Binary Fission - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how tiny organisms multiply through simple cell division!
What is Binary Fission?
Binary fission is how tiny organisms like bacteria make copies of themselves! It's a simple form of asexual reproduction where one cell divides into two identical cells.
The word "binary" means "two", and "fission" means "splitting apart". So binary fission literally means "splitting into two". It's how bacteria multiply quickly - some can double their numbers every 20 minutes!
This process happens in prokaryotes (organisms without a nucleus) like bacteria and archaea. Unlike humans who need two parents, organisms using binary fission only need one parent to create offspring!
Science Fact!
Under ideal conditions, one bacterium could produce over 1 billion descendants in just 10 hours through binary fission!
How Binary Fission Works
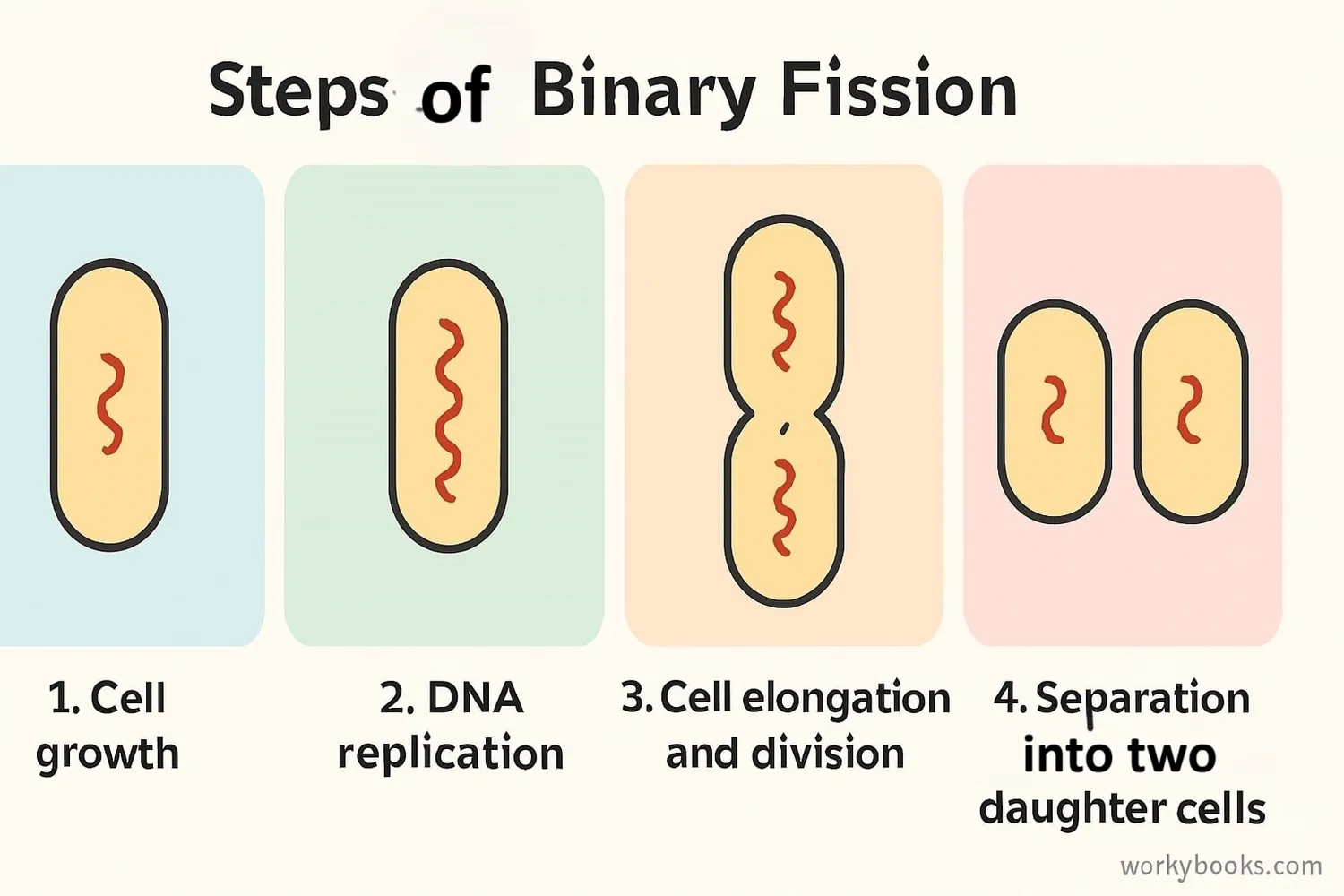
Binary fission is a straightforward process with just a few steps. Here's how it works:
Growth
The cell grows to nearly double its size
DNA Replication
The DNA makes an identical copy of itself
Separation
DNA copies move to opposite ends of the cell
Division
The cell membrane pinches inward to form two cells
Two New Cells
Two identical daughter cells are formed
This process creates two new organisms that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Since no genetic mixing occurs, all the cells are clones of each other.
Division Speed!
E. coli bacteria can complete binary fission in just 20 minutes under ideal conditions!
Examples of Binary Fission
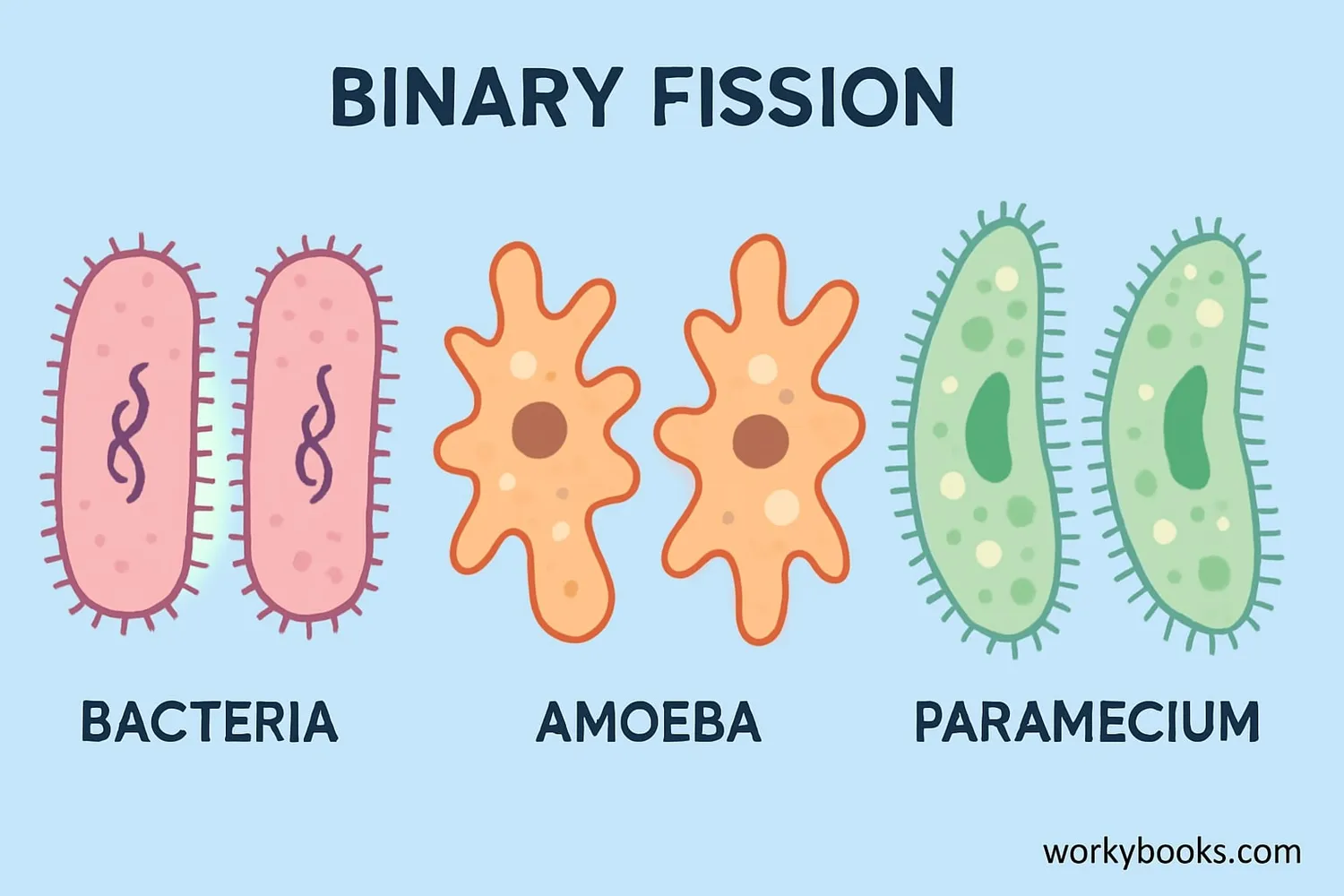
While bacteria are the most famous users of binary fission, many other organisms use this reproduction method:
Bacteria
All bacteria reproduce through binary fission
Amoeba
Single-celled protists that divide through binary fission
Paramecium
Ciliated protists that use a modified form of binary fission
Interesting Fact!
Some organisms like Euglena use a special type of binary fission called longitudinal fission where they split lengthwise!
Binary Fission vs Mitosis
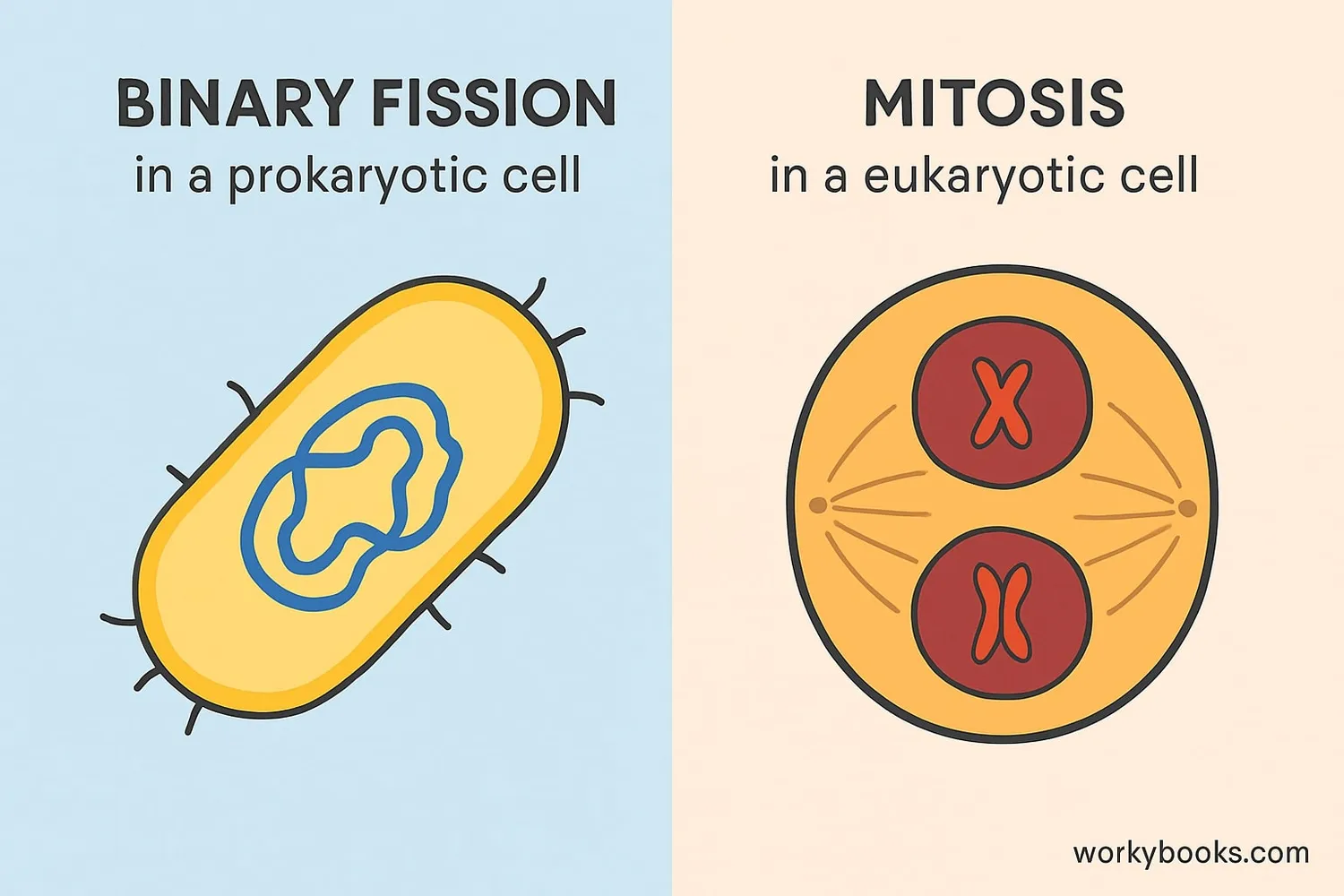
While both processes involve cell division, binary fission and mitosis have important differences:
| Feature | Binary Fission | Mitosis |
|---|---|---|
| Organisms | Prokaryotes (bacteria, archaea) | Eukaryotes (plants, animals, fungi) |
| Cell Type | Simple cells without nucleus | Complex cells with nucleus |
| DNA Organization | Single circular chromosome | Multiple linear chromosomes |
| Process | Simple division without phases | Complex process with multiple phases |
| Result | Two identical cells | Two identical cells (in body cells) |
The main difference is that binary fission occurs in prokaryotes without a nucleus, while mitosis occurs in eukaryotes with a nucleus. Binary fission is simpler and faster, while mitosis is more complex and precise.
Binary Fission Quiz
Test your knowledge about binary fission with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about binary fission:
Fascinating Binary Fission Facts
Discover some amazing facts about binary fission!
Speed Record
Some bacteria can complete binary fission in just 10 minutes! At this rate, one bacterium could theoretically produce over 68 billion descendants in 12 hours.
Ancient Process
Binary fission is one of the oldest reproduction methods on Earth, dating back at least 3.5 billion years to the earliest life forms!
Space Division
Bacteria can perform binary fission in space! Scientists have studied how microgravity affects this process during space missions.
Perfect Copies?
While daughter cells are nearly identical, small genetic mutations can occur during DNA replication, leading to variations that help bacteria adapt.





