Storm Surge - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about coastal flooding during tropical storms and hurricanes
What is Storm Surge?
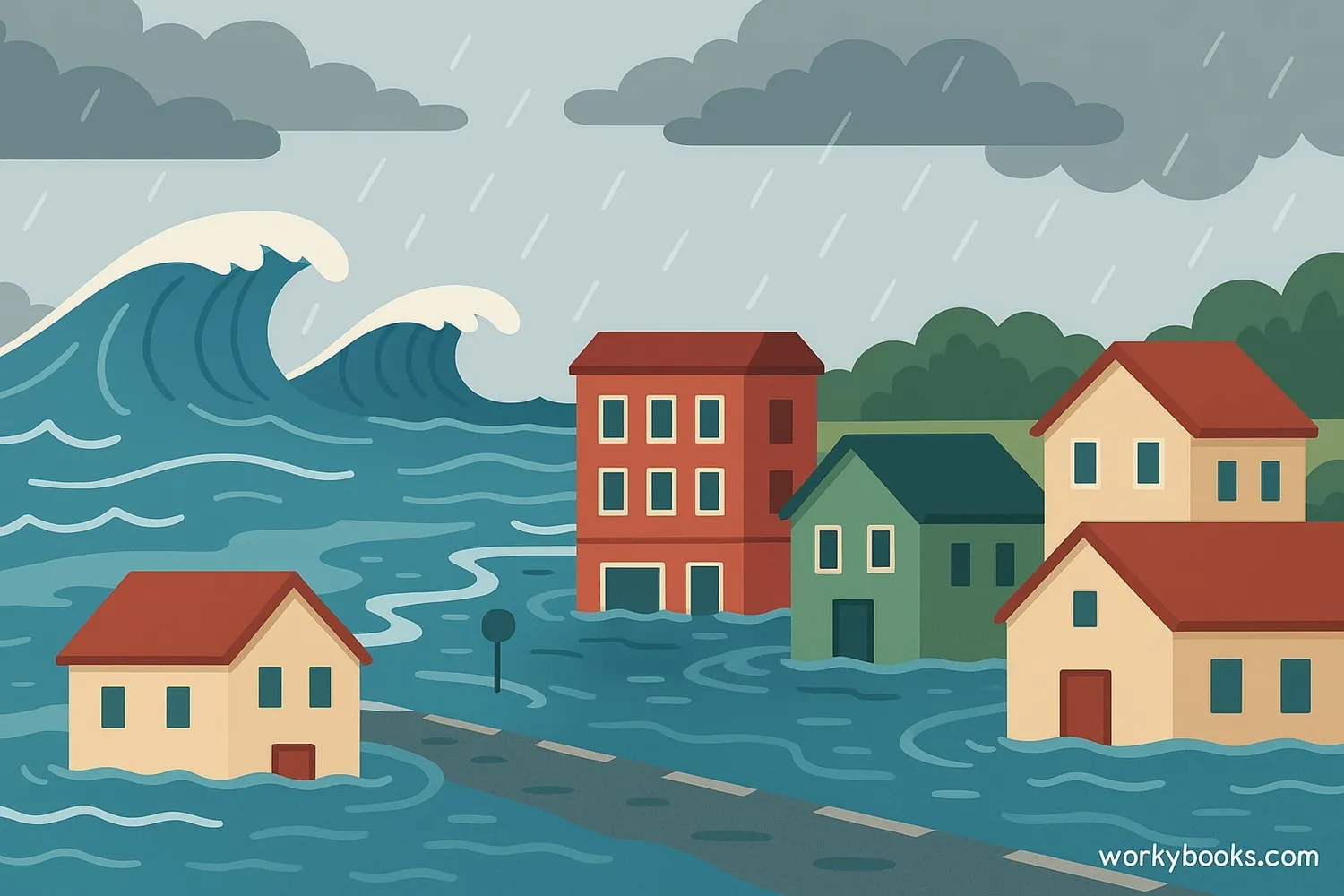

A storm surge is a rise in sea level caused by storms like hurricanes or typhoons. It happens when strong winds from the storm push ocean water toward the shore. This "wall of water" can cause severe flooding in coastal areas.
Storm surges are different from regular waves because they involve the entire ocean rising, not just surface waves. During a powerful storm like Hurricane Sandy (2012), storm surges can reach over 10 feet high and flood many miles inland!
Key Fact
Storm surge is the most dangerous part of a hurricane or tropical storm. It causes more deaths and damage than the high winds!
How Storm Surges Form
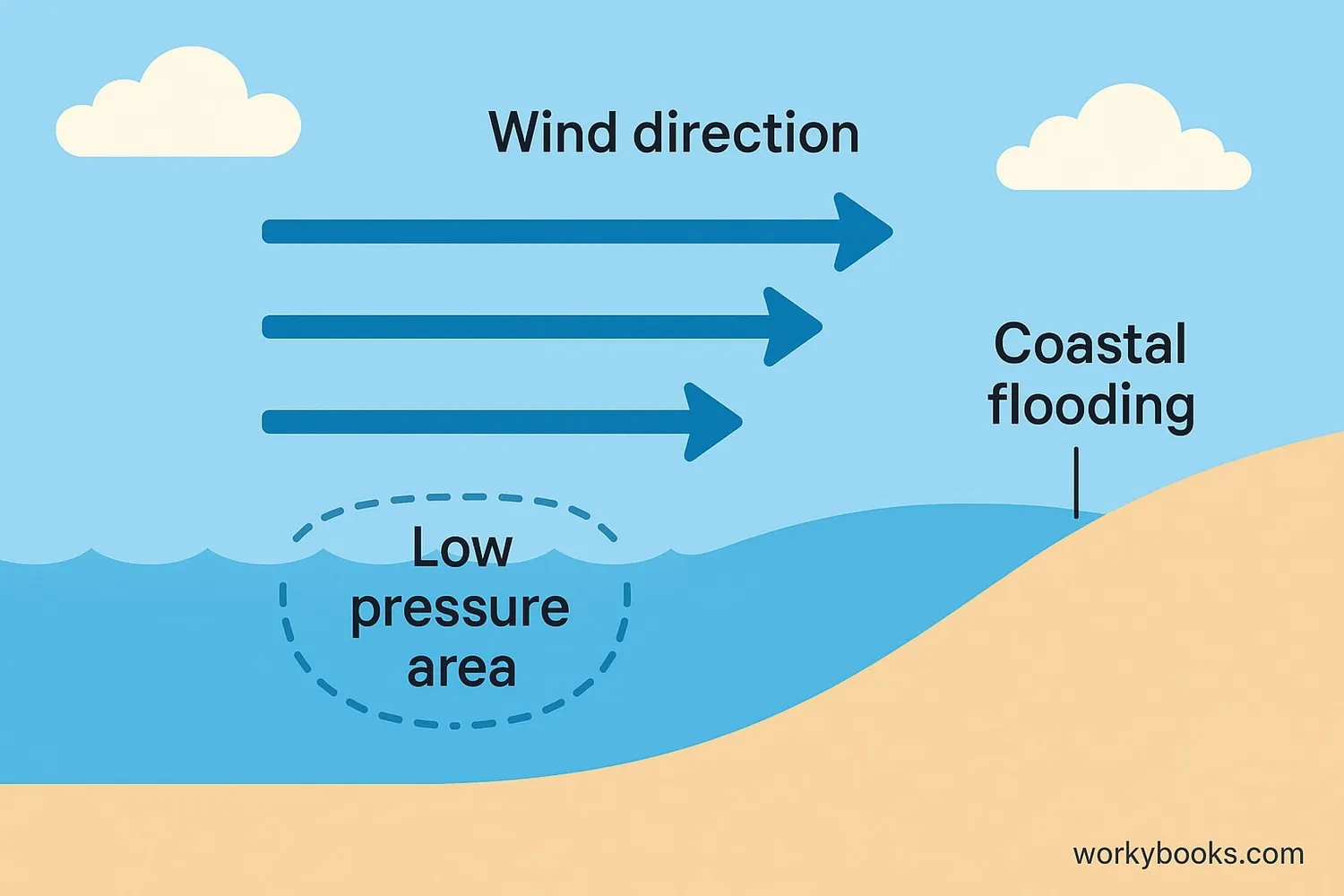
Storm surges form through a combination of powerful forces:
Wind Push
Strong winds push ocean water toward the coast
Low Pressure
Low air pressure in the storm "lifts" the ocean surface
Waves
Large waves form on top of the rising water
Coastal Shape
Shallow coastal areas and bays amplify the surge
High Tide
Surges combined with high tides cause maximum flooding
Scientists use ensemble prediction to forecast storm surges. This means they run many computer models with slightly different conditions to understand all possible outcomes. This helps communities prepare for different flooding scenarios.
Climate Change Connection
As sea levels rise due to climate change, storm surges become higher and more destructive. Even small sea level rises can dramatically increase flooding areas.
Storm Surge Impacts and Risks

Storm surges create significant dangers for coastal regions:
Property Damage
Flooding can destroy homes, businesses, and infrastructure
Environmental Harm
Saltwater damages ecosystems and wildlife habitats
Human Safety
Fast-rising water puts lives at risk and requires evacuations
Some of the most devastating storm surges in history include:
• Hurricane Katrina (2005): 28-foot surge flooded New Orleans
• Hurricane Sandy (2012): 14-foot surge flooded New York City
• Typhoon Haiyan (2013): 20-foot surge in the Philippines
Coastal communities use hydrodynamic modeling to predict storm surge impacts and build protective barriers like seawalls and levees.
Storm Surge Quiz
Test your knowledge about storm surges with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about storm surges:
Storm Surge Facts
Discover amazing information about storm surges:
Record Height
The highest recorded storm surge was during the 1899 Cyclone Mahina in Australia, reaching an incredible 43 feet (13 meters) high!
Fast Flooding
Storm surge waters can rise as fast as 1 foot every 10 minutes in extreme conditions, giving people very little time to escape.
Prediction Power
Modern storm surge models can predict flooding with remarkable accuracy up to 5 days in advance, saving countless lives.
Not Just Water
Storm surge water contains dangerous debris, sewage, chemicals, and even sea creatures! After Hurricane Katrina, sharks were spotted swimming in flooded streets.




