Amphibians - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the fascinating world of frogs, toads, salamanders, and their incredible life cycles!
What are Amphibians?
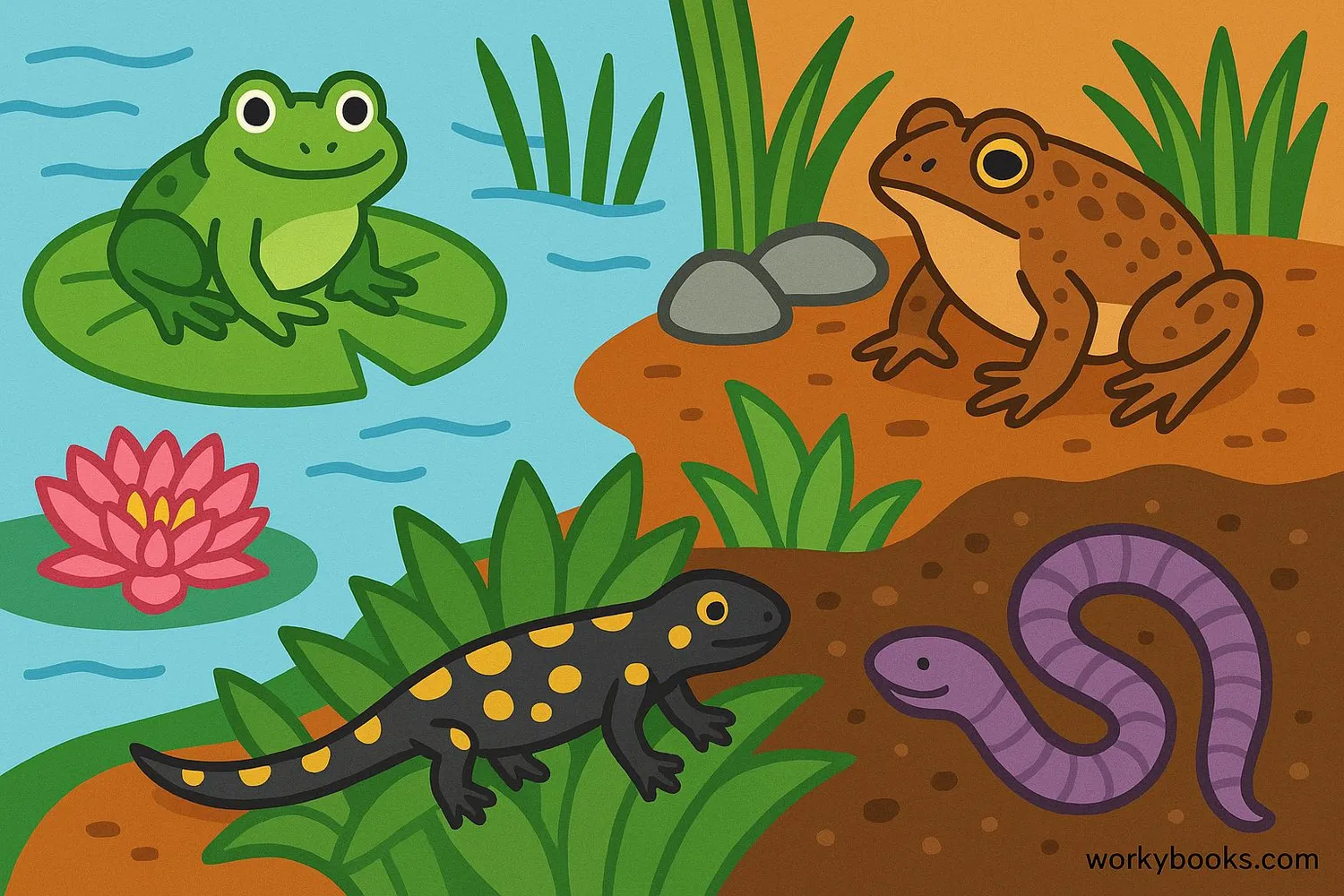

Amphibians are special vertebrate animals that can live both in water and on land! The word "amphibian" comes from Greek and means "double life" - perfect for animals that live in two worlds.
There are three main types of amphibians:
• Frogs and toads - Great jumpers with long back legs
• Salamanders - Lizard-like with long tails
• Caecilians - Legless amphibians that look like worms or snakes
What makes amphibians special? They have smooth, moist skin that helps them breathe, they're cold-blooded, and most go through an amazing transformation called metamorphosis!
Amazing Fact!
Amphibians were the first vertebrates to walk on land over 360 million years ago!
The Amazing Amphibian Life Cycle
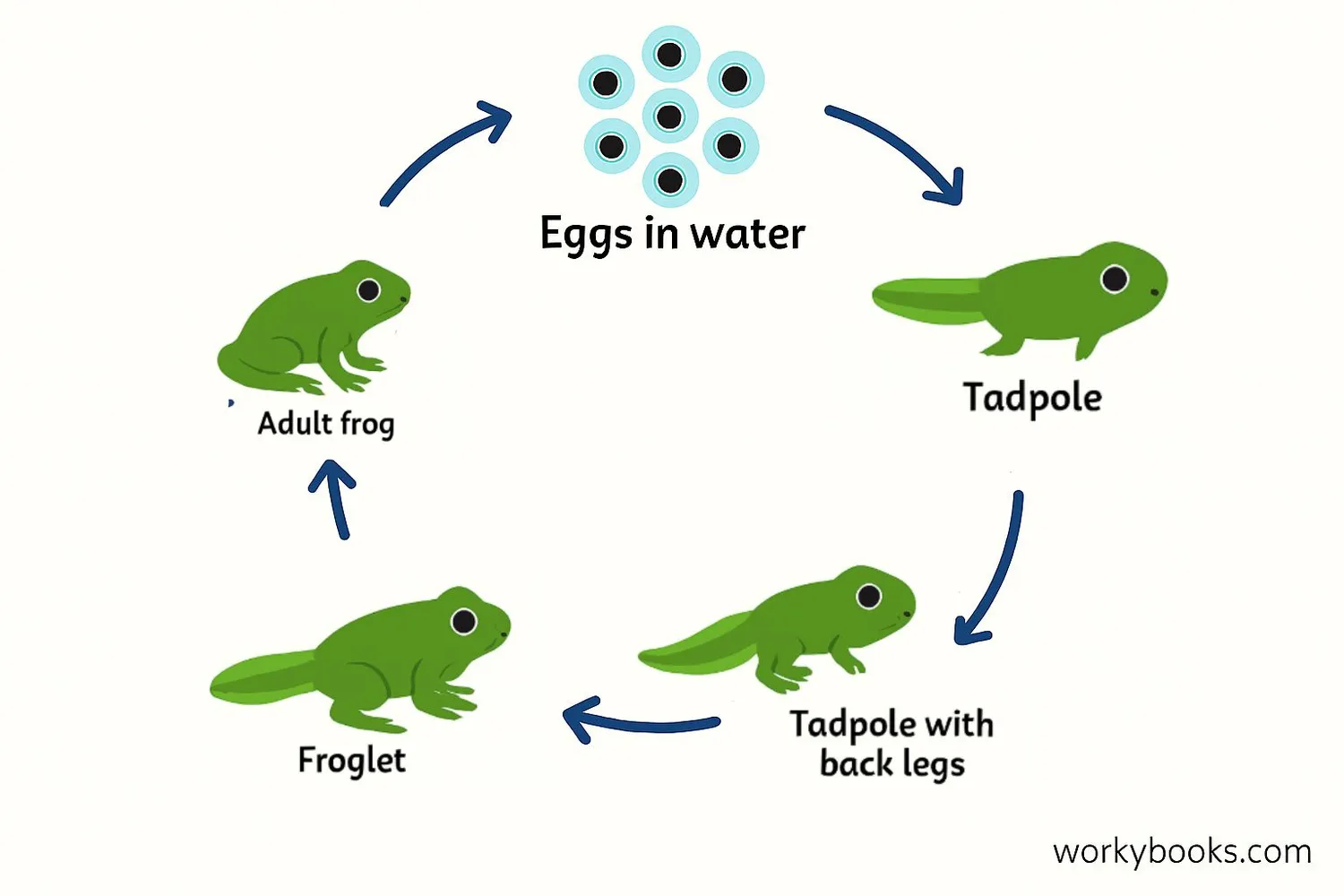
The amphibian life cycle is one of nature's most fascinating transformations! This process is called metamorphosis, which means "complete change." Let's explore the frog's life cycle as an example:
Egg Stage
Frogs lay jelly-like eggs in water, often in clusters
Tadpole
Baby frog with gills and tail that lives only in water
Growth
Back legs develop, then front legs, lungs form
Froglet
Tail shrinks, can breathe air but still mostly aquatic
Adult Frog
Fully developed, lives on land but returns to water
This incredible transformation can take just a few weeks or several years depending on the species and environment. Salamanders also go through metamorphosis, but they keep their tail throughout their life!
Nature's Design!
Some salamanders never fully metamorphose! Axolotls keep their gills and live their entire lives underwater.
Why Amphibians are Important
Amphibians play vital roles in our ecosystems and are often called "environmental indicators" because their health tells us about the health of our environment:
Environmental Indicators
Sensitive skin makes them first to show pollution problems
Ecosystem Balance
They control insect populations and are food for larger animals
Medical Research
Their unique biology helps scientists develop new medicines
Unfortunately, amphibians are facing serious threats:
• Habitat loss from development and pollution
• Climate change affecting their environments
• A deadly fungus disease affecting populations worldwide
Protecting amphibians means protecting wetlands and freshwater habitats that many other species also depend on!
Amphibians Quiz
Test your amphibian knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about amphibians:
Amazing Amphibian Trivia
Discover some incredible facts about amphibians!
Super Jumpers
The South African sharp-nosed frog can jump over 10 feet - that's 44 times its body length! If humans could jump like this, we could leap over a basketball court in one bound!
Poison Power
The golden poison dart frog has enough toxin to kill 10 adults! Indigenous people used their poison on blowdart tips. Just one frog has 1 milligram of batrachotoxin - enough to kill about 10,000 mice!
Regeneration Experts
Salamanders can regrow lost limbs, tails, eyes, and even parts of their heart and brain! Scientists study them to learn how we might someday regenerate human body parts.
Freeze Survivors
Wood frogs can survive being frozen solid! During winter, their bodies produce special antifreeze that protects their cells while up to 65% of their body water turns to ice. In spring, they thaw and hop away!




