Homologous Structures - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how similar body parts in different animals show evolutionary connections!
What are Homologous Structures?
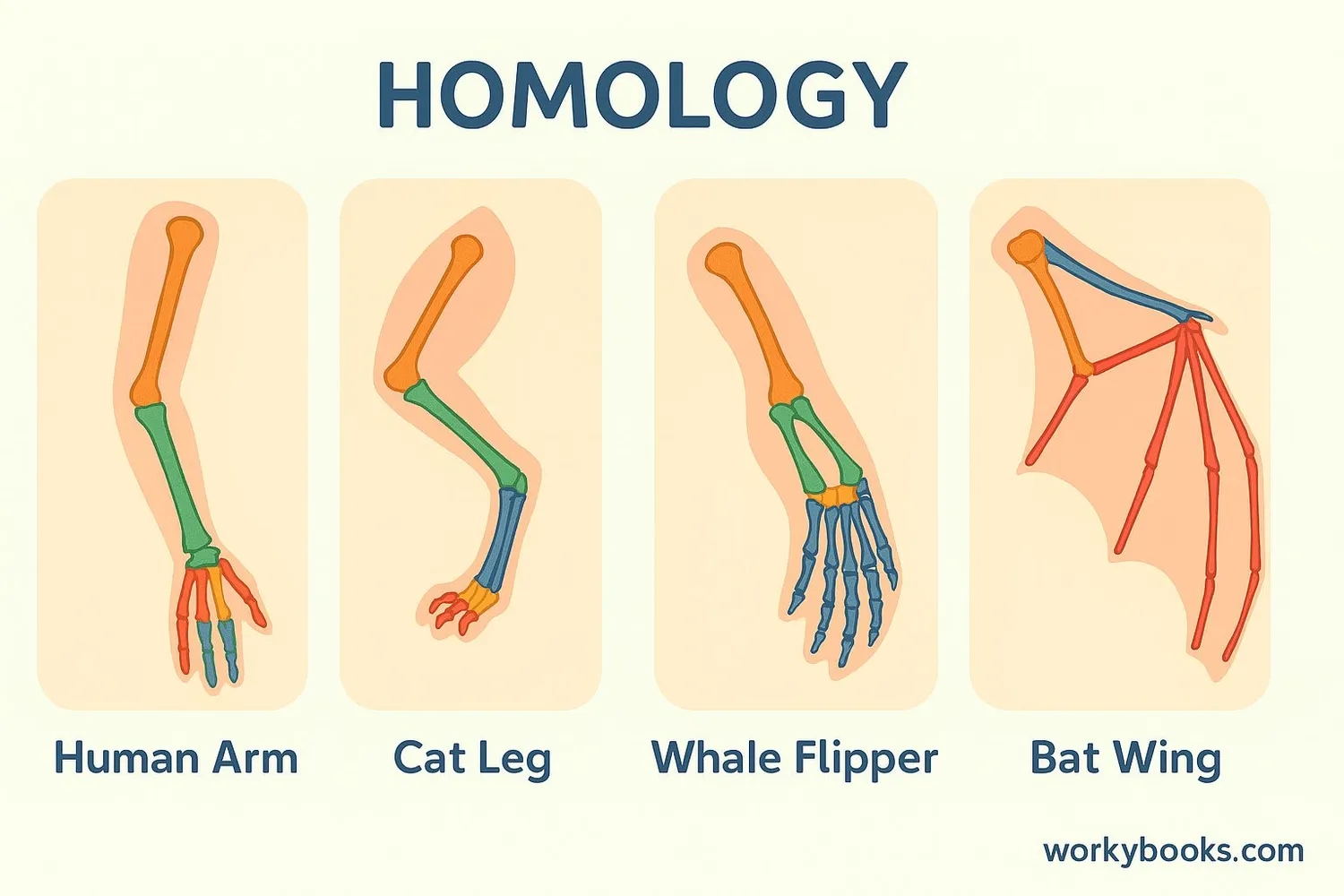
Homologous structures are body parts in different animals that have similar bone structure and development, but might have different functions. These similarities suggest that these animals share a common ancestor from long ago.
Think of homologous structures like different vehicles built from the same set of building blocks. A truck, car, and bus might look different and have different jobs, but they all have similar parts like wheels, engines, and steering wheels. In the same way, a human arm, a bat's wing, and a whale's flipper might look very different on the outside, but they share similar bone structures underneath!
Key Point!
Homologous structures show that different species evolved from a common ancestor, adapting to different environments over millions of years.
Examples of Homologous Structures
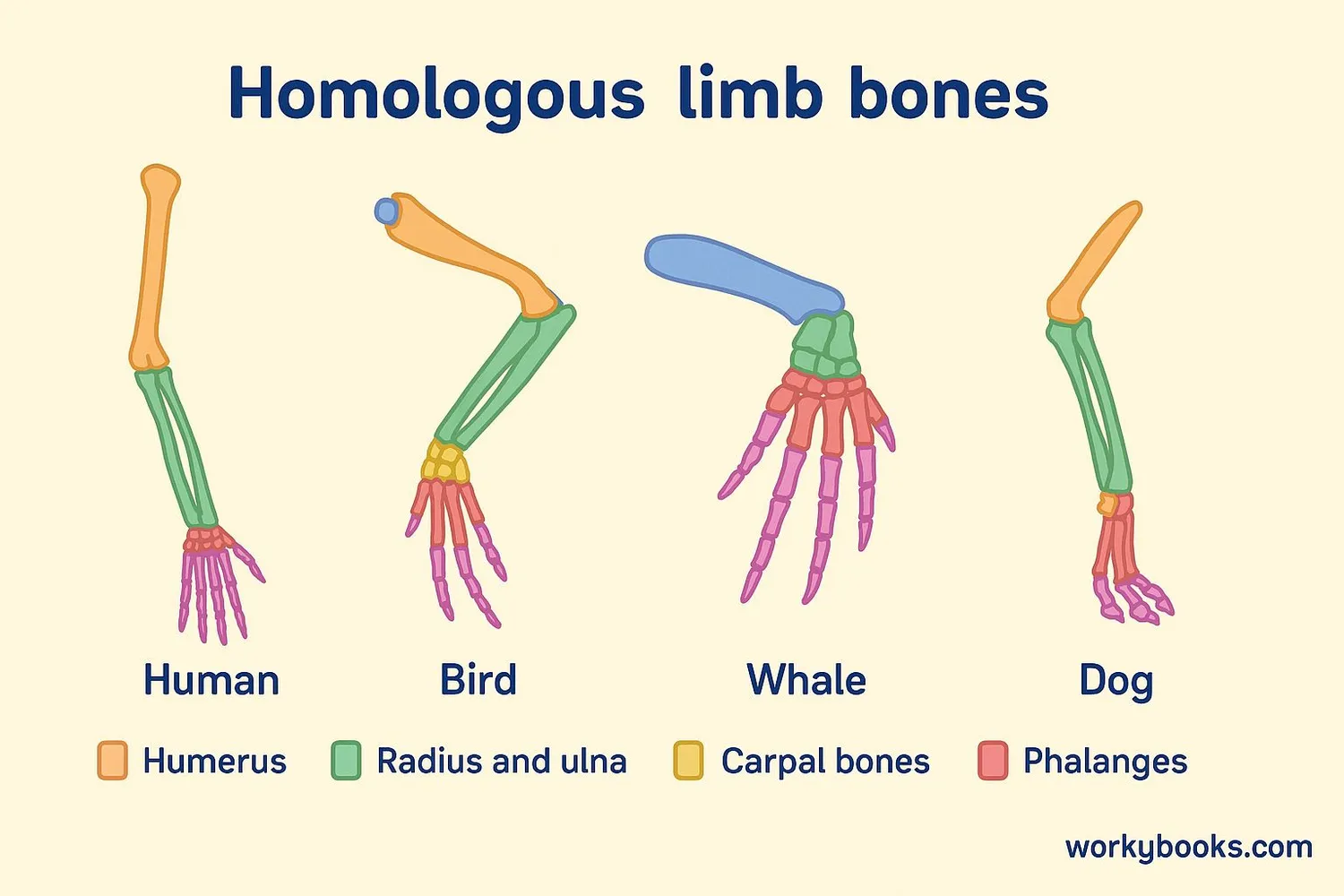
Here are some excellent examples of homologous structures found in nature:
Limbs of Mammals
Human arms, cat legs, whale flippers, and bat wings all have the same basic bone structure
Plant Leaves
Regular leaves, cactus spines, and pea tendrils all evolved from the same basic leaf structure
Vertebrate Hearts
Hearts in fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals share the same basic structure
Mammal Ear Bones
Small bones in mammal ears evolved from jaw bones of reptile ancestors
The most famous example is the pentadactyl limb (limb with five digits) found in humans, bats, whales, and many other animals. Even though these limbs are used for walking, flying, or swimming, they all contain the same set of bones arranged in similar patterns.
Did You Know?
Whales, which have flippers for swimming, have the same arm and hand bone structure as humans, showing their evolutionary connection to land mammals!
Homologous vs Analogous Structures
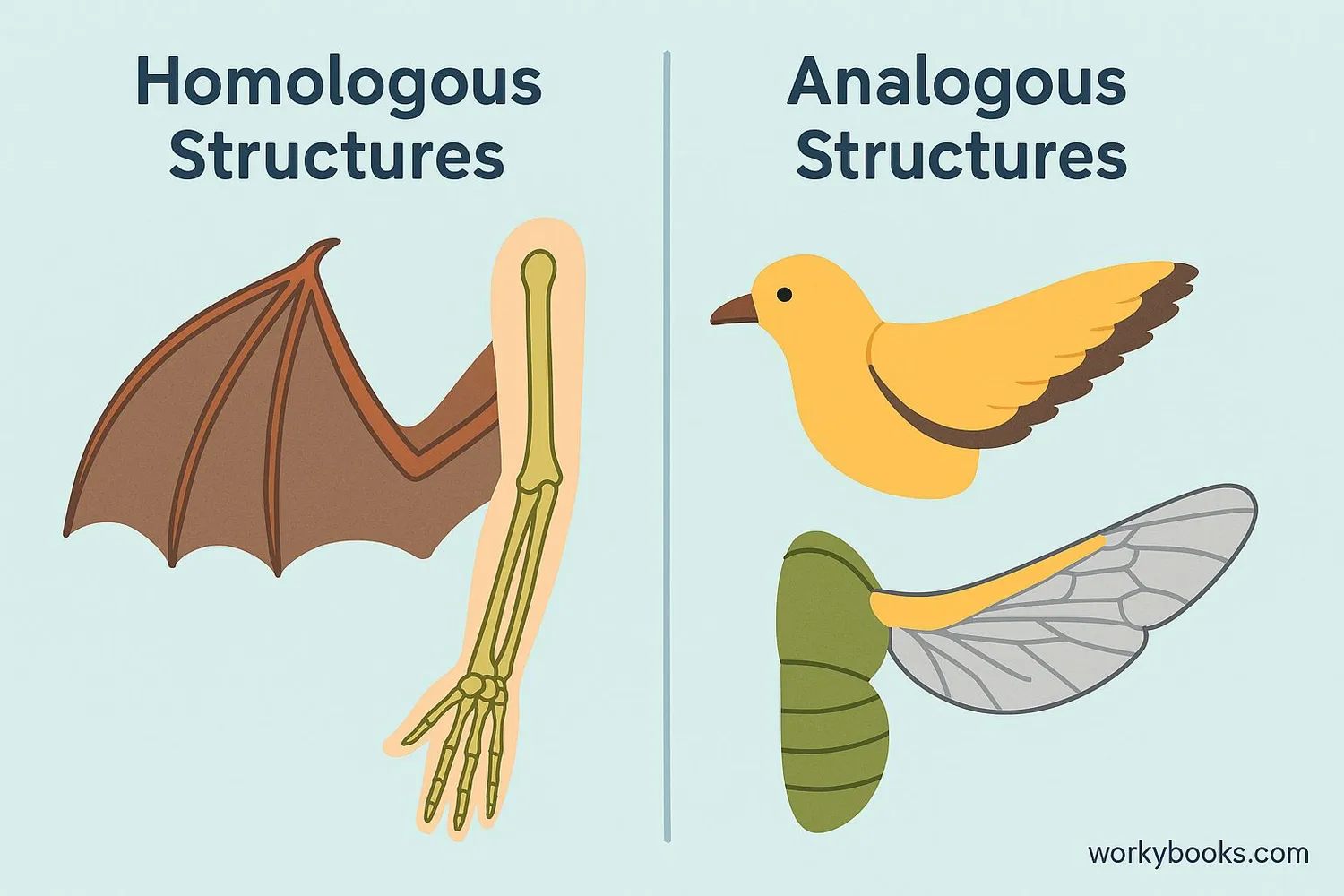
It's important to understand the difference between homologous structures and analogous structures:
| Feature | Homologous Structures | Analogous Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Same evolutionary origin | Different evolutionary origins |
| Structure | Similar internal structure | Different internal structure |
| Function | May have different functions | Have similar functions |
| Example | Human arm and bat wing | Bird wing and insect wing |
| Shows | Common ancestry | Convergent evolution |
Homologous structures show common ancestry (divergent evolution), while analogous structures show convergent evolution - where unrelated species develop similar features because they adapted to similar environments or lifestyles.
A bat wing and bird wing might seem similar because both are used for flying, but they're actually analogous, not homologous. Their bone structures are very different! A bat wing is more similar to a human arm than to a bird wing.
Homologous Structures Quiz
Test your knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about homologous structures:
Fun Facts About Homologous Structures
Discover some amazing facts about homologous structures and evolution!
Whale Ancestors
Whales have tiny hip bones buried in their bodies that don't connect to anything! These are homologous to the hip bones of land mammals and are evidence that whales evolved from land animals that returned to the sea.
Flight Connections
Bats, birds, and pterosaurs (flying reptiles) all evolved flight independently. Their wings are analogous, not homologous, as they developed from different structures: bat wings from hands, bird wings from entire arms, and pterosaur wings from a single finger!
Blind Sight
Many cave fish are blind but still have eyes homologous to sighted fish. The eyes don't work but show their evolutionary relationship to sighted ancestors. This is an example of vestigial structures—homologous structures that have lost their function.
Genetic Blueprint
Humans share about 98% of their DNA with chimpanzees, which explains why we have so many homologous structures. Even more surprising, we share about 60% of our genes with bananas, showing how all life is connected through evolution!





