Solar Eclipse - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, creating amazing celestial events!
What is a Solar Eclipse?
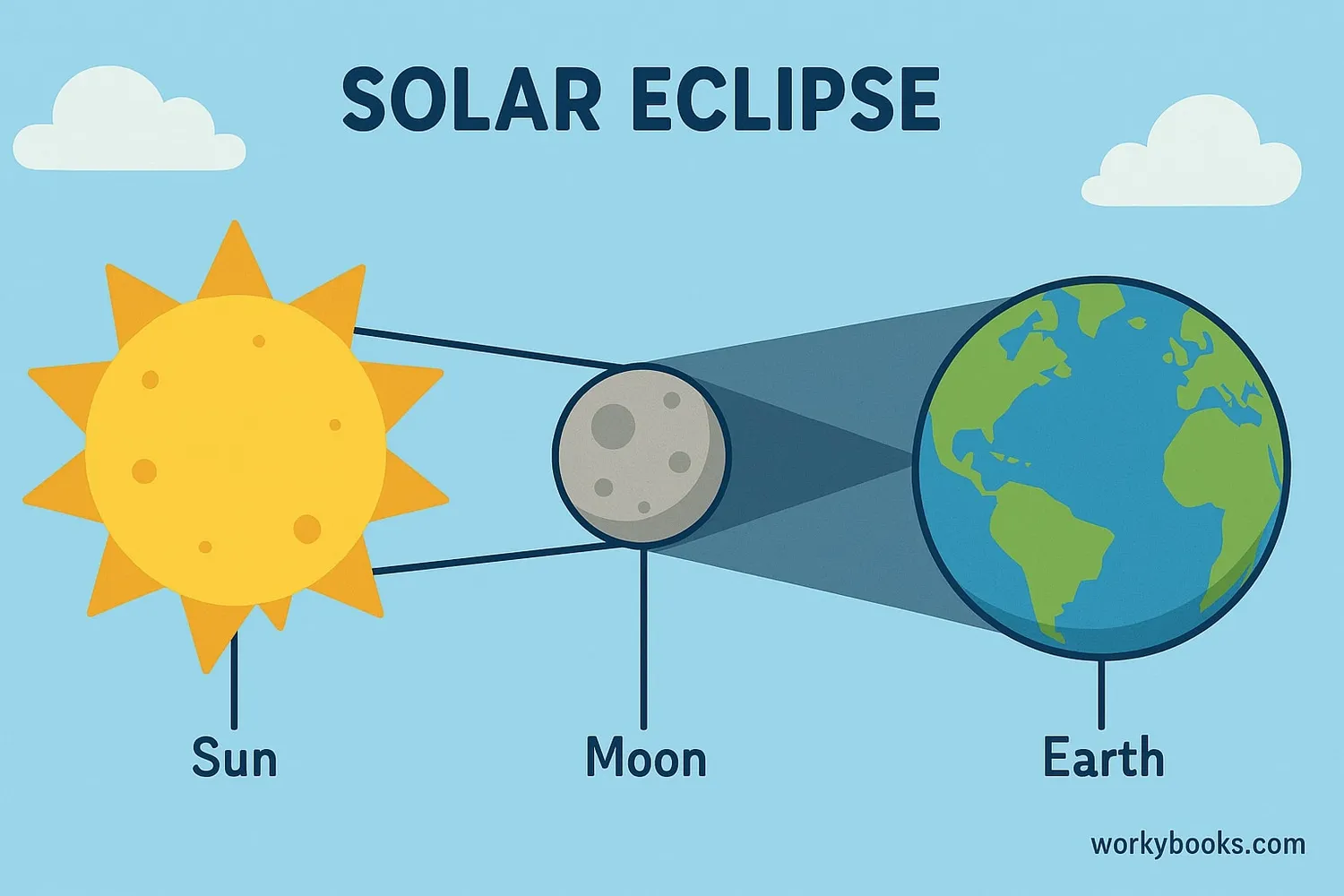
A solar eclipse is an astronomical event that happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking some or all of the Sun's light from reaching Earth. This creates a shadow on parts of our planet.
Think of it like this: when you stand under a tree on a sunny day, the leaves create small shadows on the ground. During a solar eclipse, the Moon acts like those leaves, but on a much larger scale, casting its shadow on Earth!
Solar eclipses only happen during a new moon phase, when the Moon is positioned between Earth and the Sun. But they don't happen every month because the Moon's orbit is tilted compared to Earth's orbit around the Sun.
Celestial Fact!
The Moon is about 400 times smaller than the Sun, but it's also about 400 times closer to Earth. This amazing coincidence makes them appear almost the same size in our sky, allowing for total solar eclipses!
Types of Solar Eclipses
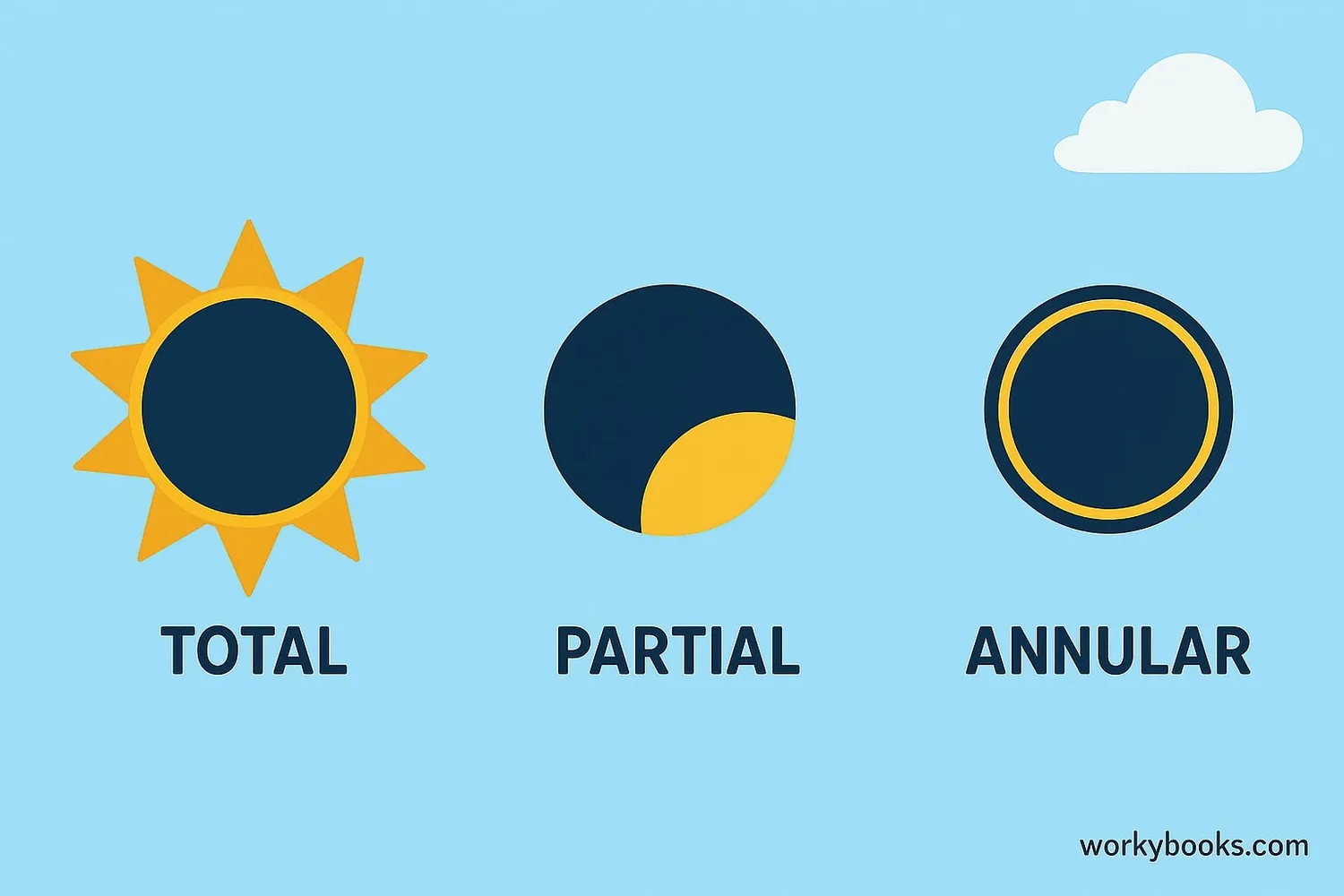
There are three main types of solar eclipses, each creating a different visual experience:
Total Solar Eclipse
The Moon completely covers the Sun's bright face, turning day into night for a few minutes. The Sun's outer atmosphere (corona) becomes visible.
Partial Solar Eclipse
The Moon only covers part of the Sun, creating a crescent-shaped Sun. This is the most common type of solar eclipse.
Annular Solar Eclipse
The Moon is too far from Earth to completely cover the Sun, leaving a "ring of fire" around the Moon's silhouette.
The type of eclipse you see depends on how perfectly the Sun, Moon, and Earth align, and on the Moon's distance from Earth. A fourth, very rare type called a hybrid eclipse shifts between total and annular along different parts of its path.
Eclipse Path!
The path of totality (where a total eclipse is visible) is never wider than about 170 miles (273 km) and often much narrower. Outside this path, people see only a partial eclipse.
How Solar Eclipses Happen
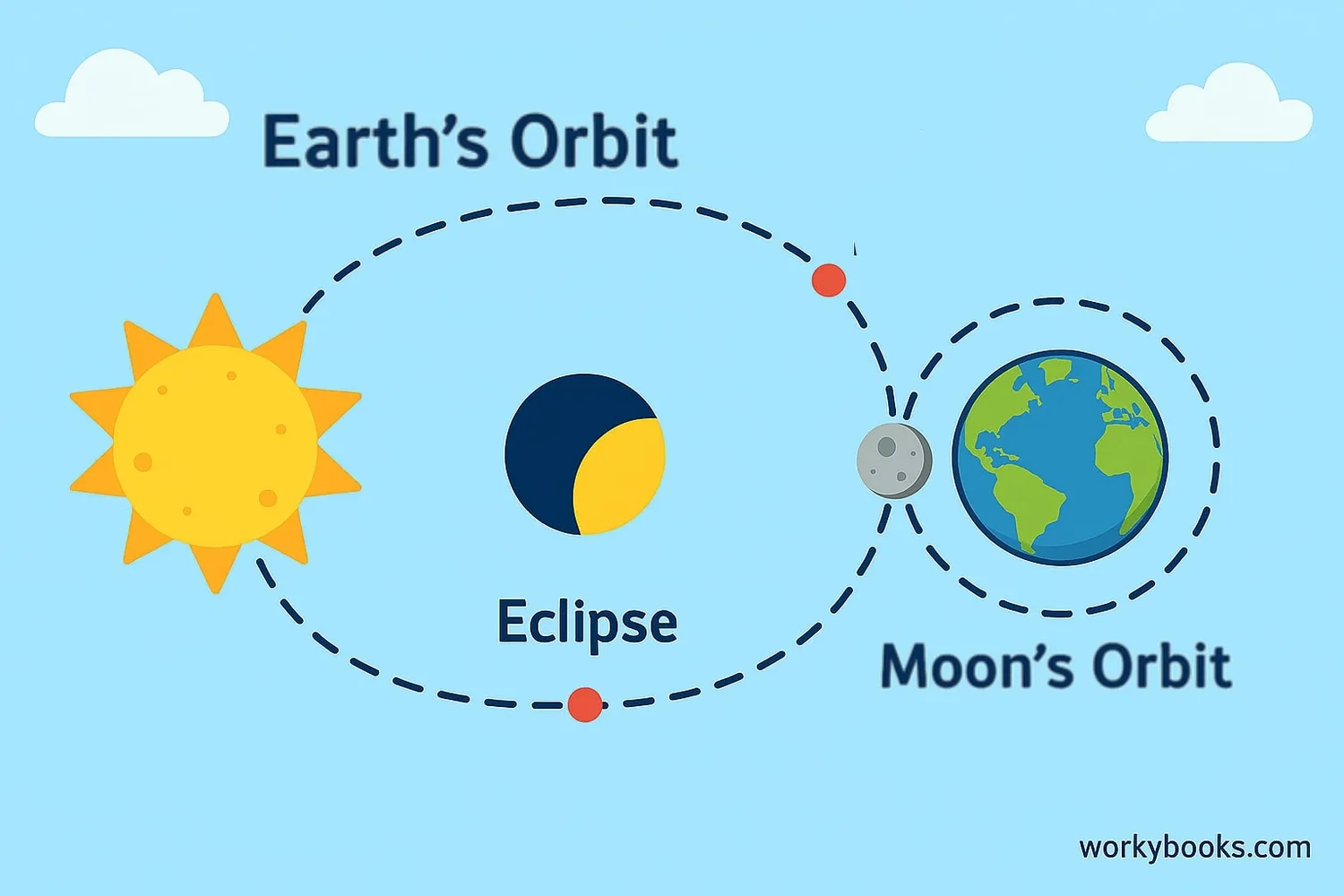
Solar eclipses happen because of the precise astronomical alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth. Here's the step-by-step process:
New Moon Phase
The Moon moves between Earth and the Sun during its monthly orbit
Orbital Alignment
The Moon's orbit crosses Earth's orbital plane at the right point
Shadow Cast
The Moon casts its shadow (umbra and penumbra) onto Earth's surface
Earth's Rotation
Earth's rotation causes the shadow to travel across the surface
Eclipse Viewing
People in the shadow's path witness the eclipse from their location
The Moon's shadow has two parts: the umbra (the inner, darker shadow where the Sun is completely blocked) and the penumbra (the outer shadow where the Sun is only partially blocked). People in the umbra see a total eclipse, while those in the penumbra see a partial eclipse.
The Moon's orbit is tilted about 5 degrees to Earth's orbit around the Sun, which is why we don't have eclipses every month. Eclipses only occur when the Moon is at or very near the points where its orbit crosses Earth's orbital plane.
Solar Eclipse Safety
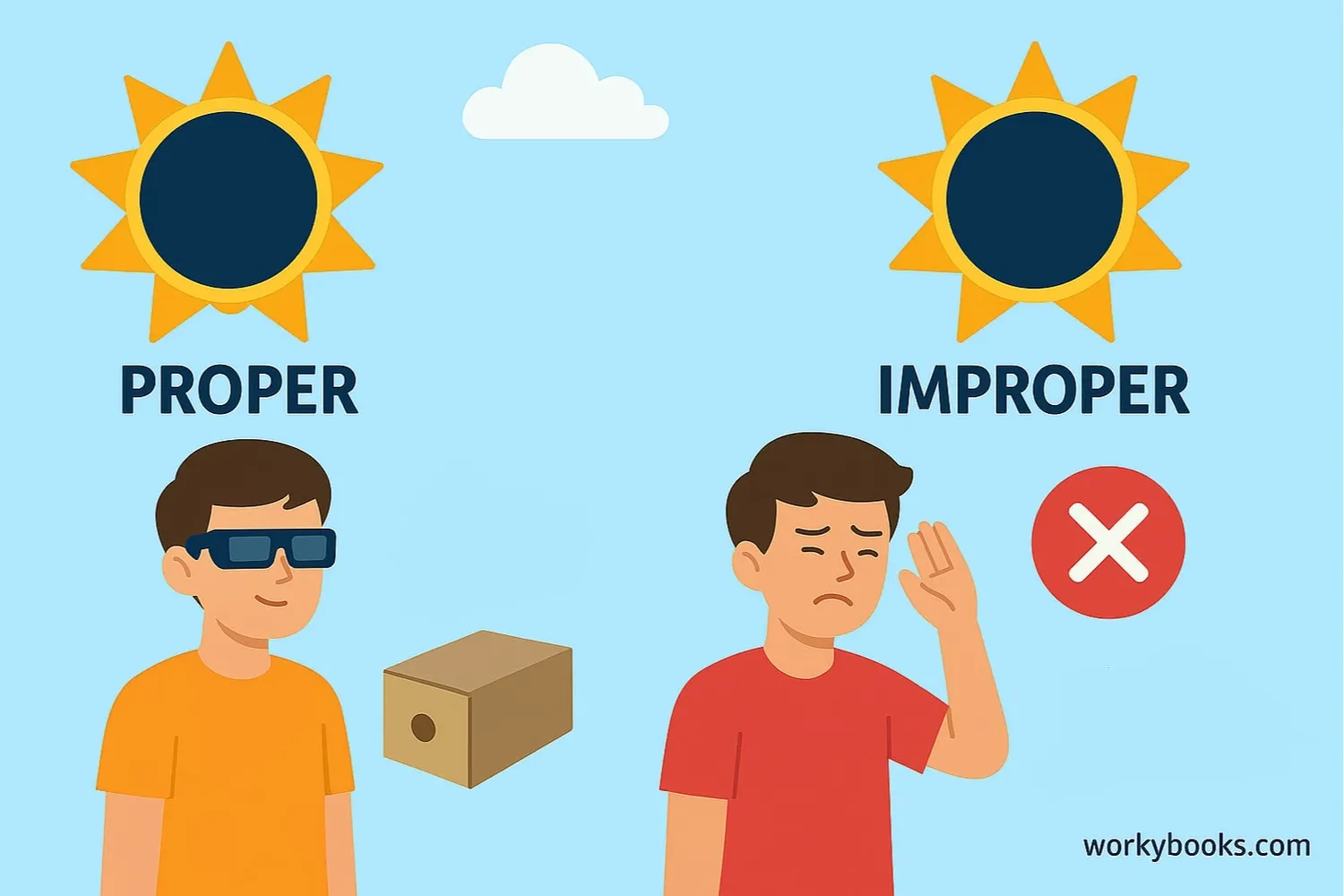
Eclipse safety is extremely important! Looking directly at the Sun without proper protection can permanently damage your eyes. Here's how to safely enjoy a solar eclipse:
Eclipse Glasses
Use ISO-certified solar eclipse glasses that block harmful radiation
Solar Filters
Cameras, telescopes, and binoculars need special solar filters
Pinhole Projector
Create a simple projector to view the eclipse indirectly
Important safety rules:
• Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection
• Regular sunglasses are NOT safe for viewing a solar eclipse
• Only during the brief total phase of a total eclipse (when the Sun is completely covered) is it safe to look without protection
• Supervise children at all times during eclipse viewing
With proper precautions, eclipse viewing can be a safe and unforgettable experience!
Safety First!
Damage to the retina from looking at the Sun isn't painful because the retina has no pain receptors. You might not realize the damage until hours later when vision problems appear.
Solar Eclipse Knowledge Check
Test your solar eclipse knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about solar eclipses:
Astronomy Facts
Discover some amazing facts about solar eclipses and astronomy!
Historical Records
The earliest recorded solar eclipse occurred over 4,000 years ago! Chinese astronomers documented an eclipse that happened on October 22, 2134 BCE. Ancient civilizations often viewed eclipses as omens or messages from gods.
Scientific Discoveries
Solar eclipses have helped make important scientific discoveries! During the 1919 eclipse, observations confirmed Einstein's theory of general relativity by showing how starlight bent around the Sun. Eclipses also allow scientists to study the Sun's corona.
Future Eclipses
Astronomers can predict eclipses with incredible accuracy thousands of years into the future! The longest totality in the 21st century occurred on July 22, 2009, lasting 6 minutes and 39 seconds. The next exceptionally long totality will be in 2186.
Temperature Drop
During a total solar eclipse, temperatures can drop significantly—as much as 10-15 degrees Fahrenheit! This sudden cooling happens because the Sun's radiation is blocked, similar to what occurs at sunset but much more rapidly.




