Electric Battery - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how batteries store and release energy to power our world!
What is an Electric Battery?

A battery is like a portable power bank! It's a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy when we need it.
Think of batteries as tiny energy containers. When you put batteries in a toy or remote control, they provide the electricity needed to make things work. Batteries have two ends called terminals: a positive end (+) and a negative end (-). When connected in a circuit, electricity flows from the negative to the positive terminal, powering devices along the way.
Energy Fact!
The first battery was invented in 1800 by Alessandro Volta, which is why we measure electricity in volts!
How Batteries Work
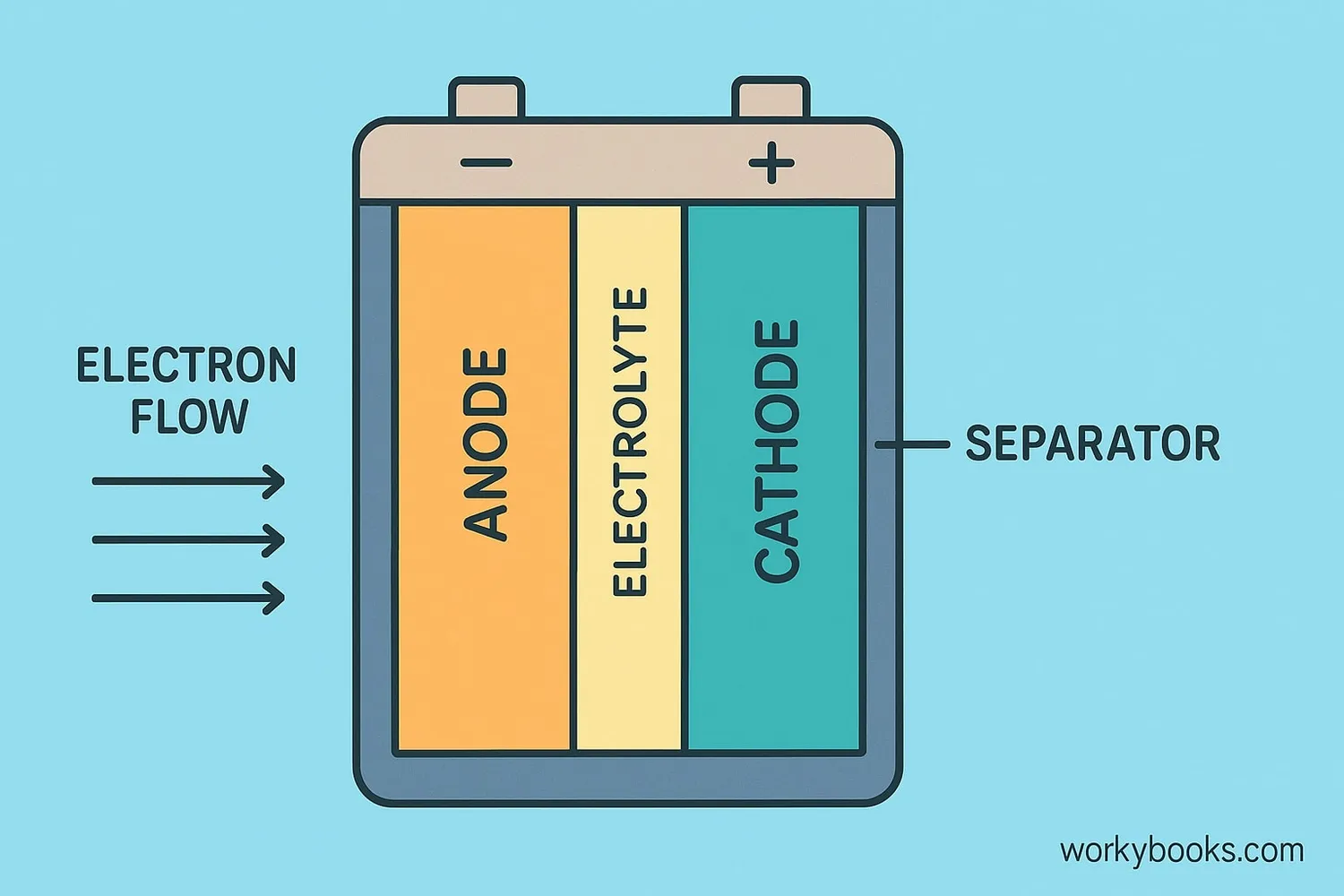
Batteries work through a chemical reaction that creates electrical energy. Every battery has three main parts:
Anode
The negative terminal where electrons flow out
Cathode
The positive terminal where electrons enter
Electrolyte
A chemical paste that allows ions to move
When you connect a battery to a device, a chemical reaction starts inside. Electrons flow from the anode through your device to the cathode, powering it. At the same time, ions move through the electrolyte to balance the charge. This flow of electrons is electricity!
Electron Flow!
Electrons move at nearly the speed of light - about 186,000 miles per second! That's why devices turn on instantly.
Types of Batteries
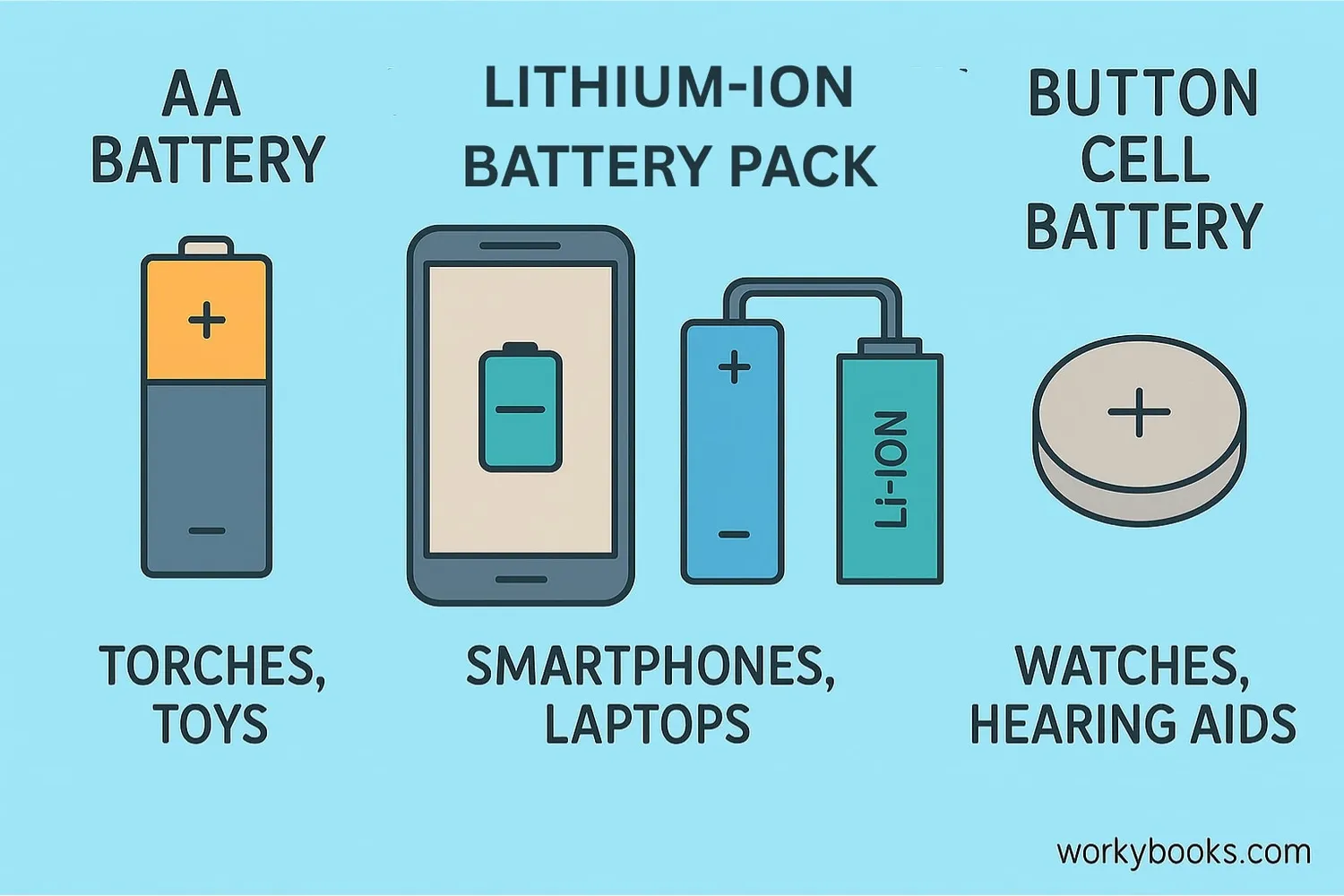
Batteries come in many shapes and sizes for different purposes. Here are the most common types:
AA/AAA Batteries
Common in remotes, toys, and small electronics
Lithium-ion
Used in phones, laptops, and electric vehicles
Car Batteries
Lead-acid batteries that start engines and power lights
Button Cells
Tiny batteries for watches, hearing aids, and calculators
Batteries also differ by how they're used:
• Single-use batteries (like alkaline AA) are used once then recycled
• Rechargeable batteries (like lithium-ion) can be used hundreds of times
• Deep-cycle batteries provide steady power over long periods
Why Batteries Matter
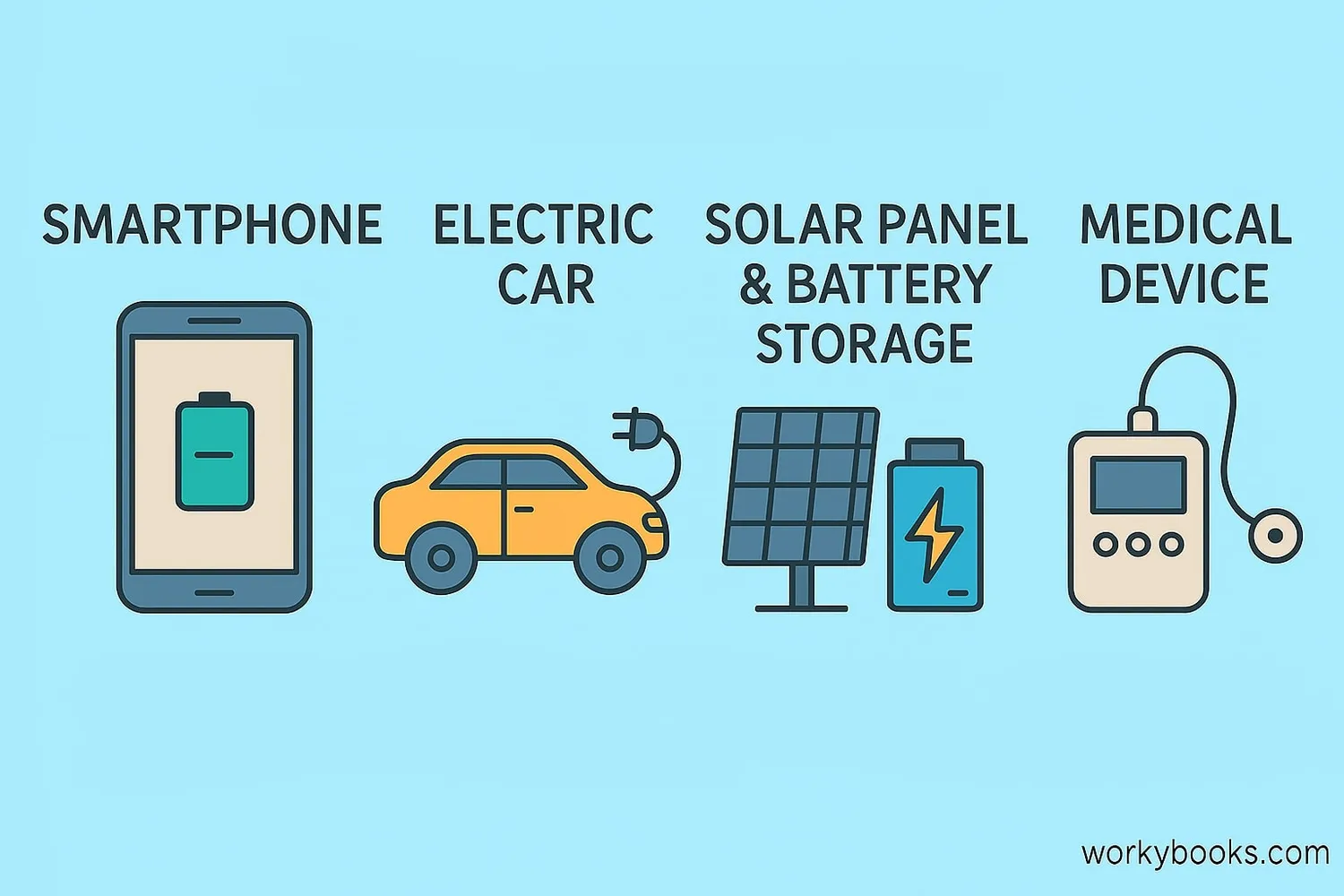
Batteries are essential in our modern world! Here's why they're so important:
Portable Power
Make devices mobile without needing cords
Energy Storage
Store renewable energy from sun and wind
Medical Devices
Power life-saving equipment like pacemakers
Without batteries, we wouldn't have:
• Portable electronics like phones and laptops
• Electric vehicles that reduce pollution
• Emergency flashlights during power outages
• Remote controls for TVs and other devices
• Many life-saving medical devices
As we develop better batteries, we can store more renewable energy and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels!
Battery Knowledge Quiz
Test your battery knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about batteries:
Battery Trivia
Discover amazing facts about batteries!
Ancient Battery
The Baghdad Battery, dating back to 200 BC, may be the world's oldest battery! This clay pot contained an iron rod surrounded by a copper cylinder and may have produced electricity with an acidic liquid.
Size Matters
The world's largest battery is in California and can power 300,000 homes for 4 hours! The smallest battery is thinner than a human hair and powers microscopic devices.
Recycling Power
Recycling one car battery provides enough lead to make 10 new batteries! Nearly all lead-acid batteries are recycled - the highest recycling rate of any consumer product.
Future Batteries
Scientists are developing batteries made from sand, seawater, and even viruses! Future batteries might charge in seconds, last for months, and be made from eco-friendly materials.





