Chlorophyll - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how plants turn sunlight into energy and why they're green!
What is Chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that makes photosynthesis possible. It's a special molecule found in structures called chloroplasts inside plant cells. Think of chlorophyll as nature's solar panel - it captures sunlight and turns it into energy that plants can use!
The name "chlorophyll" comes from Greek words meaning "green leaf." Without chlorophyll, plants wouldn't be able to make their own food, and life as we know it wouldn't exist. This amazing green pigment is the reason why most plants look green to our eyes.
Plant Fact!
Chlorophyll is found in all green plants, algae, and some bacteria. It's what makes plants the primary producers in most ecosystems!
How Chlorophyll Works
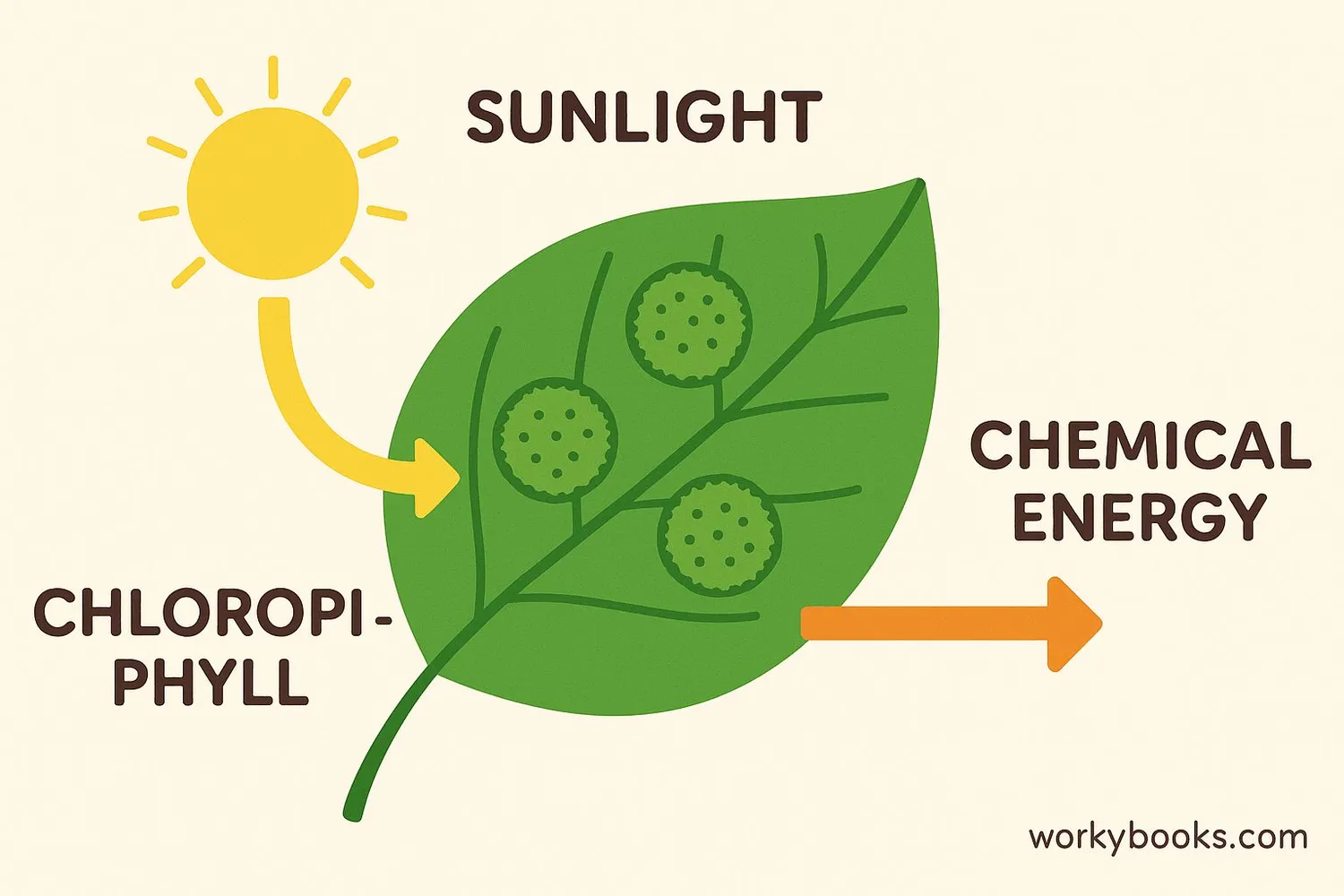
Chlorophyll works by capturing light energy from the sun and using it to power the process of photosynthesis. Here's how this amazing process works:
Light Absorption
Chlorophyll molecules absorb sunlight
Water Splitting
Water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen
Carbon Dioxide Use
CO₂ from the air combines with hydrogen
Glucose Creation
Sugars (glucose) are formed for plant energy
Oxygen Release
Oxygen is released into the atmosphere
The photosynthesis formula is:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Which means: Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
Chlorophyll is essential for the first step of this process. Without it, plants couldn't capture the sun's energy to start making food.
Energy Conversion
Chlorophyll converts light energy into chemical energy with incredible efficiency - better than any solar panel humans have invented!
Types of Chlorophyll
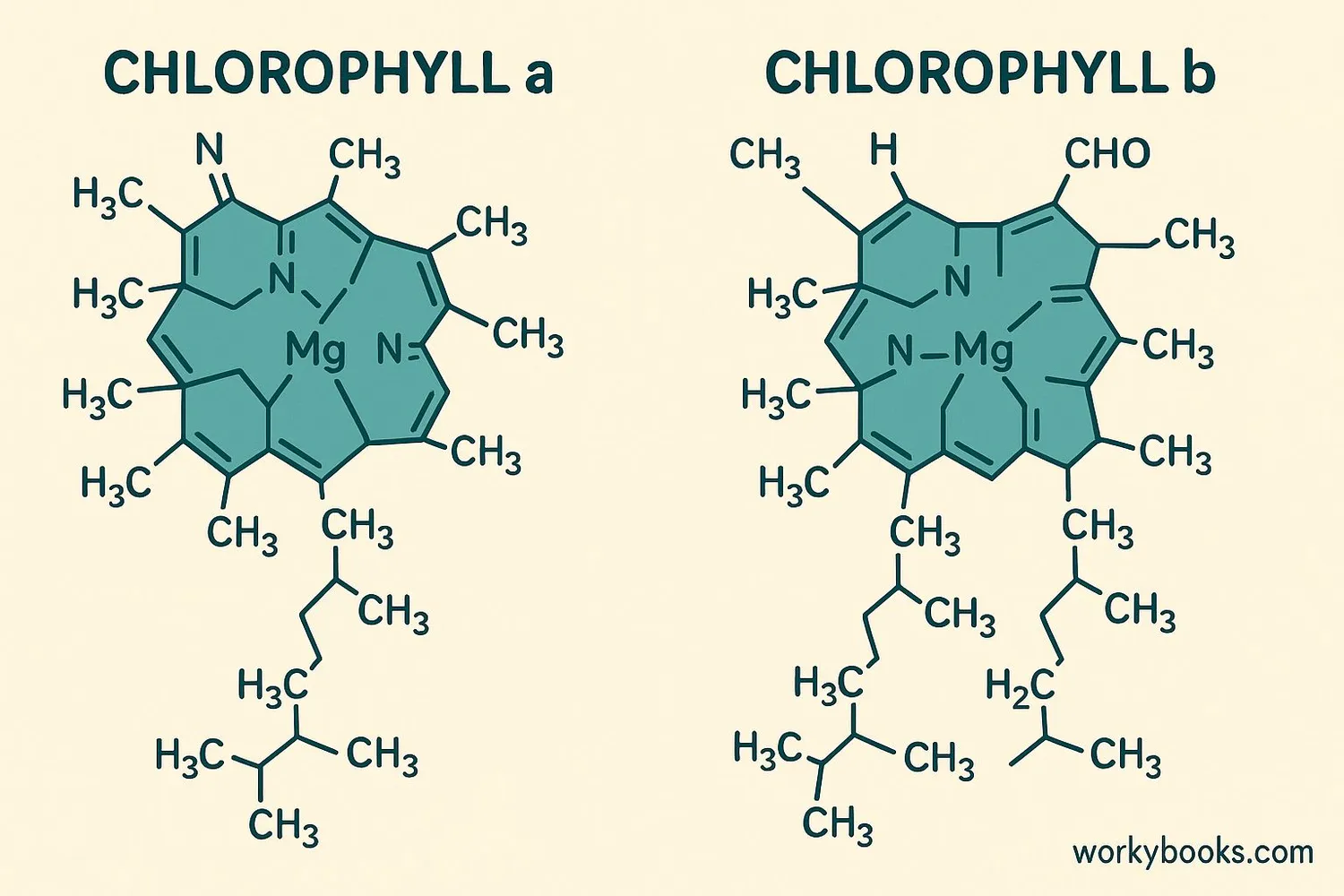
There are several types of chlorophyll found in nature, but the most important in plants are:
Chlorophyll A
Blue-green pigment that directly converts sunlight to energy
Chlorophyll B
Yellow-green pigment that passes energy to chlorophyll A
Chlorophyll A is present in all plants that perform photosynthesis. It's the primary pigment that actually converts light to energy.
Chlorophyll B is an accessory pigment that absorbs different wavelengths of light and transfers the energy to chlorophyll A. This allows plants to capture more light energy than they could with chlorophyll A alone.
Other types include chlorophyll C and D found in algae, and bacteriochlorophyll in certain bacteria.
Why is Chlorophyll Green?
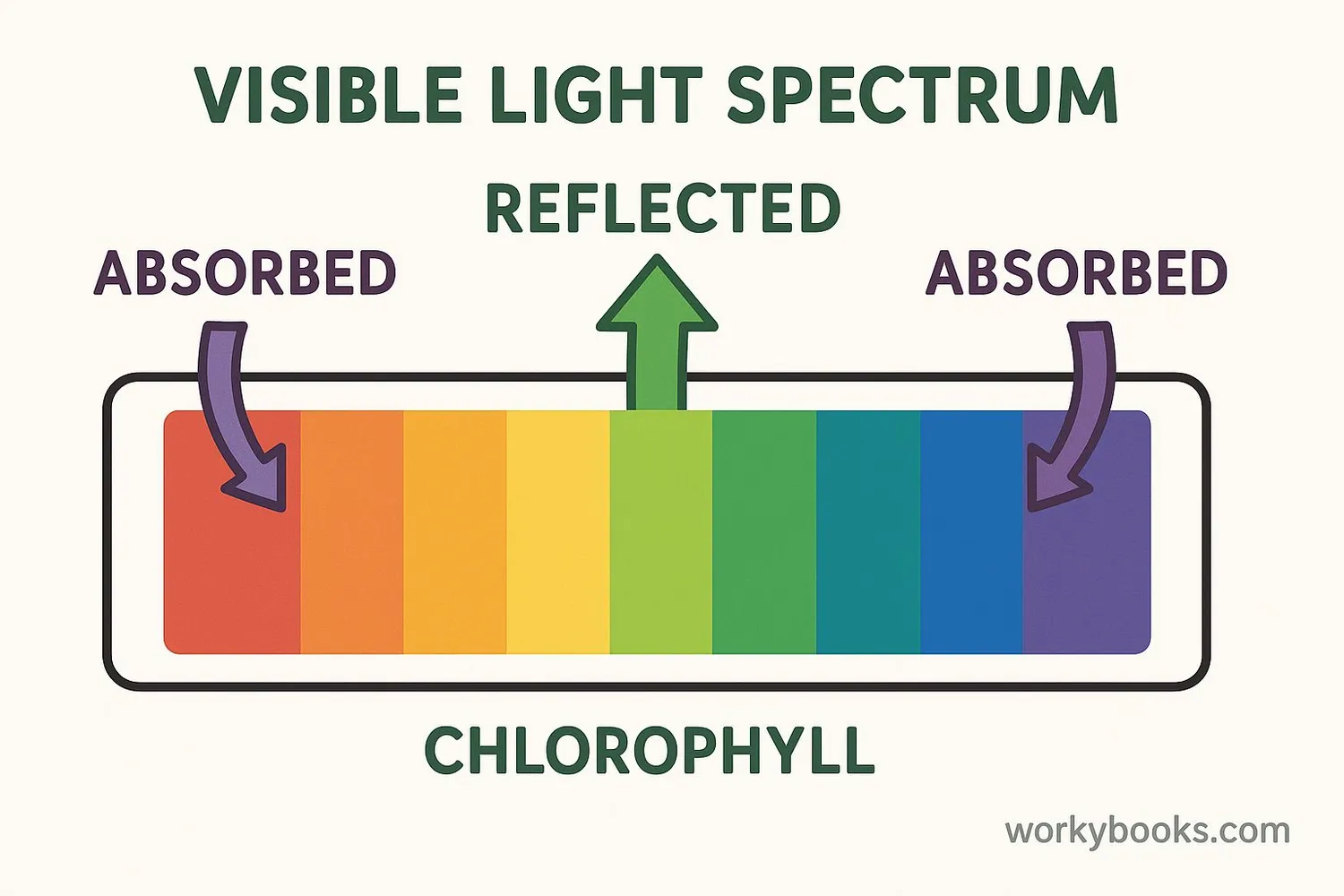
Chlorophyll appears green because of the way it interacts with light. Here's the science behind the color:
Light Absorption
Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red light wavelengths
Light Reflection
Green light is not absorbed but reflected
Color Perception
Our eyes see the reflected green light
Sunlight contains all colors of the rainbow. Chlorophyll molecules are especially good at absorbing blue and red light because these wavelengths have just the right amount of energy for photosynthesis. Green light isn't absorbed as effectively, so it bounces off the leaves and reaches our eyes.
This is why plants look green to us! In autumn, when chlorophyll breaks down, we see other pigments like carotenoids (orange and yellow) that were there all along.
Evolutionary Advantage
Scientists believe chlorophyll evolved to absorb blue and red light because these wavelengths penetrate water better, helping aquatic plants survive.
Plant Science Quiz
Test your chlorophyll knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about chlorophyll:
Fun Chlorophyll Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about chlorophyll and plants!
Ocean Green
Most of Earth's chlorophyll is found in the ocean! Microscopic phytoplankton contain chlorophyll and produce about 50% of the world's oxygen.
Energy Efficiency
Chlorophyll converts sunlight to energy with about 2-4% efficiency. While this seems low, it's actually more efficient than most solar panels!
Space Agriculture
Scientists are studying how to grow plants in space using artificial light optimized for chlorophyll absorption to feed astronauts on long missions.
Molecular Cousin
Chlorophyll has a similar structure to hemoglobin in our blood! The main difference is that chlorophyll has magnesium at its center, while hemoglobin has iron.





