Dividend - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how division works by understanding the dividend - the number being divided
What is a Dividend?
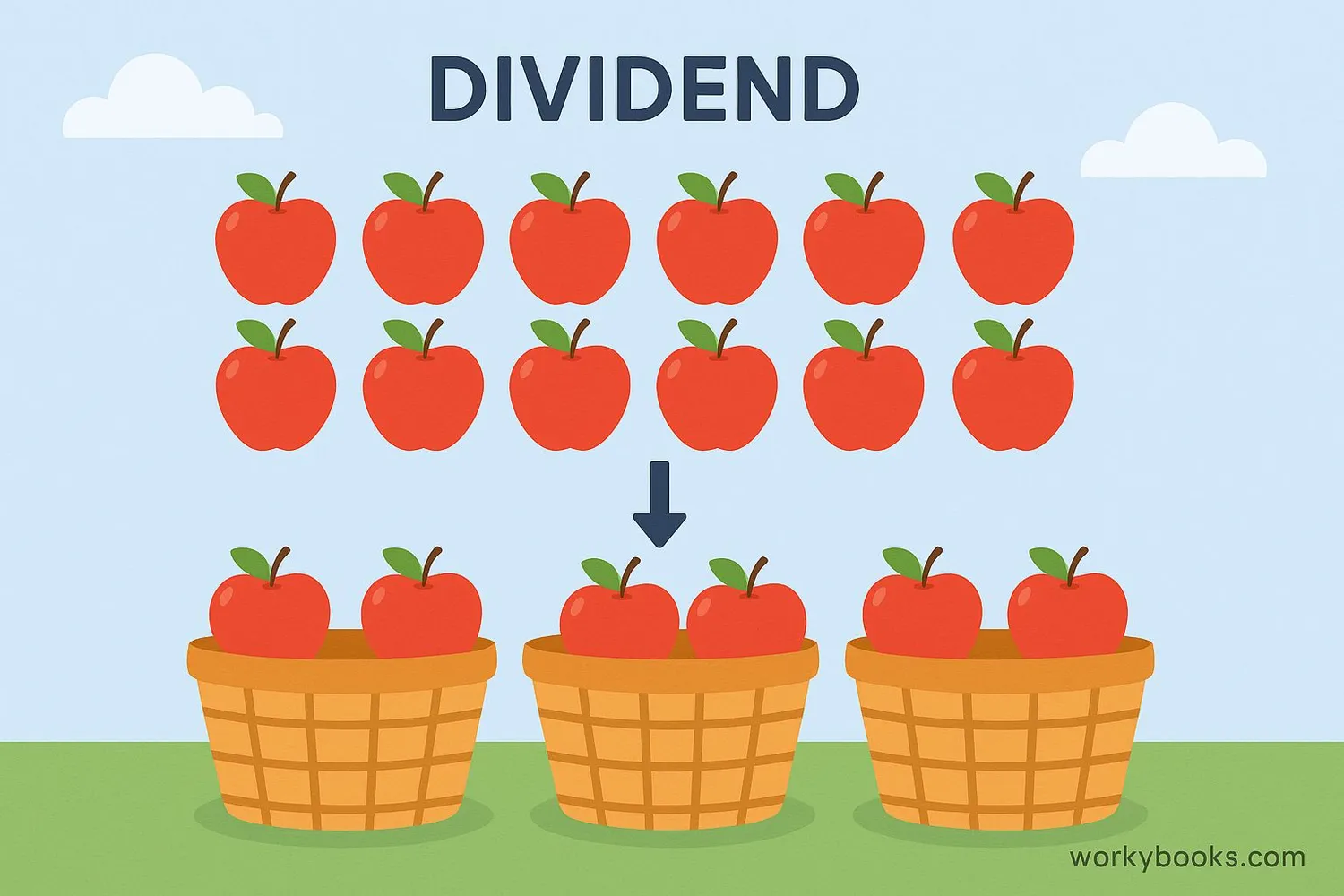
In division, the dividend is the number that is being divided or separated into equal parts.
It's the total amount that you start with before you begin dividing.
Think of the dividend as the whole pizza that you want to share with your friends.
If you have 8 slices of pizza and want to share them equally with 4 friends,
the dividend would be 8 because that's the total number of slices you're dividing.
The dividend always comes first in a division problem.
For example, in the division equation 12 ÷ 3 = 4,
12 is the dividend because it's the number being divided into groups.
Key Concept
Dividend = The total amount being divided
Parts of a Division Problem

Every division problem has four important parts:
Division Equation
2. Divisor: The number of groups you're dividing into
3. Quotient: The answer to the division problem (amount in each group)
4. Remainder: The amount left over that can't be divided equally
Example
If you have 15 cookies and want to share them equally with 4 friends:
15 (dividend) ÷ 4 (divisor) = 3 (quotient) with remainder 3
Each friend gets 3 cookies, and 3 cookies remain.
Remember
The dividend is always larger than or equal to the divisor in simple division problems.
How to Find the Dividend
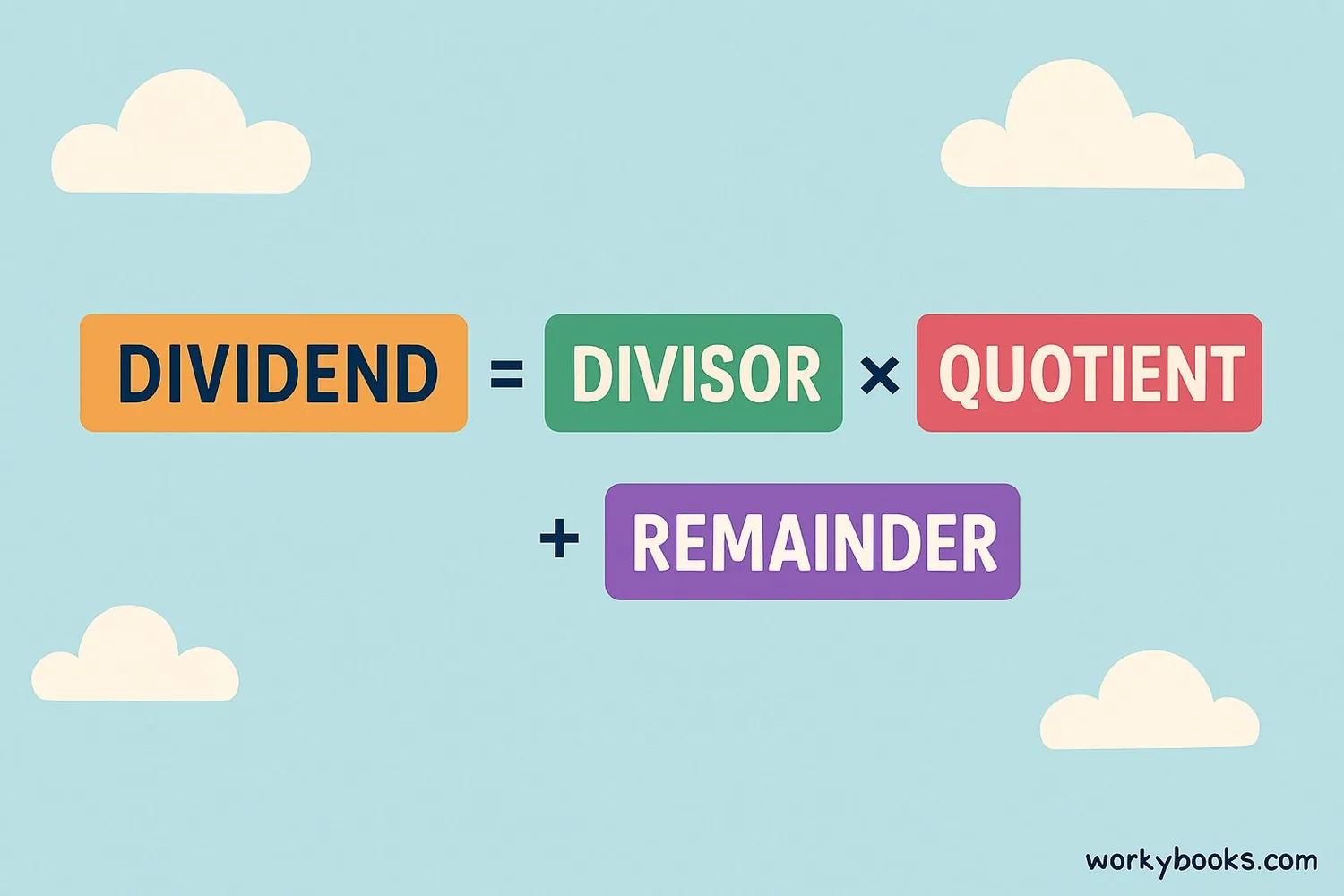
If you know the divisor, quotient, and remainder, you can find the dividend using this formula:
Dividend Formula
Example: If you divide some cookies equally among 5 friends, and each friend gets 4 cookies with 2 cookies left over, how many cookies were there to start with?
Step 1: Identify the divisor (number of groups) → 5 friends
Step 2: Identify the quotient (amount per group) → 4 cookies
Step 3: Identify the remainder (leftover amount) → 2 cookies
Step 4: Calculate: (5 × 4) + 2 = 20 + 2 = 22 cookies
So the dividend (original number of cookies) is 22.
Remember
This formula works because division is the opposite of multiplication. If you multiply the divisor and quotient, then add the remainder, you get back to the original dividend.
Dividend Examples

Let's look at more examples of dividends in different situations:
Example 1: Sharing Books
Mrs. Smith has 36 books to divide equally among 6 students.
36 (dividend) ÷ 6 (divisor) = 6 (quotient)
Each student gets 6 books. Dividend = 36
Example 2: Pizza Party
You have 15 pizza slices to share equally with 4 friends.
15 (dividend) ÷ 4 (divisor) = 3 (quotient) with remainder 3
Each person gets 3 slices, and 3 slices remain. Dividend = 15
Example 3: School Supplies
Mr. Johnson wants to distribute 48 pencils equally to his 8 students.
48 (dividend) ÷ 8 (divisor) = 6 (quotient)
Each student gets 6 pencils. Dividend = 48
Practice Tip
Look for division problems around you. When you see sharing or grouping, identify the dividend!
Dividend Quiz
Test your understanding with these questions. Choose the best answer for each.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about dividends:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about division and math:
Ancient Division
The concept of division dates back to ancient Egypt around 2000 BC. Egyptians used fractions to represent division problems, with a special symbol for division.
Division Symbol
The division symbol (÷) is called an obelus. It was first used by Swiss mathematician Johann Rahn in 1659 in his book "Teutsche Algebra".
Division by Zero
Division by zero is undefined. No matter how many times you try to divide something by nothing, it doesn't make mathematical sense. This is an important rule in mathematics.
Largest Division Problem
The largest division problem ever solved involved numbers with over 2 billion digits! It took computers more than 100 days to complete the calculation.





