Arctic Fox - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about the amazing adaptations of this snow-white survivor
What is an Arctic Fox?

The Arctic Fox (Vulpes lagopus) is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere. These remarkable animals are well known for their:
• Pure white winter coat that camouflages them in snow
• Compact body shape that conserves heat
• Thick fur covering even their footpads
• Bushy tail used for balance and warmth
Arctic Foxes are about the size of a large house cat, measuring 18-26 inches long (not including their tail) and weighing 6-12 pounds. They live 3-6 years in the wild.
Name Meaning
The scientific name "Vulpes lagopus" means "hare-footed fox" because their furry feet resemble a rabbit's!
Arctic Fox Habitat
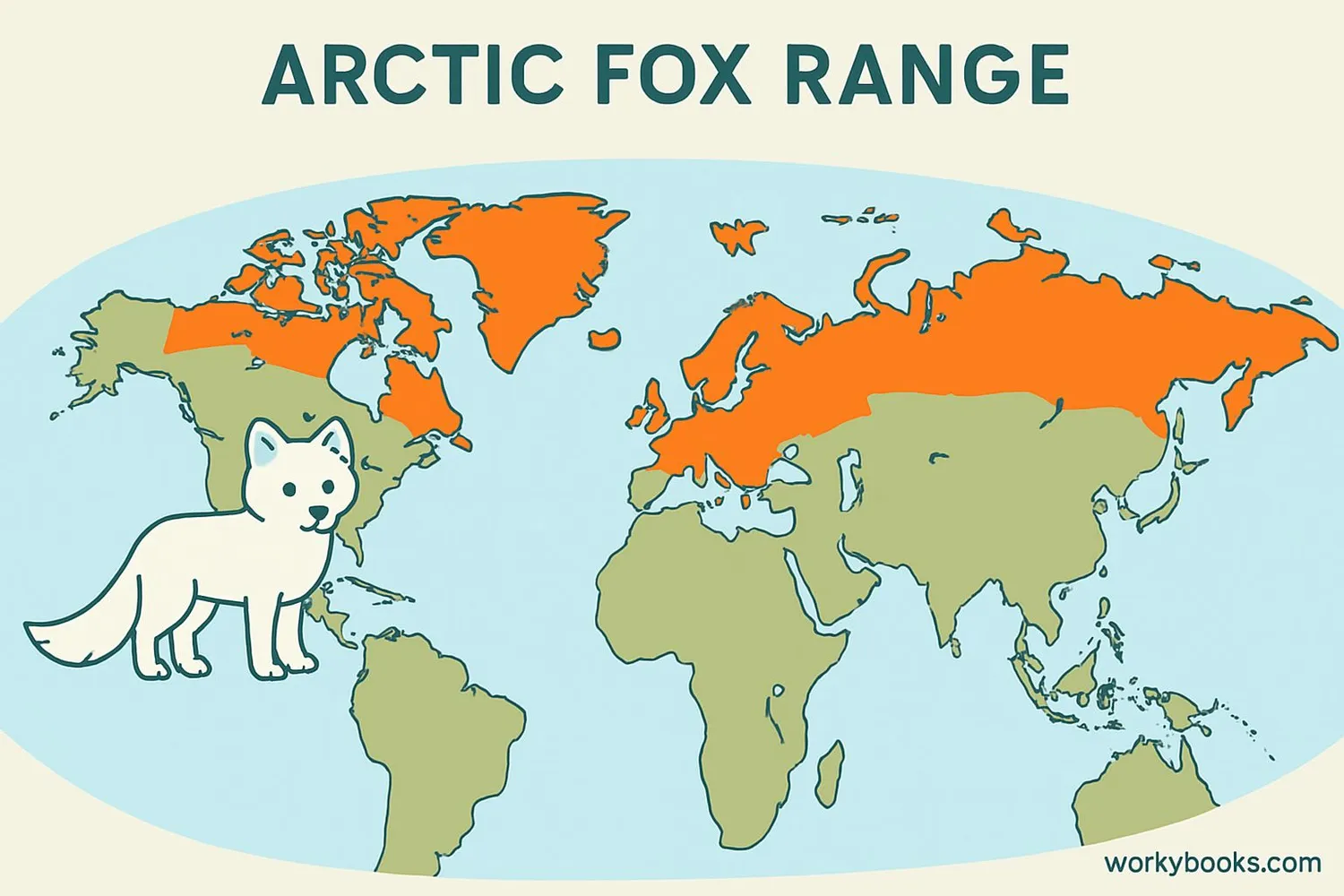
Arctic Foxes live in some of the coldest places on Earth! Their habitat includes:
Tundra Regions
Treeless plains with permanently frozen ground
Arctic Coastlines
Areas near sea ice where they hunt marine life
Mountainous Areas
Some populations live in alpine tundra
These foxes are found across the Arctic Circle in:
• Northern Canada and Alaska
• Greenland
• Scandinavia
• Russia
• Iceland (where they are the only native land mammal)
Their range can extend southward during winter months when food is scarce.
Arctic Fox Adaptations
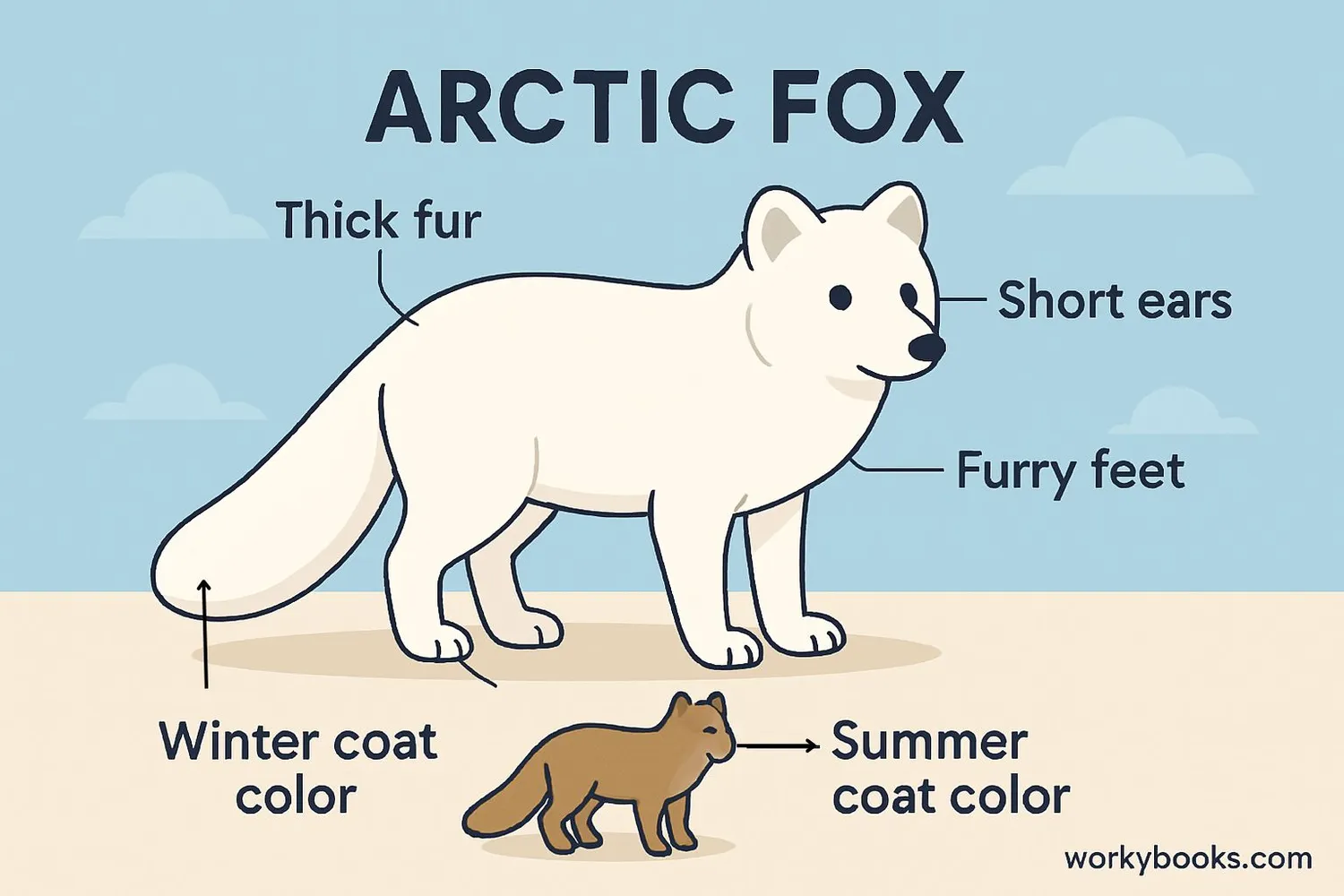
Arctic Foxes have incredible adaptations that help them survive temperatures as low as -58°F (-50°C):
Insulating Fur
The densest fur of any Arctic mammal with 20,000 hairs/cm²
Seasonal Colors
White in winter, brown/gray in summer for camouflage
Furry Feet
Hair-covered footpads act like snowshoes
Heat Retention
Short ears and muzzle reduce heat loss
Food Storage
Caches extra food under snow for winter
Temperature Regulation
Arctic Foxes can maintain a consistent body temperature of 104°F (40°C) even when outside temperatures drop to -58°F (-50°C)!
Arctic Fox Diet
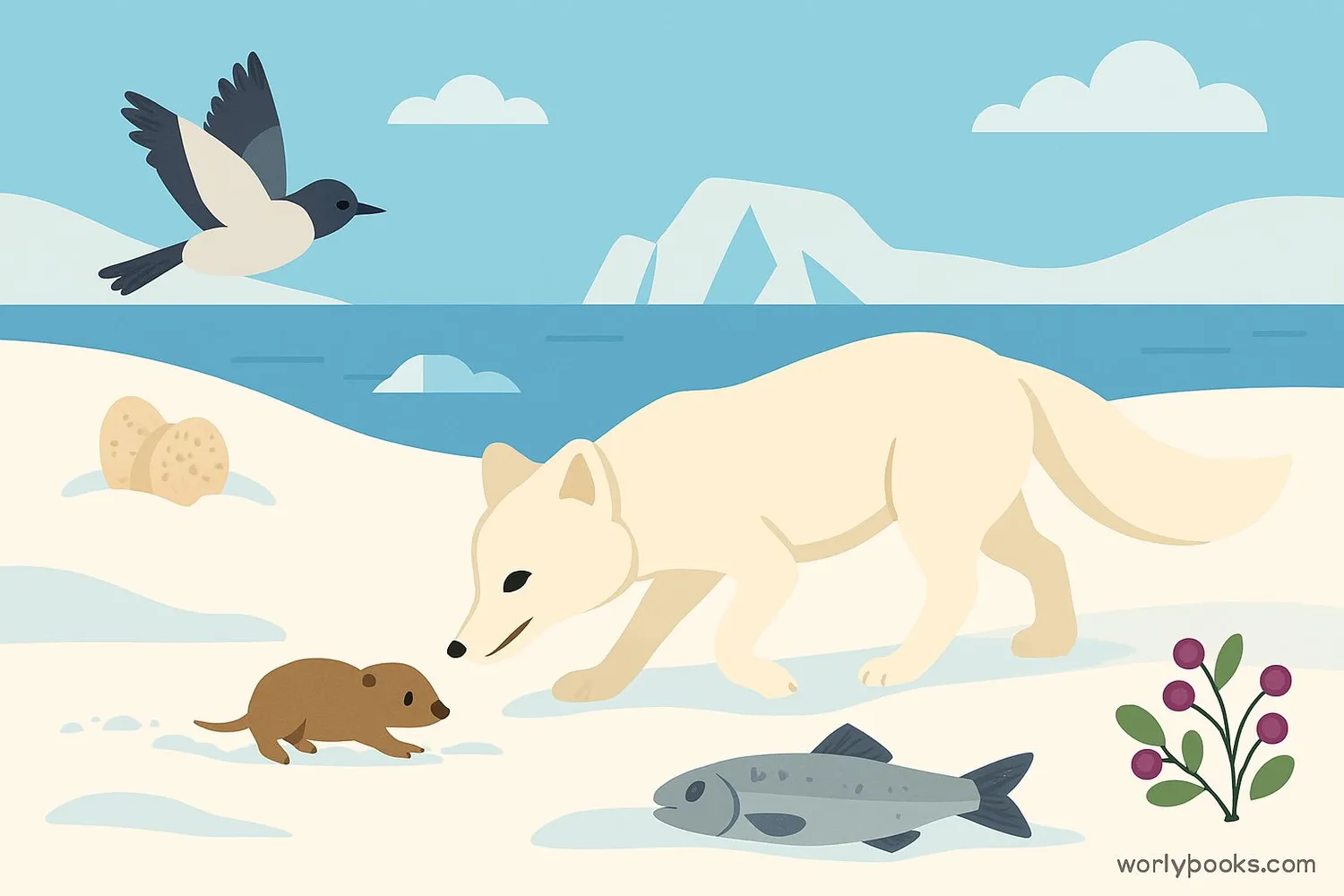

Arctic Foxes are opportunistic eaters with a varied diet that changes with the seasons:
Primary Food
Lemmings (small rodents) make up most of their diet
Secondary Food
Birds, eggs, fish, and seal carcasses
Summer Additions
Berries, seaweed, and insects when available
Hunting behaviors:
• Can hear lemmings moving under 4-5 inches of snow
• Leap straight up to break through snow and catch prey
• Follow polar bears to scavenge leftover seal meat
• Store extra food in underground caches for winter
An Arctic Fox needs to eat about 20 lemmings per day to survive!
Arctic Fox Quiz
Test your Arctic Fox knowledge with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Arctic Foxes:
Arctic Fox Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about Arctic Foxes!
Population Changes
Arctic Fox populations can fluctuate dramatically with lemming numbers - in good years there may be many foxes, while in poor years few survive. This is called a "boom and bust" cycle.
Long Distance Travelers
Some Arctic Foxes migrate incredible distances - one was tracked traveling over 2,700 miles (4,400 km) from Norway to Canada in just 76 days!
Family Life
Arctic Fox families stay together in large dens that may be used for centuries by generations of foxes. Some dens have over 100 entrances!
Survival Experts
Arctic Foxes can survive temperatures as low as -58°F (-50°C) before increasing their metabolic rate to stay warm. Their winter fur provides such good insulation that they start shivering only at -94°F (-70°C)!




