Law of Superposition - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how rock layers reveal Earth's history
What is the Law of Superposition?

The Law of Superposition is a fundamental principle in geology that helps scientists understand Earth's history. It states that in any sequence of undisturbed rock layers, the oldest layer is at the bottom and each higher layer is younger than the one below it.
Think of it like a stack of books or newspapers. The book at the bottom of the pile was placed there first (oldest), while the book on top was added most recently (youngest). Rock layers form the same way - new sediment settles on top of older layers.
Geology Fact!
The Law of Superposition was first described by Danish scientist Nicolas Steno in 1669! That's over 350 years ago!
How the Law of Superposition Works
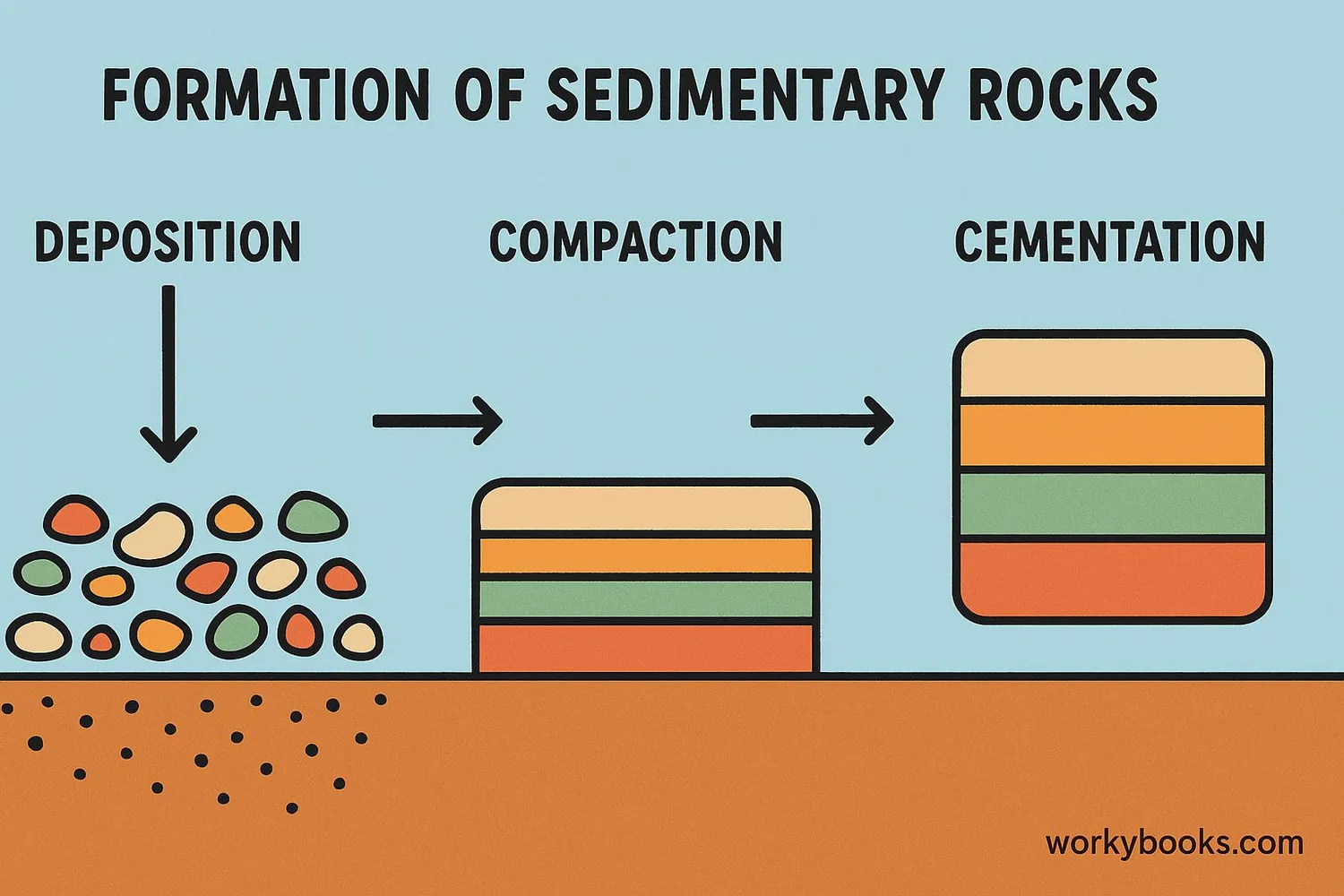
The Law of Superposition works because of how sedimentary rocks form. When sediments like sand, mud, or pebbles settle in water or on land, they form horizontal layers called strata. Over time, these layers build up:
Deposition
Sediments settle and form a new layer
Burial
New layers cover older sediments
Compaction
Weight presses layers together
Cementation
Minerals glue sediments into rock
Uplift
Earth movements expose layers
This process creates a timeline in the rocks. Geologists study these layers to understand:
• How environments changed over time
• What ancient life was like (through fossils)
• When important geological events happened
The Law of Superposition only works when rock layers haven't been disturbed by earthquakes, folding, or other geological events.
Rock Record!
The Grand Canyon has rock layers that are over 1.8 billion years old at the bottom and 270 million years old at the top!
Why the Law of Superposition Matters
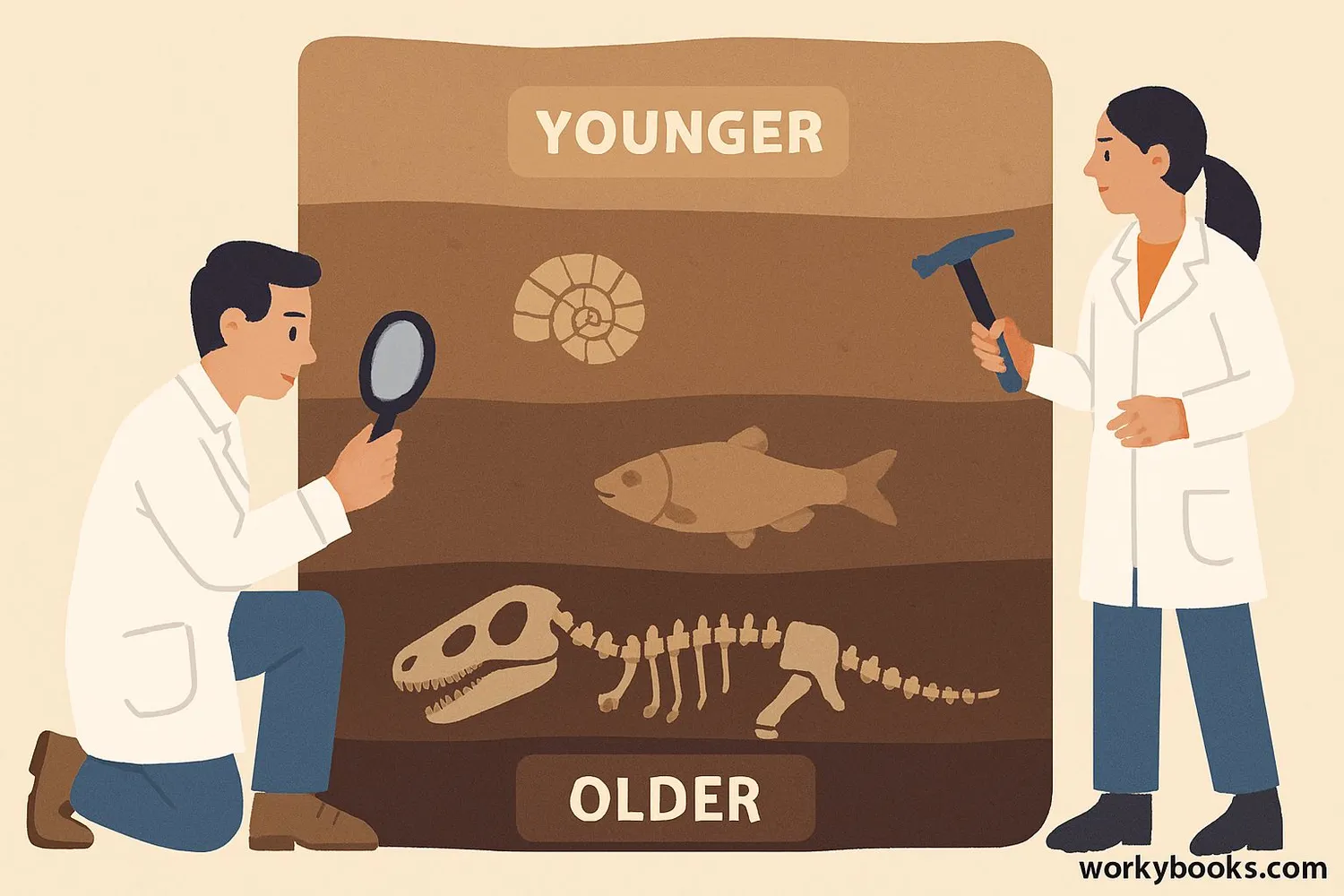
The Law of Superposition is crucial for understanding Earth's history and the development of life. Here's why geologists rely on this principle:
Relative Dating
Determines the age of rocks and fossils compared to others
Fossil Records
Shows how life forms changed over geological time
Earth History
Reveals past climates, environments, and events
Without the Law of Superposition, we couldn't:
• Understand the sequence of life on Earth
• Determine the relative ages of rocks
• Reconstruct ancient environments
• Locate important resources like oil and minerals
This principle helps create geological maps and is fundamental to the science of stratigraphy - the study of rock layers.
Rock Layer Quiz
Test your knowledge of the Law of Superposition with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Law of Superposition:
Geology Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about rock layers and Earth's history!
Deep Time
The oldest known rocks on Earth are about 4 billion years old! That's nearly as old as our planet itself. These ancient rocks are found in Canada and Australia.
Fossil Record
The fossil record shows that 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth are now extinct! Rock layers preserve evidence of these lost worlds.
Layer Thickness
The thickest sedimentary rock layer on Earth is in the Himalayas. It's over 25,000 meters thick - that's more than twice the height of Mount Everest!
Moon Layers
The Law of Superposition also applies to the Moon! Astronauts brought back moon rocks that show layers formed by ancient lava flows and meteor impacts.





