Life Cycle of a Star - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how stars form, live, and die in this journey through stellar evolution
What is Stellar Evolution?
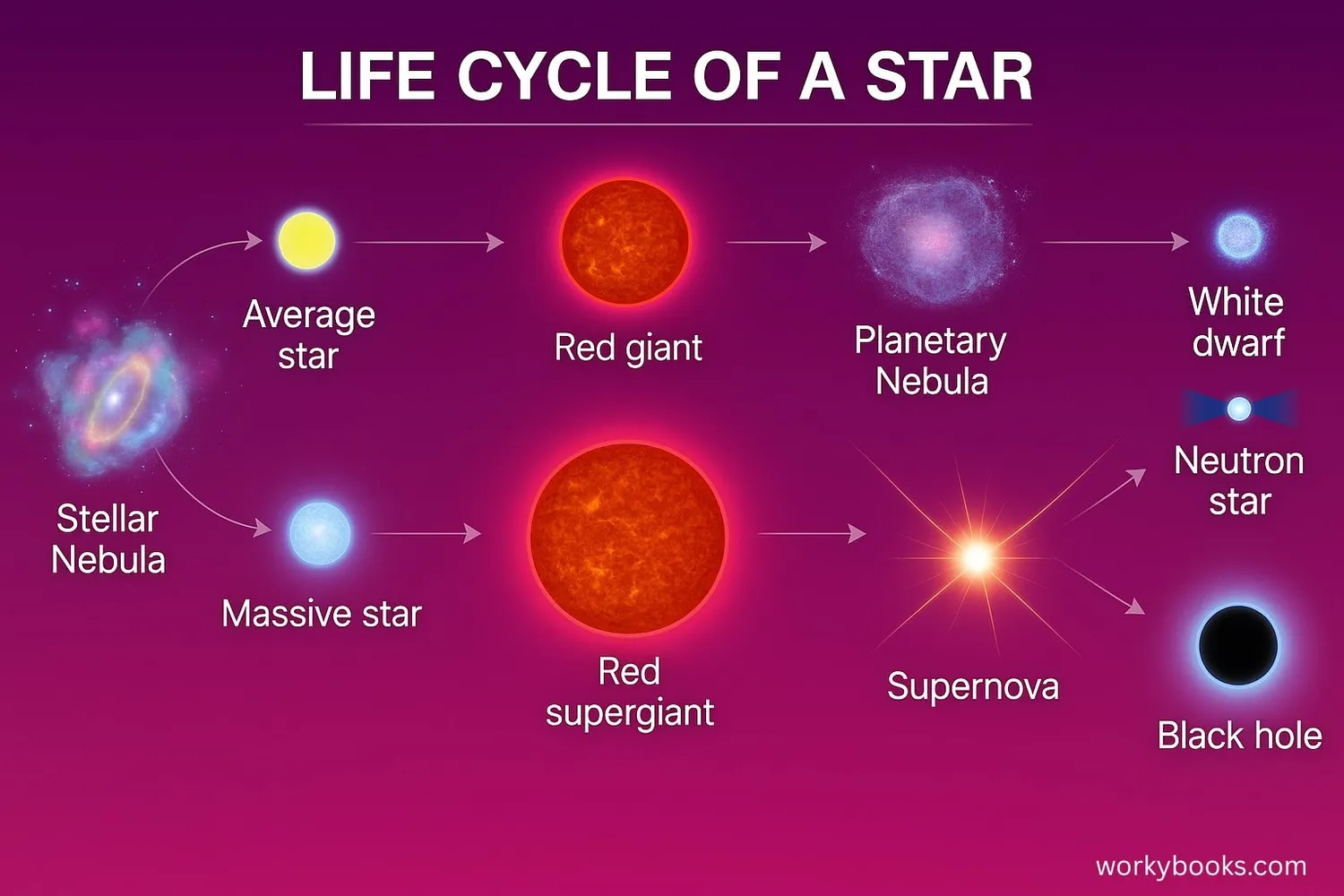
Stellar evolution describes how stars change over their lifetimes, from birth to death. Just like living things, stars are born, grow through different stages, and eventually die. The life cycle of a star depends on how much matter it contains - its mass.
Smaller stars like our Sun have different life cycles than massive stars. Understanding this process helps us learn about the universe and how elements like carbon and oxygen were created in stars!
Did You Know?
Stars spend about 90% of their lives in the main sequence stage, fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores!
Star Formation

Stars begin their lives in vast clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. These cosmic nurseries contain mostly hydrogen gas with some heavier elements:
Nebula Formation
Huge clouds of gas and dust form in space
Gravitational Collapse
Gravity pulls material together into dense regions
Protostar
The collapsing cloud forms a hot, dense core
As the protostar grows, its core gets hotter and denser. When the temperature reaches about 15 million degrees Celsius, nuclear fusion begins - hydrogen atoms smash together to form helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy.
Space Fact!
The Orion Nebula is one of the closest star-forming regions to Earth, about 1,344 light-years away. You can see it with binoculars!
Main Sequence Stars
When nuclear fusion begins, the star enters the main sequence stage. This is the longest period in a star's life. Our Sun is currently in this stable phase, which will last about 10 billion years total.
During this stage, stars maintain a balance between:
• Gravity pulling inward
• Energy from fusion pushing outward
The size and color of a main sequence star depends on its mass. More massive stars are larger, hotter, and bluer, while smaller stars are cooler and redder.
Star Colors
Star colors indicate their temperature: blue stars are hottest (over 25,000°C), yellow like our Sun are medium (5,500°C), and red stars are coolest (below 3,500°C).
Red Giants & Supergiants
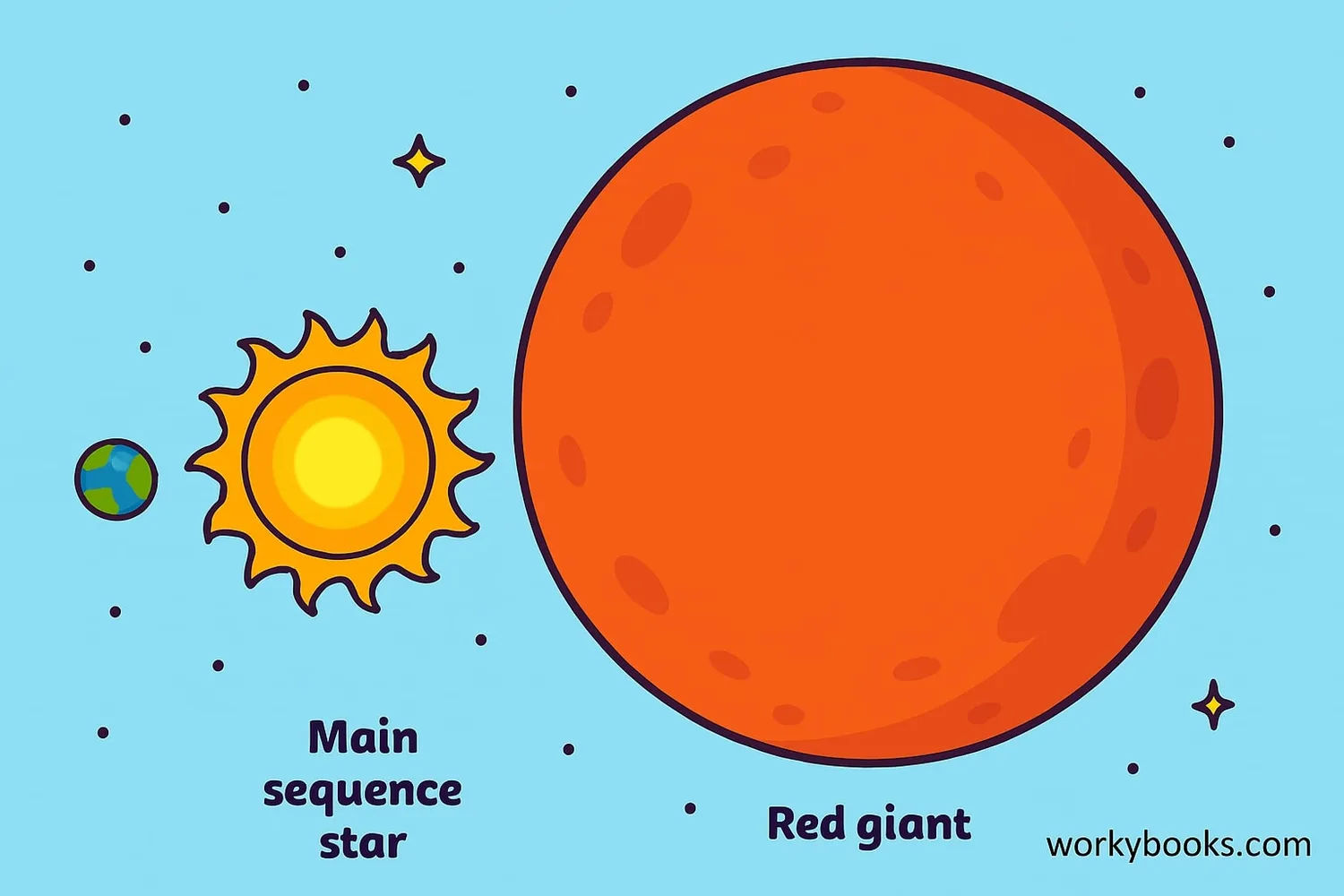
When a star runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core, it begins to change:
Red Giant
(Sun-sized stars)
Star expands 100-1000× its original size
Red Supergiant
(Massive stars)
Expands to enormous sizes, up to 1,500× the Sun
As the core contracts, the outer layers expand and cool, turning red. The star begins fusing helium into heavier elements like carbon and oxygen.
For Sun-like stars, this expansion will eventually engulf Mercury, Venus, and possibly Earth! But don't worry - this won't happen for another 5 billion years.
Space Fact!
The red supergiant Betelgeuse is so large that if placed at the center of our Solar System, it would extend beyond Jupiter's orbit!
Stellar Endings
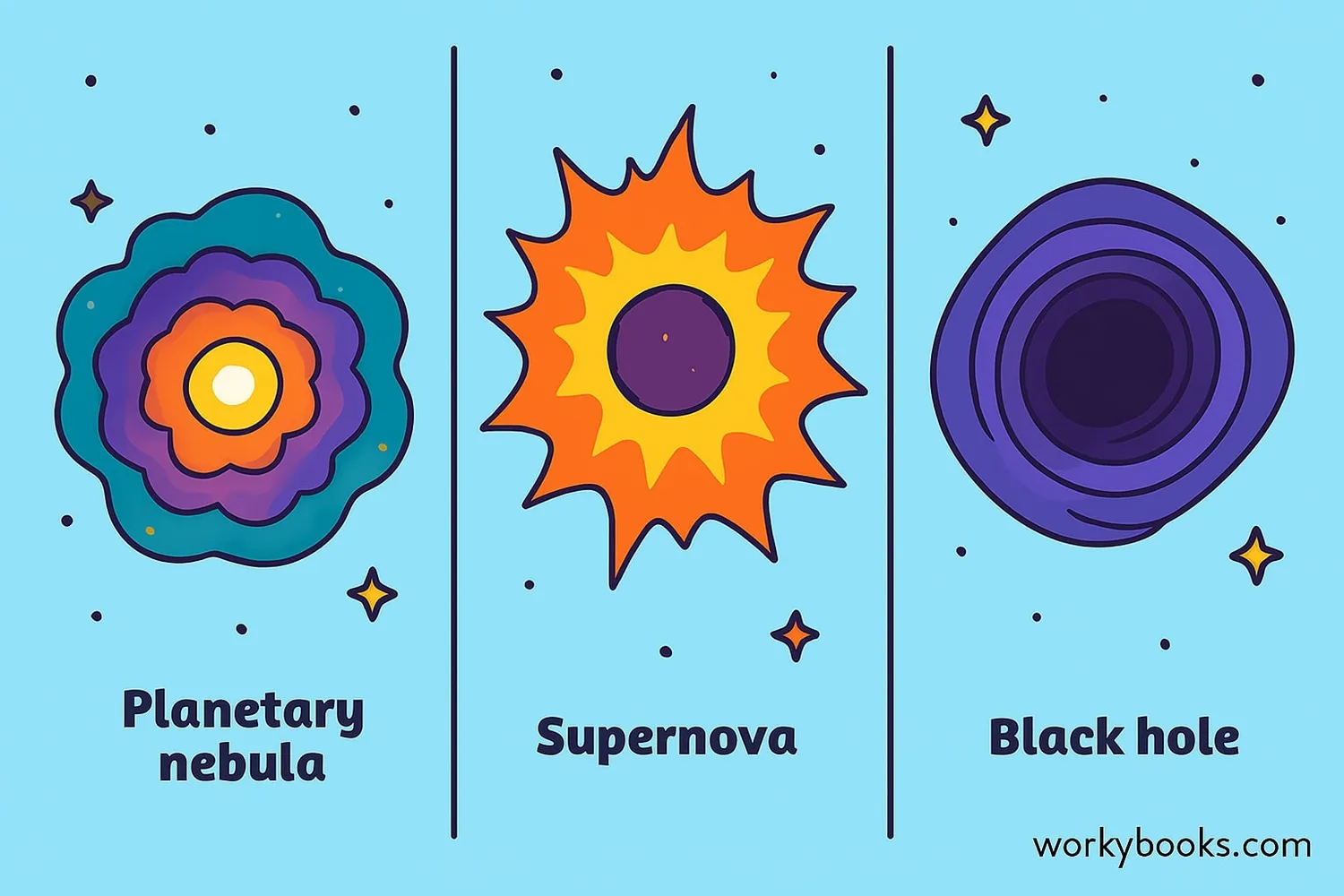
How a star ends its life depends on its initial mass:
Low-Mass Stars
(Like our Sun)
Become red giants then shed outer layers as planetary nebulae, leaving behind white dwarfs
Massive Stars
(8-25× Sun's mass)
Explode as supernovae, leaving neutron stars
Super-Massive Stars
(Over 25× Sun's mass)
Collapse into black holes after supernova explosions
White dwarfs are Earth-sized but contain a Sun's worth of mass. They gradually cool over billions of years.
Supernovae are spectacular explosions that briefly outshine entire galaxies and create heavy elements like gold and uranium.
Neutron stars are city-sized but so dense that a teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! Some become pulsars that beam radiation like cosmic lighthouses.
Black holes form when massive stars collapse beyond the neutron star stage. Their gravity is so strong that not even light can escape!
Chandrasekhar Limit
This important limit (1.4 times the Sun's mass) determines whether a star becomes a white dwarf or collapses further. Stars above this limit become neutron stars or black holes.
Stellar Evolution Quiz
Test your knowledge about the life cycle of stars with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about stellar evolution:
Space Trivia
Discover amazing facts about stars and stellar evolution:
Supernova Power
A supernova explosion can briefly outshine an entire galaxy containing billions of stars! The energy released in 10 seconds equals what our Sun produces in 10 billion years.
Neutron Star Density
Neutron stars are so dense that a sugar-cube-sized amount would weigh about 1 billion tons on Earth - as much as Mount Everest!
Stellar Factories
All elements heavier than helium were created inside stars! The oxygen we breathe, carbon in our bodies, and gold in jewelry were forged in stellar cores and supernova explosions.
Diamond Stars
Some white dwarfs crystallize as they cool, forming gigantic diamond-like structures. The largest known is the diamond star BPM 37093, which is about 4,000 km across!




