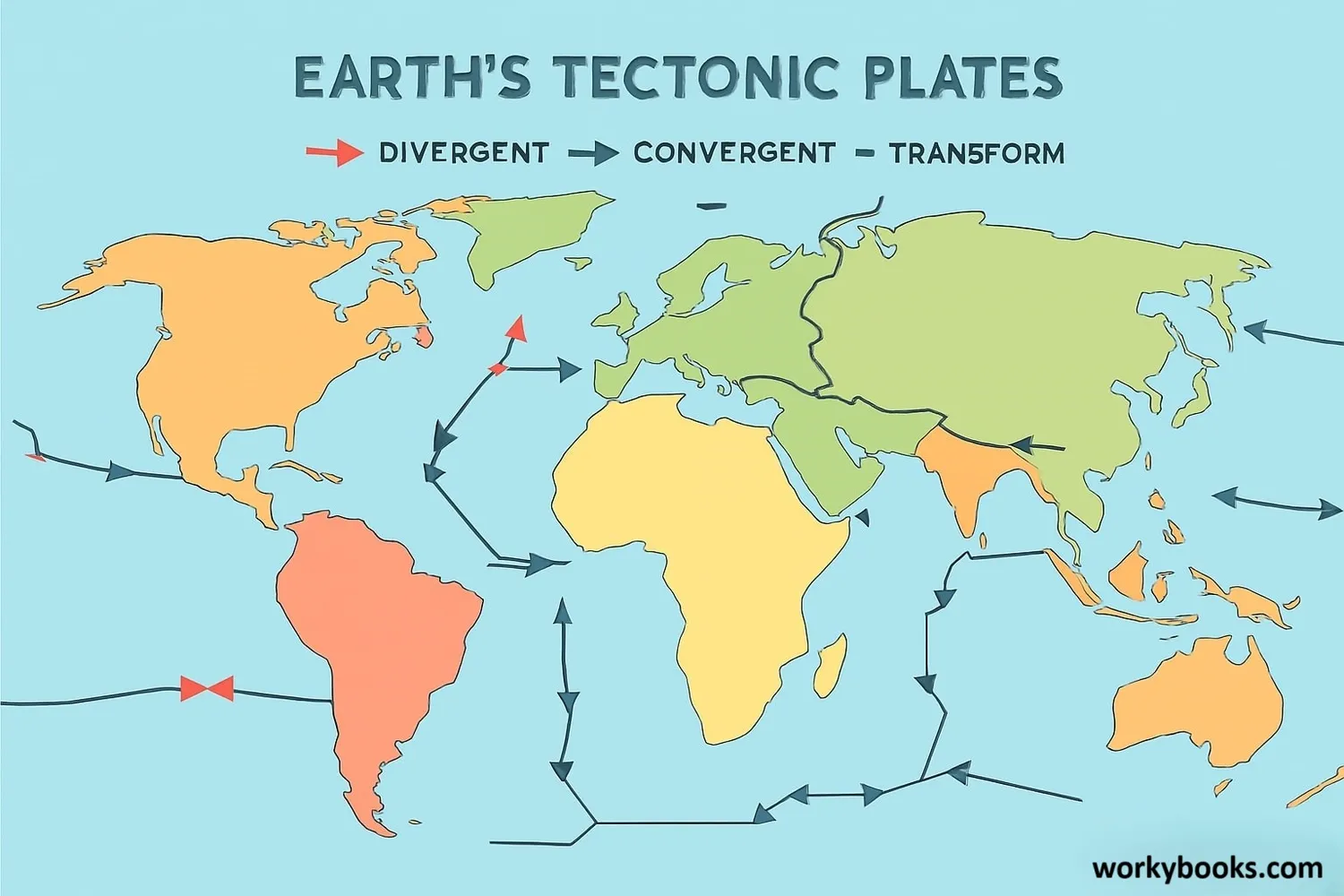
The key to understanding continental drift is plate tectonics. Earth's outer layer (the lithosphere) is broken into several large pieces called tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them.
There are three main types of plate boundaries where movement occurs:
Divergent
Plates move apart, creating new crust
Convergent
Plates collide, forming mountains or subducting
Transform
Plates slide past each other horizontally
This movement is powered by convection currents in Earth's mantle. Hot material rises, cools near the surface, and sinks back down, creating a circular motion that slowly moves the plates above.
Plate Power!
The Pacific Plate moves faster than any other, moving about 7-10 cm per year - that's as fast as hair grows!
Evidence for Continental Drift
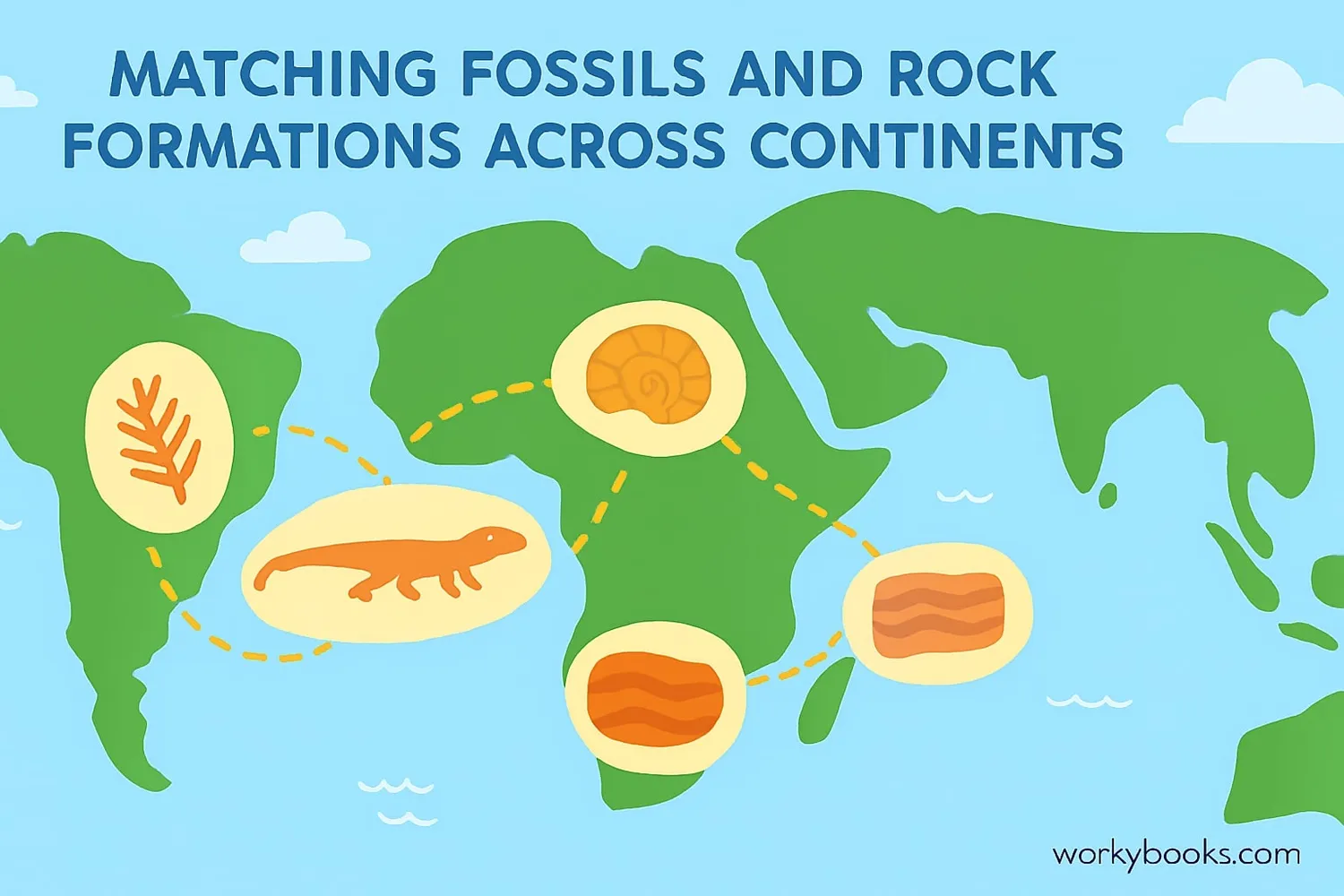
Scientists have found many pieces of evidence that support the theory of continental drift:
Continental Fit
The coastlines of continents like South America and Africa fit together like puzzle pieces
Fossil Evidence
Identical fossils of plants and animals found on continents now separated by oceans
Rock Formations
Matching mountain ranges and rock types on different continents
Glacial Evidence
Glacial deposits in warm regions that were once near the South Pole
These pieces of evidence show that continents now separated by vast oceans were once connected. For example, fossils of the freshwater reptile Mesosaurus are found only in South America and Africa - impossible unless these continents were once joined!
Continental Drift Quiz
Test your knowledge about continental drift with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about continental drift:
Fun Continental Drift Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about continental drift!
Fastest Moving Continent
Australia is moving north at about 7 cm per year - so fast that GPS coordinates need regular updates! By 2020, Australia had moved so much that the entire continent's latitude and longitude were officially adjusted.
Future Oceans
In about 10 million years, East Africa will split from the rest of the continent, creating a new ocean! The East African Rift is widening at 6-7 mm per year, and eventually will fill with seawater.
Ancient Connections
Antarctica was once connected to Australia and South America and had a tropical climate! Fossil evidence shows it was home to forests and dinosaurs before drifting south and freezing over.
Growing Mountains
The Himalayas are still growing because India is pushing into Asia at 5 cm per year! This collision began about 50 million years ago and created the world's highest mountains.




