Exosphere - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover Earth's outermost atmospheric layer where our atmosphere meets space
What is the Exosphere?
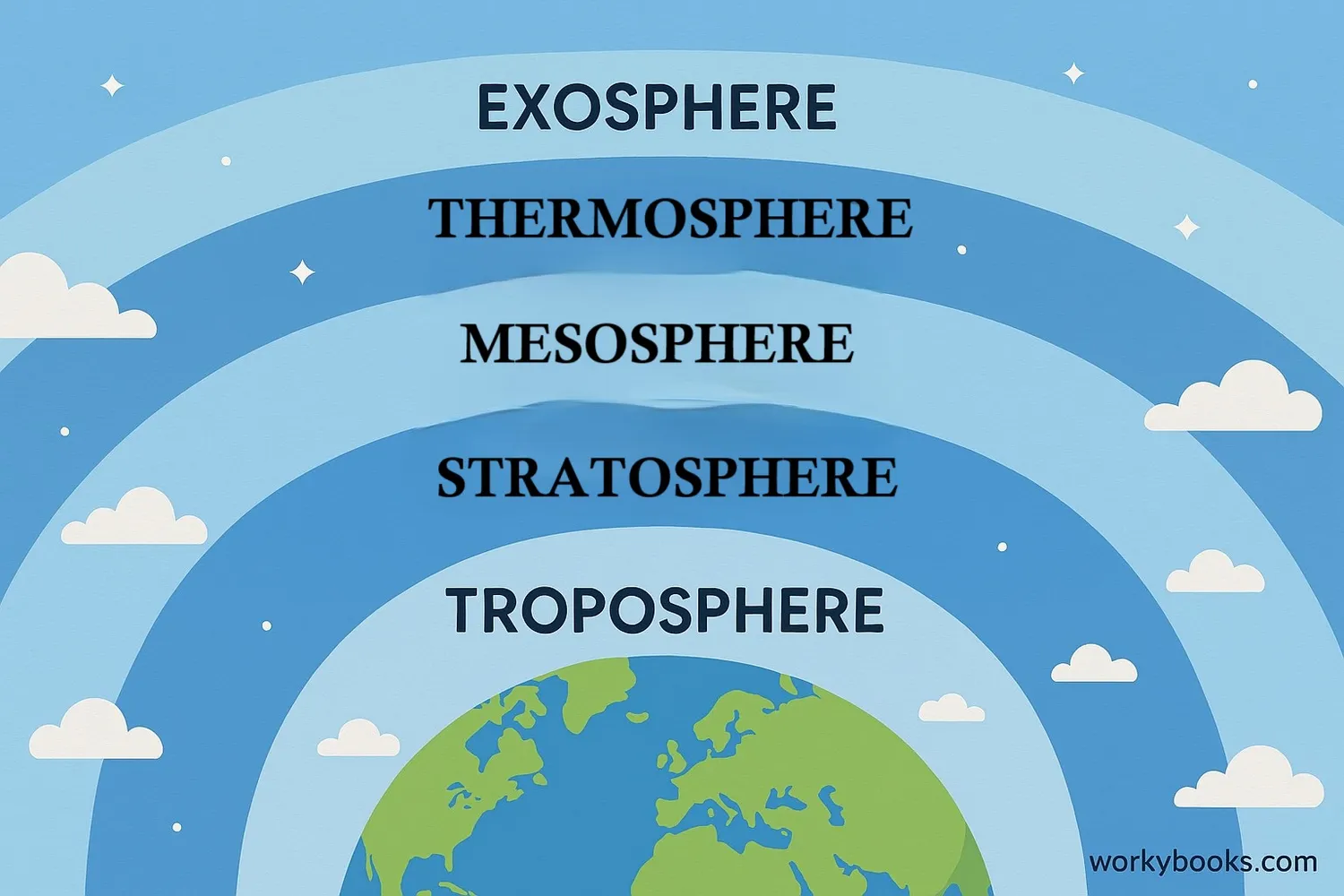
The exosphere is the very outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, where our atmosphere gradually merges with outer space. It's the final frontier between our planet and the vast universe beyond.
Think of the exosphere as the "fringe" of our atmosphere - it's extremely thin, with gas molecules spaced very far apart. This layer begins at about 500-1,000 kilometers (300-600 miles) above Earth's surface and extends outward for thousands of kilometers, gradually becoming the solar wind.
The word "exosphere" comes from the Greek word "exo" meaning "outside" - it's literally the outer sphere of our atmosphere.
Did You Know?
The exosphere is so thin that it's considered almost a vacuum - there's very little air there compared to what we breathe at Earth's surface!
Characteristics of the Exosphere
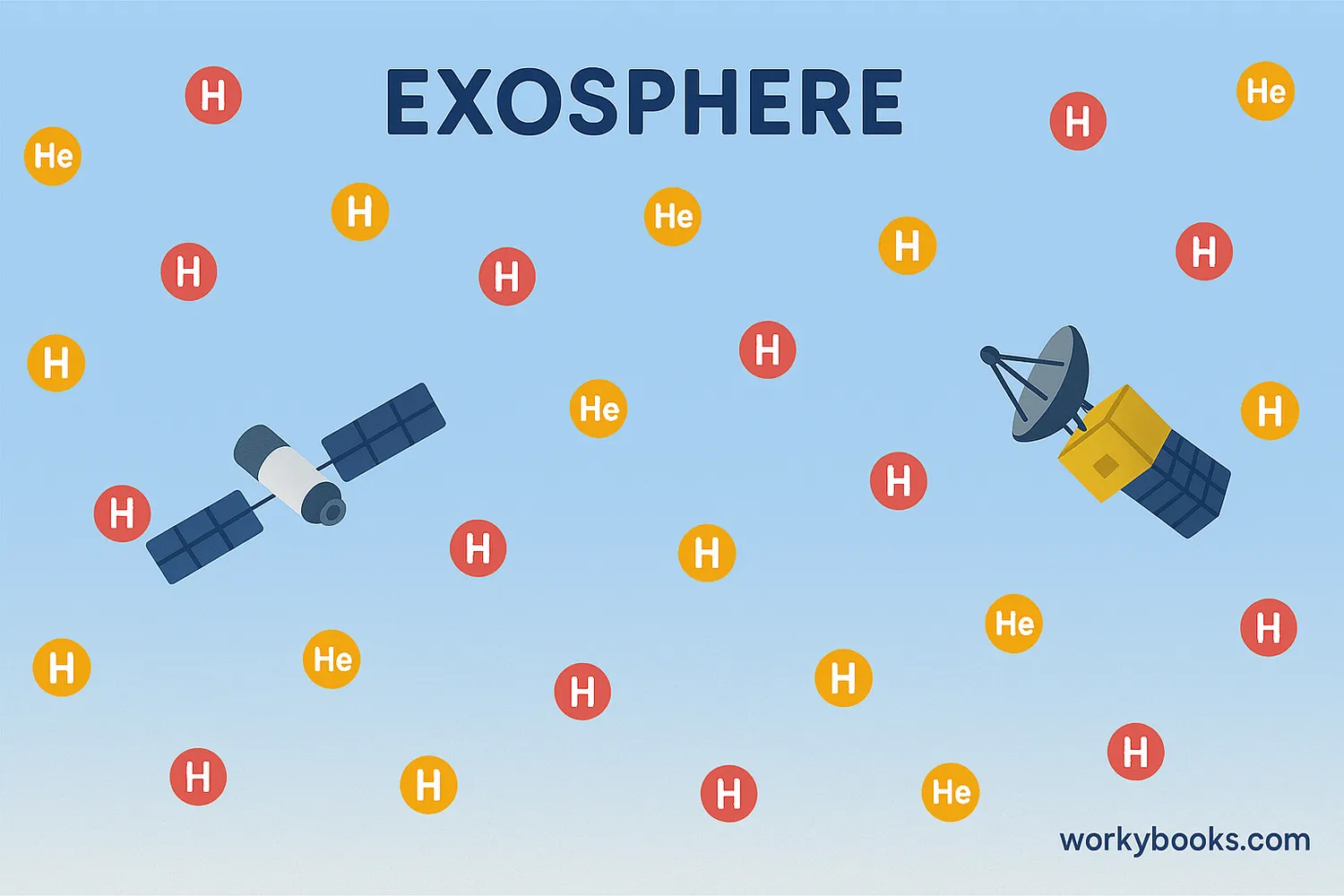
The exosphere has several unique characteristics that make it different from the other atmospheric layers:
Extremely Thin
Gas particles are very far apart and rarely collide
Light Gases
Mainly contains hydrogen and helium, the lightest gases
No Clear Boundary
Gradually fades into space without a definite upper limit
Satellite Zone
Where many satellites orbit Earth
Escape Zone
Fast-moving particles can escape Earth's gravity
In the exosphere, the air is so thin that the concept of temperature changes. Unlike lower atmospheric layers, we can't measure temperature in the usual way because molecules are so far apart. Instead, we measure the kinetic energy (movement energy) of individual particles, which can be extremely high.
Satellite Central!
The International Space Station orbits just below the exosphere, but many weather and communication satellites orbit within the exosphere itself!
Why the Exosphere is Important
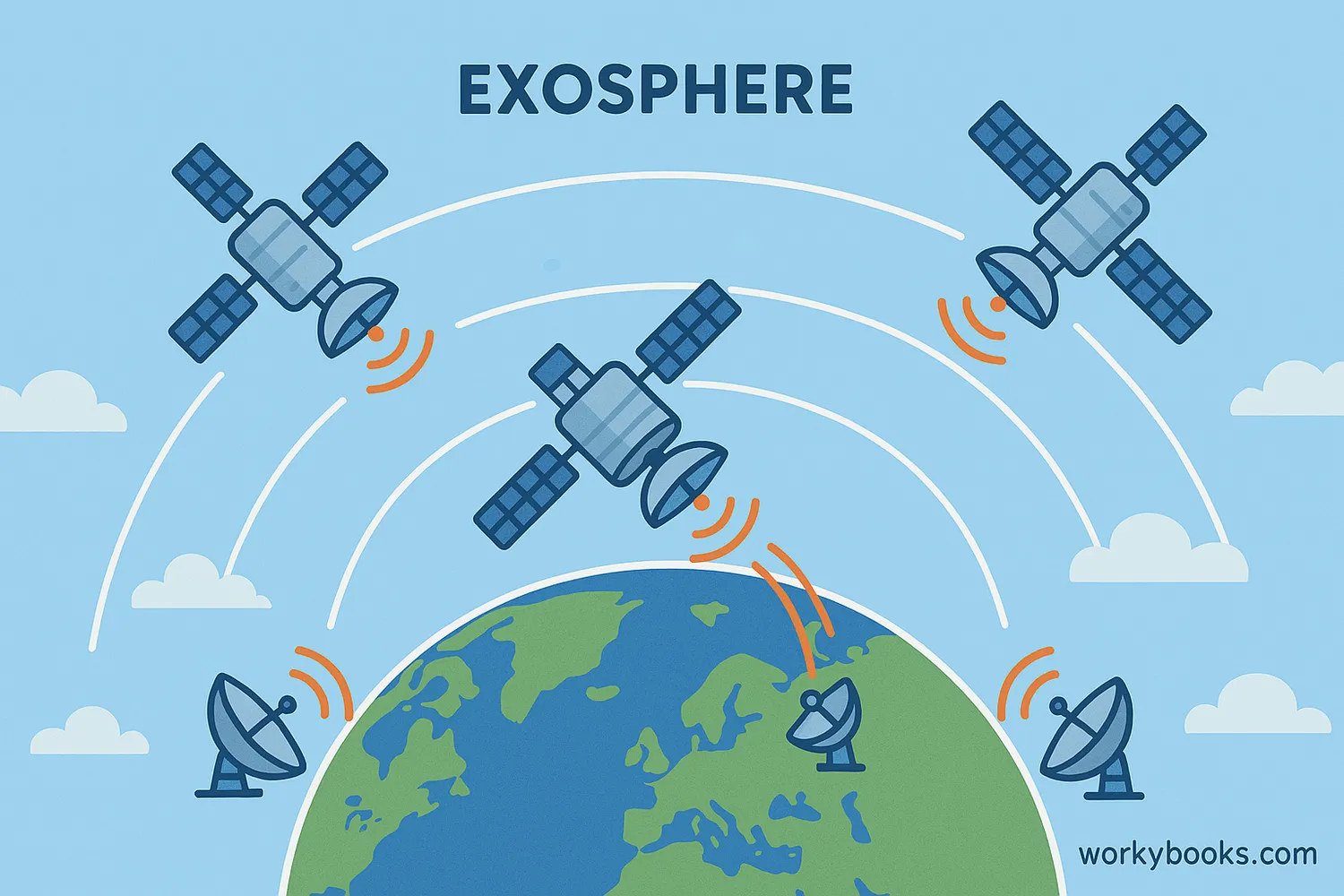
Though it's the thinnest part of our atmosphere, the exosphere plays several crucial roles:
Satellite Operations
Provides a stable environment for satellites to orbit Earth with minimal atmospheric drag
Communication
Enables satellite communications, GPS, and weather monitoring
Transition Zone
Acts as a buffer between Earth's atmosphere and the harsh environment of space
The exosphere also helps scientists understand:
• How atmospheric gases escape into space over time
• The interaction between Earth's atmosphere and solar wind
• The long-term changes in our atmosphere
• Conditions that affect satellite operations and space exploration
Without the exosphere, many of our modern technologies like satellite TV, GPS navigation, and weather forecasting would be much more difficult or impossible!
Exosphere Quiz
Test your knowledge about the exosphere with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the exosphere:
Exosphere Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about the exosphere!
Incredible Height
The exosphere is so vast that if Earth were the size of a basketball, the exosphere would extend outward about the length of a football field!
Satellite City
There are over 2,000 active satellites orbiting in or near the exosphere, plus thousands of pieces of "space junk" from old satellites and rockets!
Speedy Particles
Gas particles in the exosphere move so fast that some reach escape velocity and drift off into space! Earth loses about 3 kg of hydrogen and 50 g of helium every second this way.
Night Glow
The exosphere creates a faint glow called "airglow" that can be seen from space. This happens when atoms and molecules in the exosphere release energy they absorbed from the sun during the day.





