Desert Rain Frog - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the unique amphibian that squeaks like a toy!
What is a Desert Rain Frog?
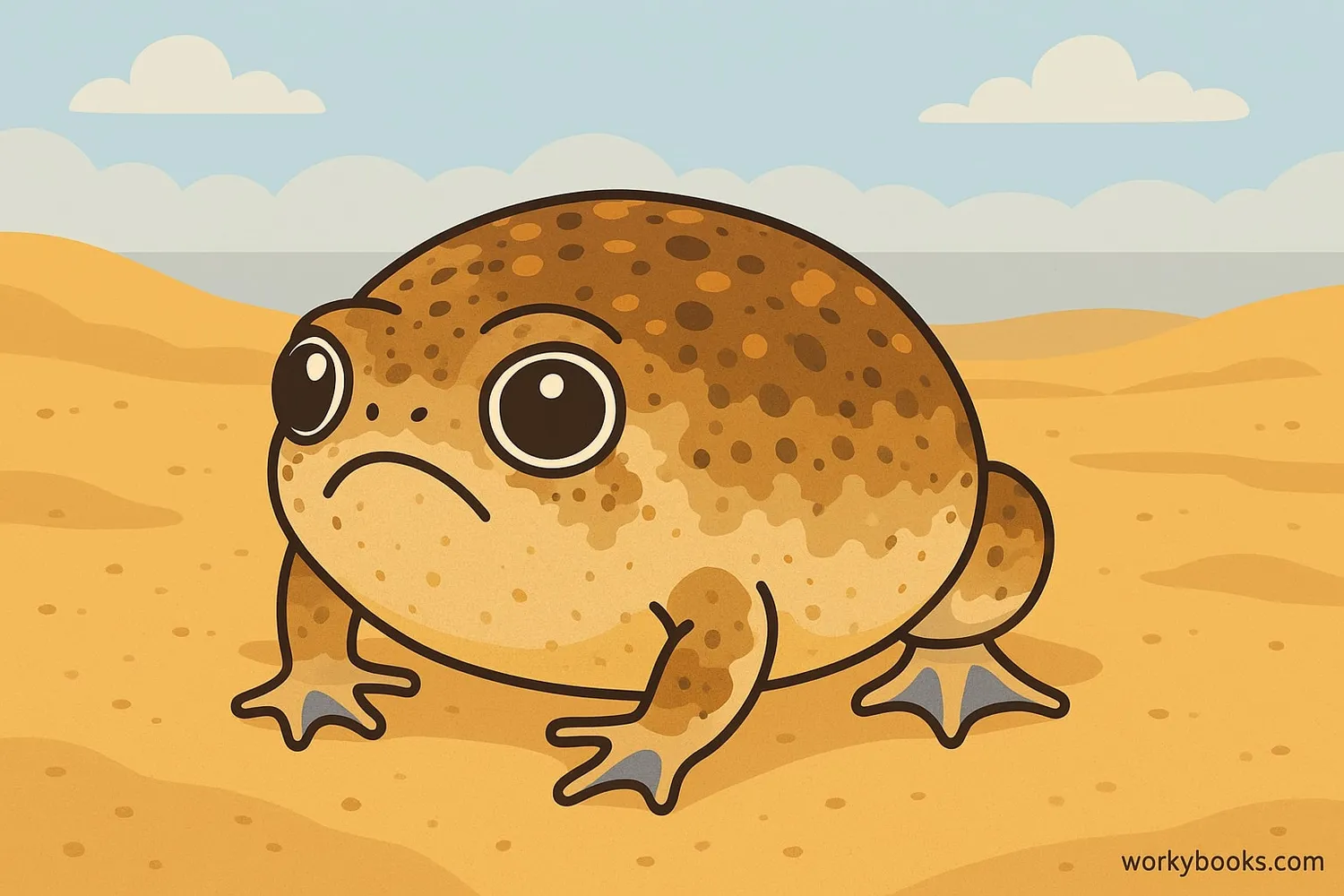

The Desert Rain Frog (Breviceps macrops) is a small, round amphibian known for its unique squeaky call and adorable appearance. Unlike most frogs, it has a plump body, short legs, and webbed feet perfect for digging in the sand. These fascinating creatures are nocturnal and spend most of their time underground.
Desert Rain Frogs are about 4-6 cm (1.5-2.5 inches) long and have bulging eyes that help them see in low light. Their most famous feature is their high-pitched, squeaky call that sounds like a squeaky toy! This unique sound has made them internet celebrities.
Did You Know?
The Desert Rain Frog's scientific name "Breviceps macrops" means "short head with big eyes" - a perfect description of this unique amphibian!
Habitat & Distribution
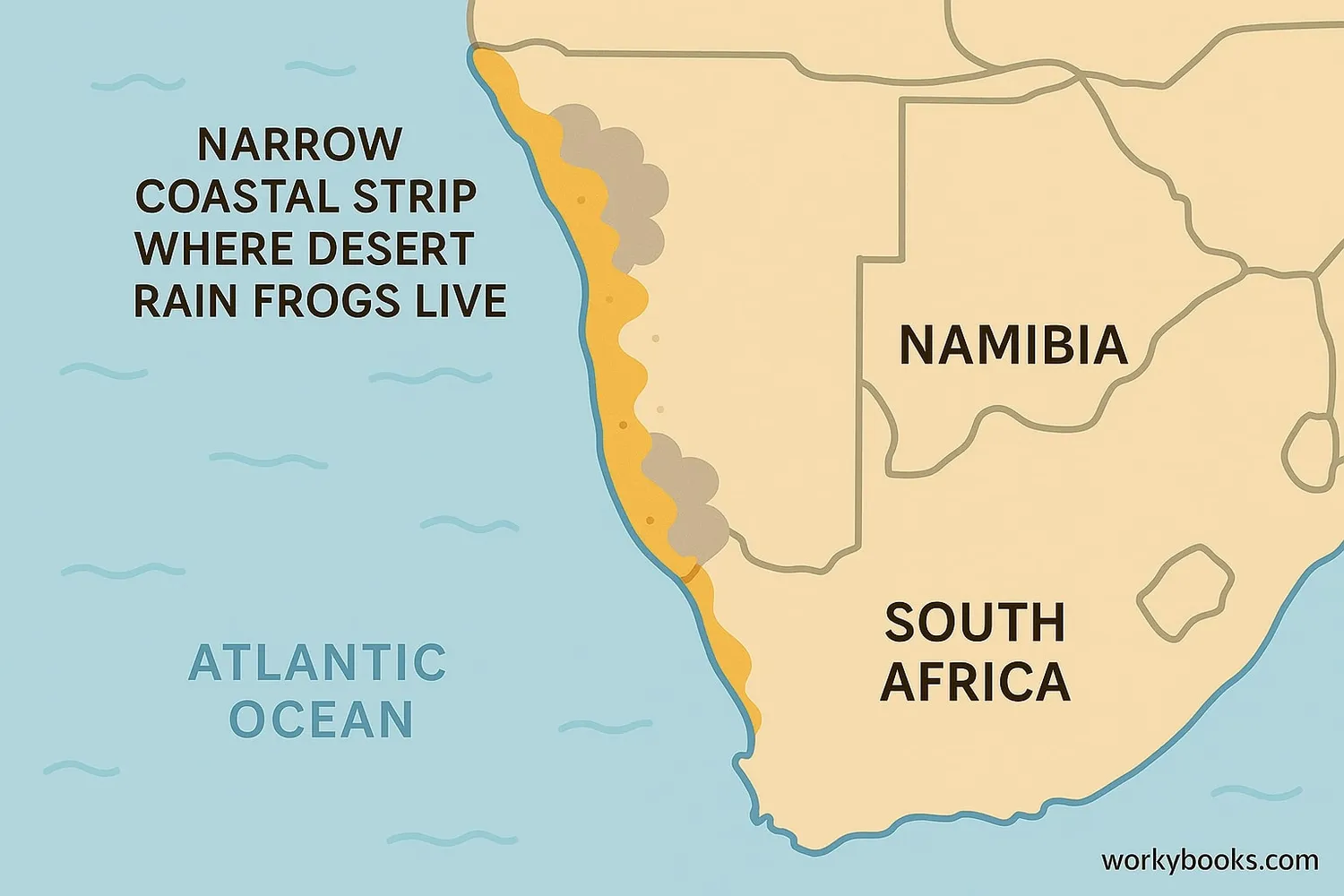
Desert Rain Frogs have a very limited habitat range. They are found only along a narrow strip of coastline in:
• Namibia (from Lüderitz to the Orange River)
• South Africa (Northern Cape province)
These frogs live in sandy areas along the coast where fog from the ocean provides moisture. They prefer dunes with sparse vegetation where they can burrow easily. Unlike what their name suggests, they don't live in true deserts but in coastal desert areas that receive moisture from fog.
Sandy Substrate
Loose sand for easy burrowing
Coastal Fog
Moisture source in dry environment
Sparse Vegetation
Shrubs and grasses for cover
Desert Survival Adaptations
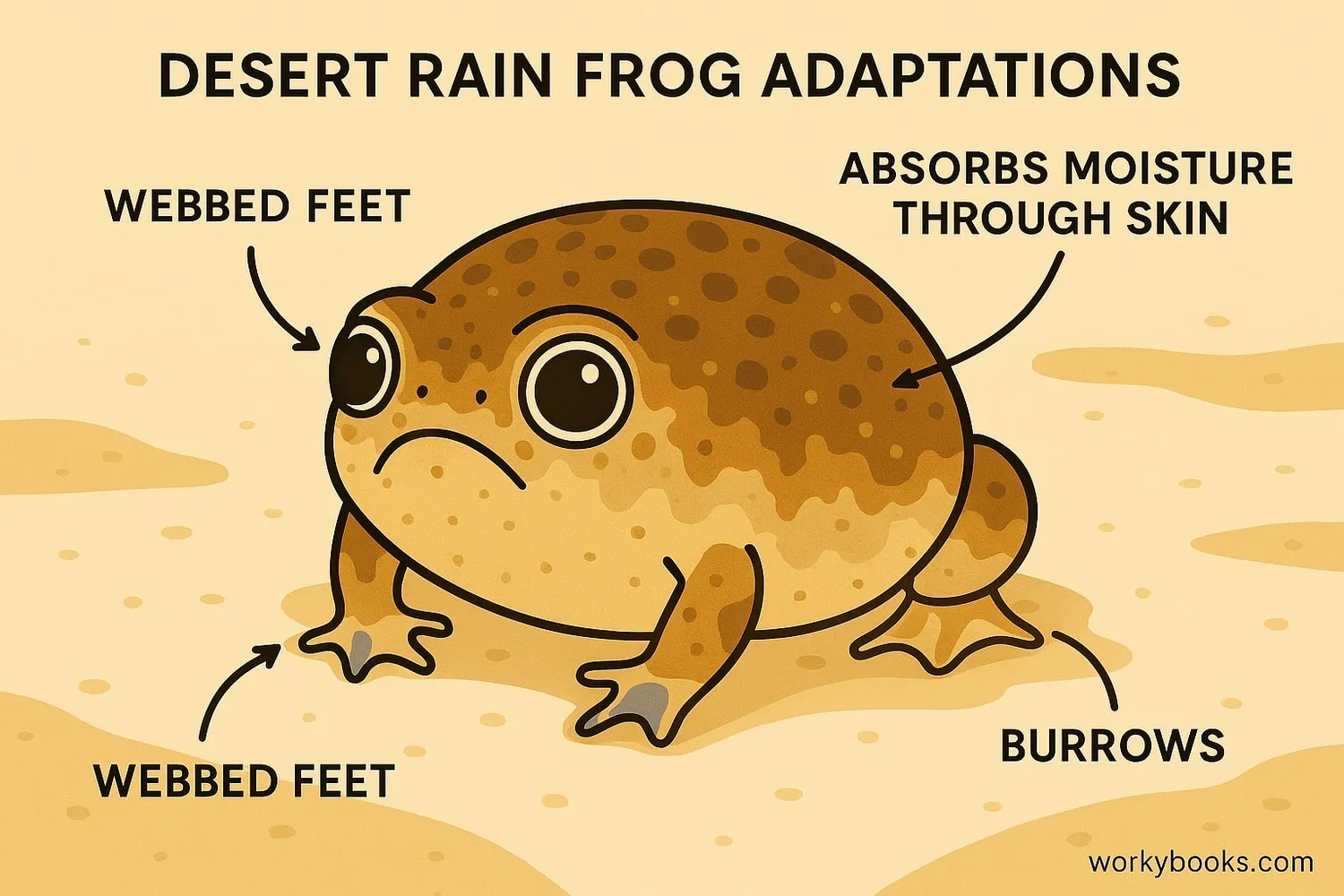
Desert Rain Frogs have amazing adaptations that help them survive in their challenging coastal desert environment:
Webbed Feet
Specialized for digging and moving through sand
Moisture Absorption
Can absorb water through their skin from damp sand
Nocturnal Lifestyle
Active at night to avoid daytime heat and predators
Burrowing
Digs tunnels in sand to stay cool and moist
Unique Vocalization
Squeaky call to communicate while conserving energy
During dry periods, Desert Rain Frogs enter a state called estivation - similar to hibernation but for surviving hot, dry conditions. They burrow deep into the sand and slow down their metabolism until moisture returns.
Behavior & Diet
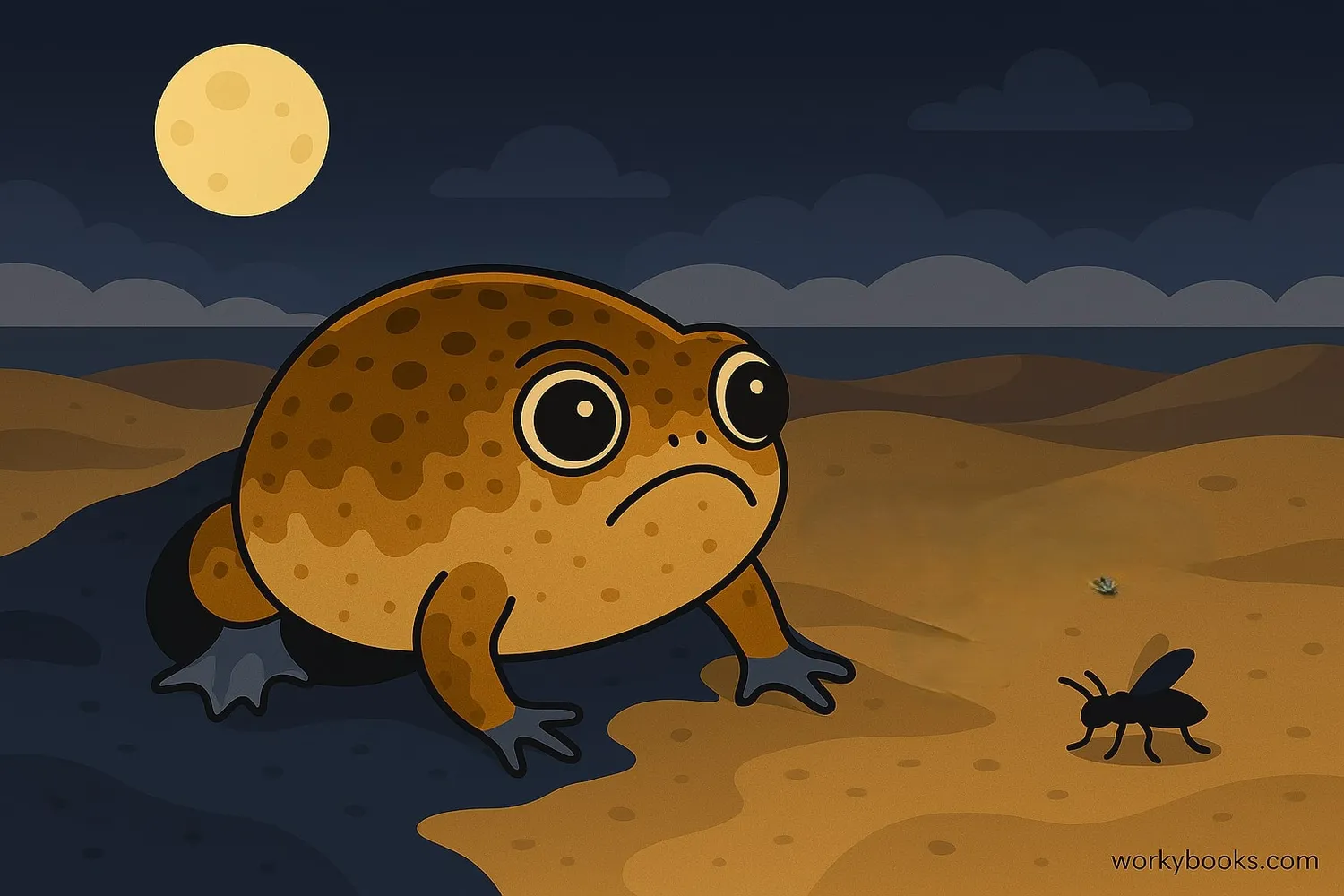

Desert Rain Frogs have fascinating behaviors that help them survive in their unique environment:
Nocturnal Activity
Come out at night to hunt and avoid heat
Burrow Dwellers
Spend days buried in cool, moist sand
Unique Mating Call
High-pitched squeak to attract mates
Diet: Desert Rain Frogs are insectivores that feed on:
• Small insects
• Ants
• Beetles
• Termites
• Other tiny invertebrates
They hunt at night, using their sticky tongues to catch prey on the sand surface. Their lifespan is estimated at 4-5 years in the wild.
Sound Fact!
The Desert Rain Frog's squeaky call sounds like "meep" or "squeak" rather than a typical frog croak. This unique sound helps it communicate while conserving moisture.
Conservation Status

The Desert Rain Frog is classified as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Its limited habitat faces several threats:
Habitat Loss
Coastal development for housing and mining
Off-Road Vehicles
Damage to dune habitats from recreational vehicles
Diamond Mining
Destruction of coastal habitats in Namibia
Conservation efforts include:
• Protecting coastal habitats
• Creating nature reserves
• Monitoring populations
• Regulating off-road vehicle use
• Raising awareness about this unique species
Climate change also threatens these frogs by altering the coastal fog patterns they depend on for moisture.
Desert Rain Frog Quiz
Test your knowledge about the Desert Rain Frog with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about the Desert Rain Frog:
Amazing Frog Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about Desert Rain Frogs:
Internet Sensation
A 2013 video of a squeaking Desert Rain Frog went viral with over 8 million views, making this little-known species famous worldwide!
Walking, Not Hopping
Unlike most frogs, Desert Rain Frogs walk rather than hop due to their compact bodies and short legs - a perfect adaptation for moving through sand!
Clever Defense
When threatened, they puff up their bodies to appear larger and more difficult for predators to swallow. They also secrete a bitter-tasting substance from their skin.
Scientific Discovery
The Desert Rain Frog was first described scientifically in 1927 by British zoologist George Albert Boulenger, which is why it's sometimes called Boulenger's Short-headed Frog.





