Predators - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how predators hunt, survive, and help balance ecosystems
What is a Predator?
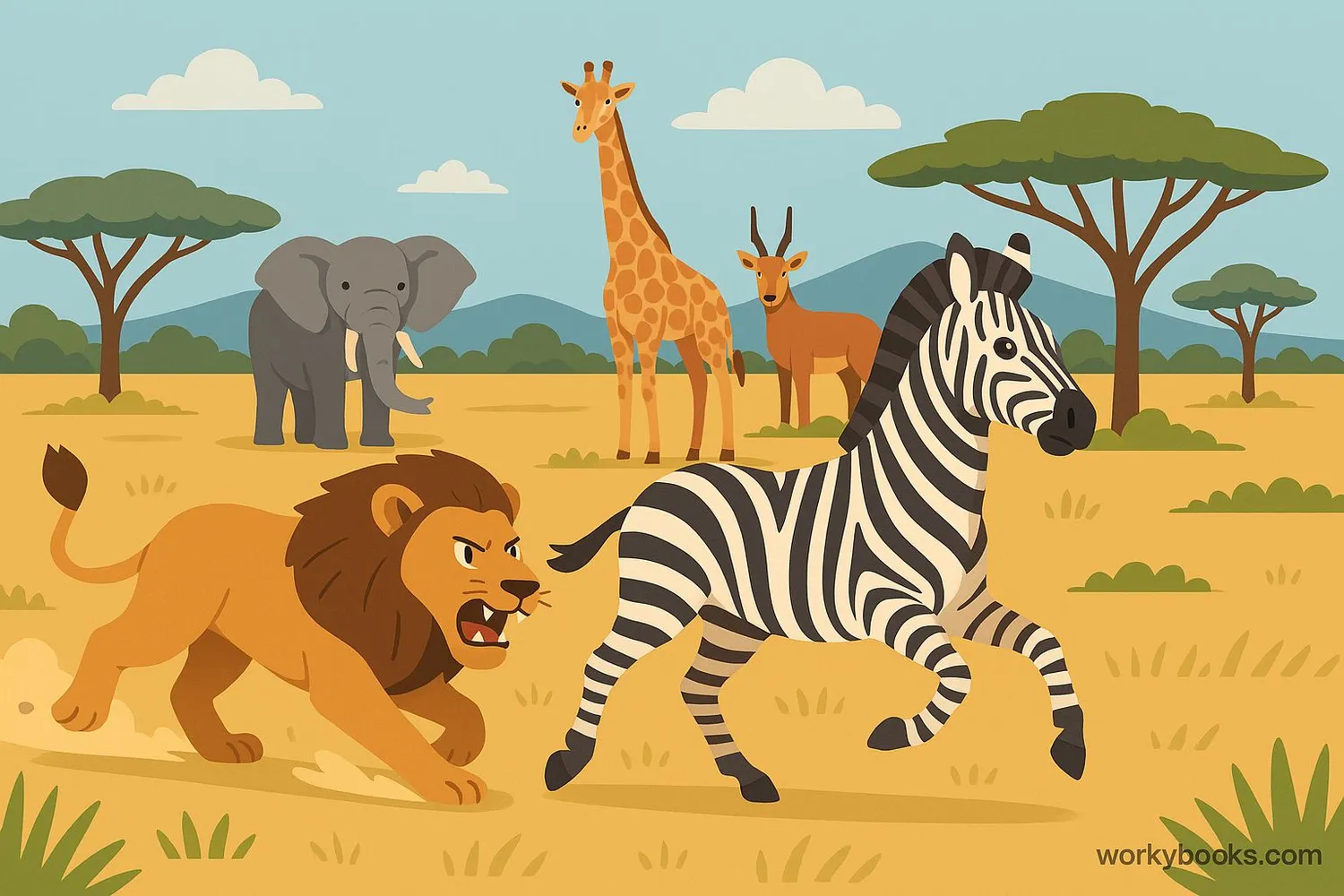

A predator is an animal that hunts and eats other animals (called prey) to survive. Predators are nature's hunters, using special skills and adaptations to catch their food. They play a crucial role in keeping ecosystems balanced.
Predators come in all sizes - from tiny spiders catching flies to massive killer whales hunting seals. All predators share one thing: they get their energy by consuming other living animals rather than plants.
Did You Know?
The word "predator" comes from the Latin word "praedator" which means "plunderer" or "to seize."
Types of Predators
Carnivores
Animals that eat only meat (lions, eagles, sharks)
Omnivores
Animals that eat both plants and animals (bears, raccoons, humans)
Apex Predators
Top predators with no natural enemies (tigers, orcas, crocodiles)
Predator Characteristics
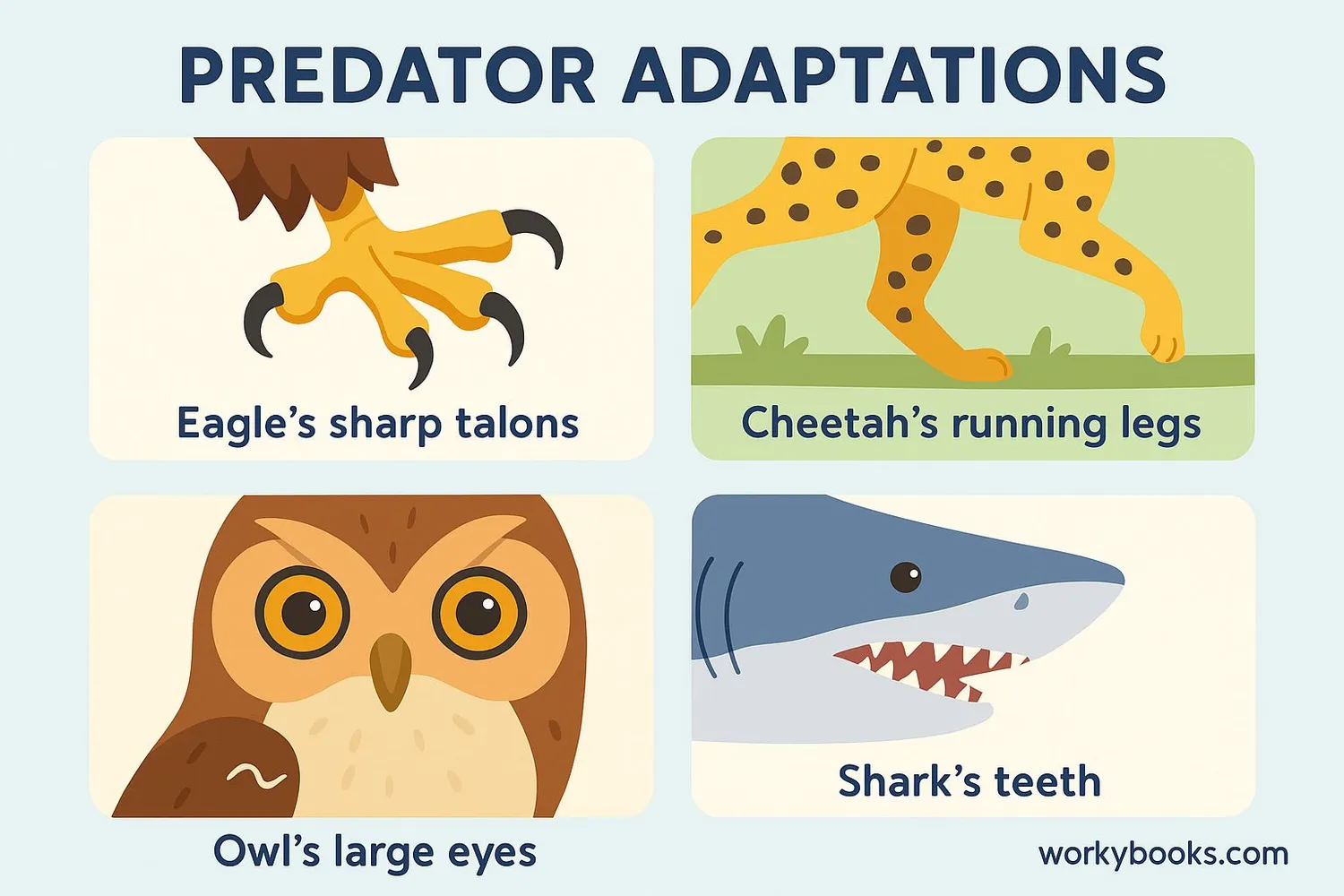
Predators have special adaptations that help them hunt successfully. These characteristics develop over many generations to make them expert hunters in their environments:
Sharp Senses
Excellent vision, hearing, or smell to detect prey (eagles can spot rabbits from miles high)
Speed & Strength
Powerful muscles for chasing or ambushing prey (cheetahs can run 70 mph)
Specialized Weapons
Claws, teeth, venom, or beaks designed for catching and killing prey
Hunting Strategies
Clever techniques like teamwork, camouflage, or traps (wolves hunt in packs)
Predator Behavior
Some predators like lions only hunt successfully about 30% of the time. Hunting is hard work that requires patience and skill!
Predators in the Ecosystem
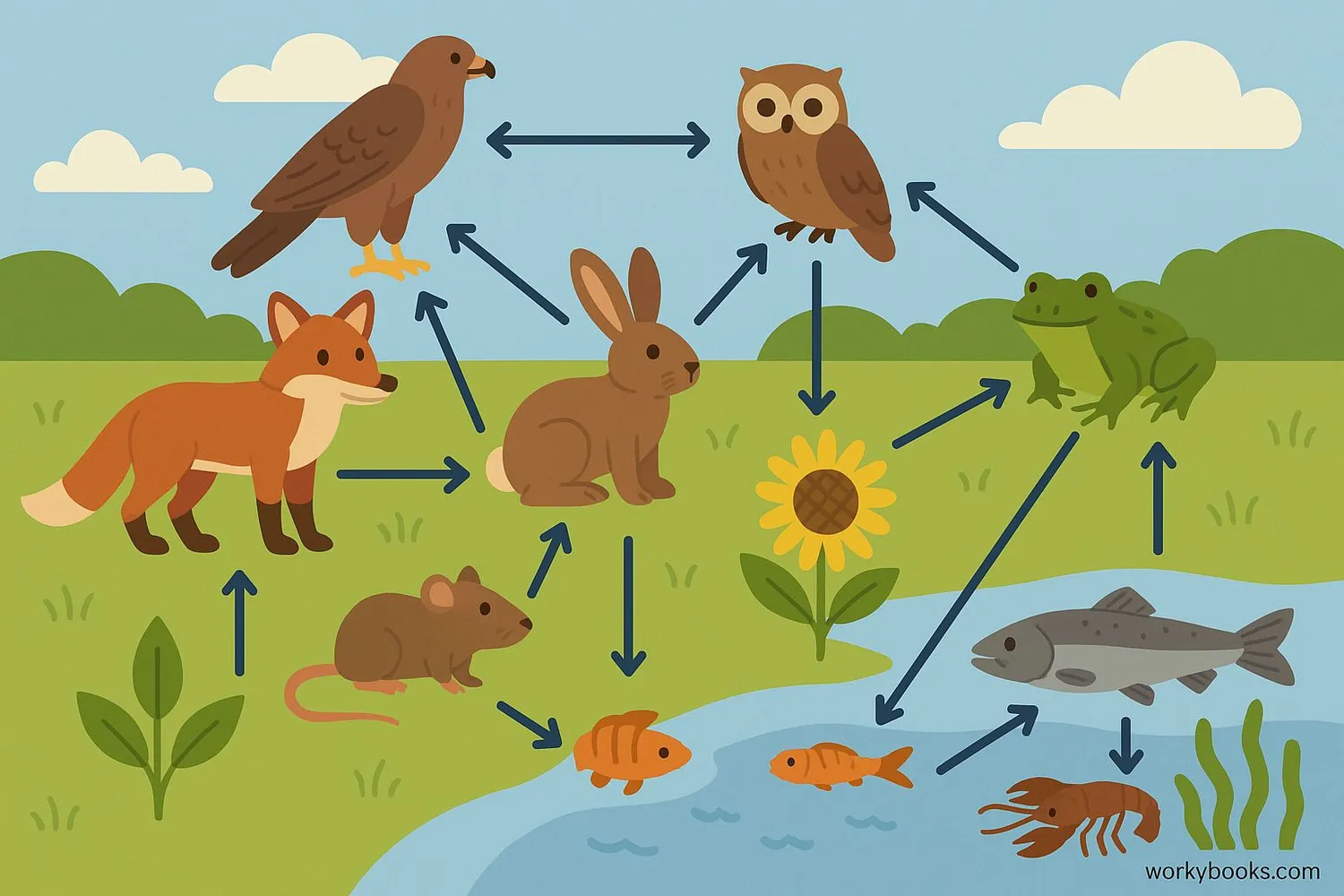
Predators are essential for healthy ecosystems. They help maintain balance in nature through:
Population Control
Keeping prey populations from growing too large and damaging habitats
Stronger Prey
Encouraging evolution by hunting weaker or sick animals first
Biodiversity
Preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem
Without predators, ecosystems can become unbalanced. For example, when wolves were removed from Yellowstone National Park, deer populations exploded and ate too many plants, which affected other animals. When wolves were reintroduced, the entire ecosystem became healthier!
Predator Quiz
Test your predator knowledge with this 5-question quiz. Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about predators:
Amazing Predator Facts
Discover some incredible facts about predators in nature:
Speed Champions
The peregrine falcon is the fastest animal, diving at over 200 mph to catch birds mid-air. Cheetahs can go from 0 to 60 mph in 3 seconds when chasing prey!
Size Extremes
The smallest predator is the fairyfly wasp (0.14mm long), while the largest is the blue whale (100 feet long) that eats tons of tiny krill each day!
Team Hunters
Wolves hunt in packs with complex strategies, while orcas work together to create waves that knock seals off ice floes. Some spiders even hunt together in groups!
Masters of Stealth
Snow leopards can silently stalk prey across rocky mountains, while anglerfish have glowing lures to attract prey in the dark ocean depths.





