The Force of Gravity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the invisible force that holds the universe together
What is Gravity?
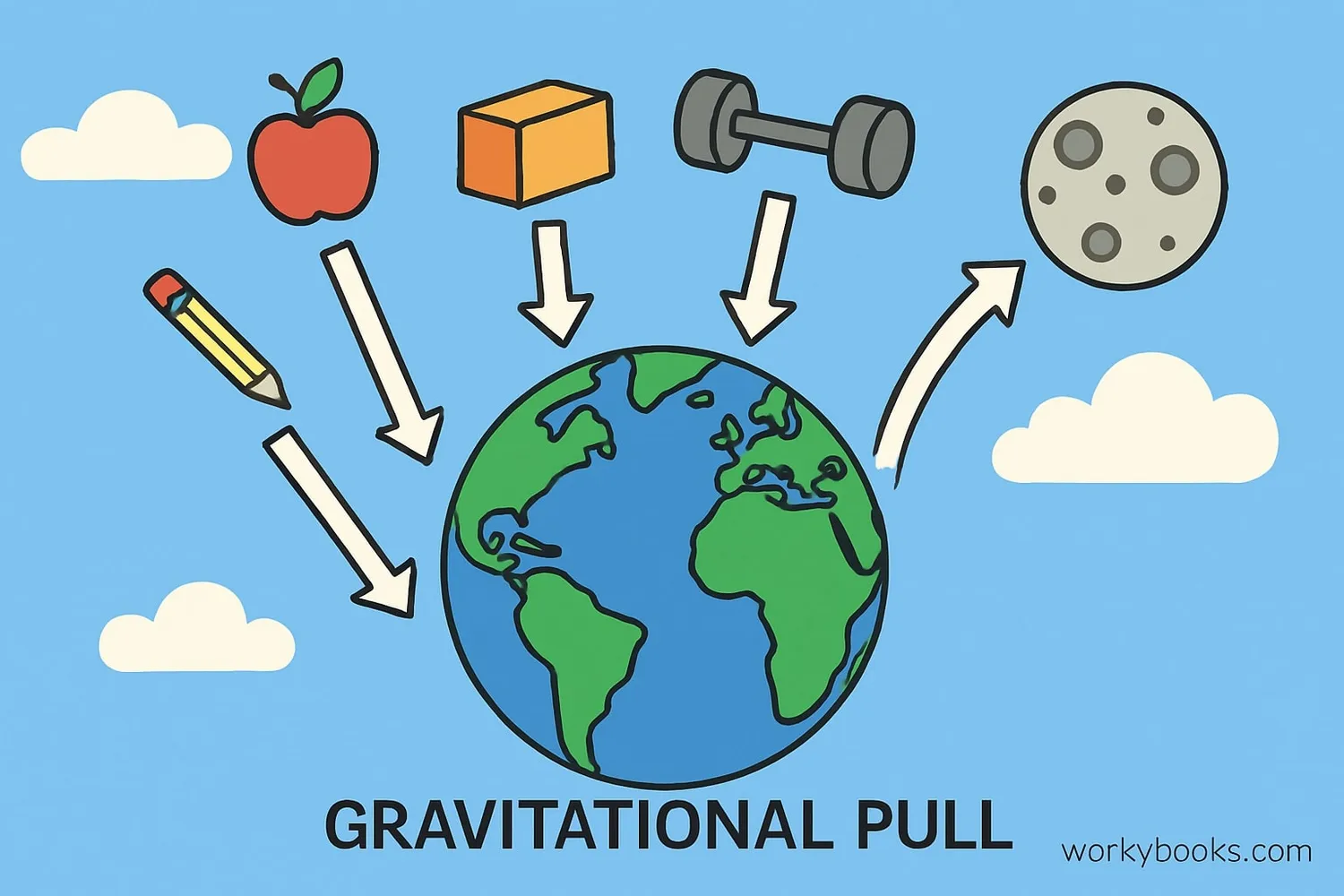
Gravity is the invisible force that pulls objects toward each other. It's what keeps your feet on the ground, holds planets in orbit around the sun, and causes apples to fall from trees!
Every object in the universe that has mass has gravity. The larger the mass, the stronger the gravitational pull. Earth's gravity gives us weight and keeps our atmosphere in place. Without gravity, we would float off into space!
Did You Know?
Gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental forces, but it works over the greatest distances!
Weight vs Mass
Mass is how much matter an object contains. Weight is the force of gravity acting on that mass.
Acceleration
On Earth, gravity accelerates objects at 9.8 m/s². All objects fall at the same rate!
Planetary Gravity
Your weight changes on different planets. On Jupiter you'd weigh 2.5x more, on Mars 38% less!
Newton's Law of Gravity
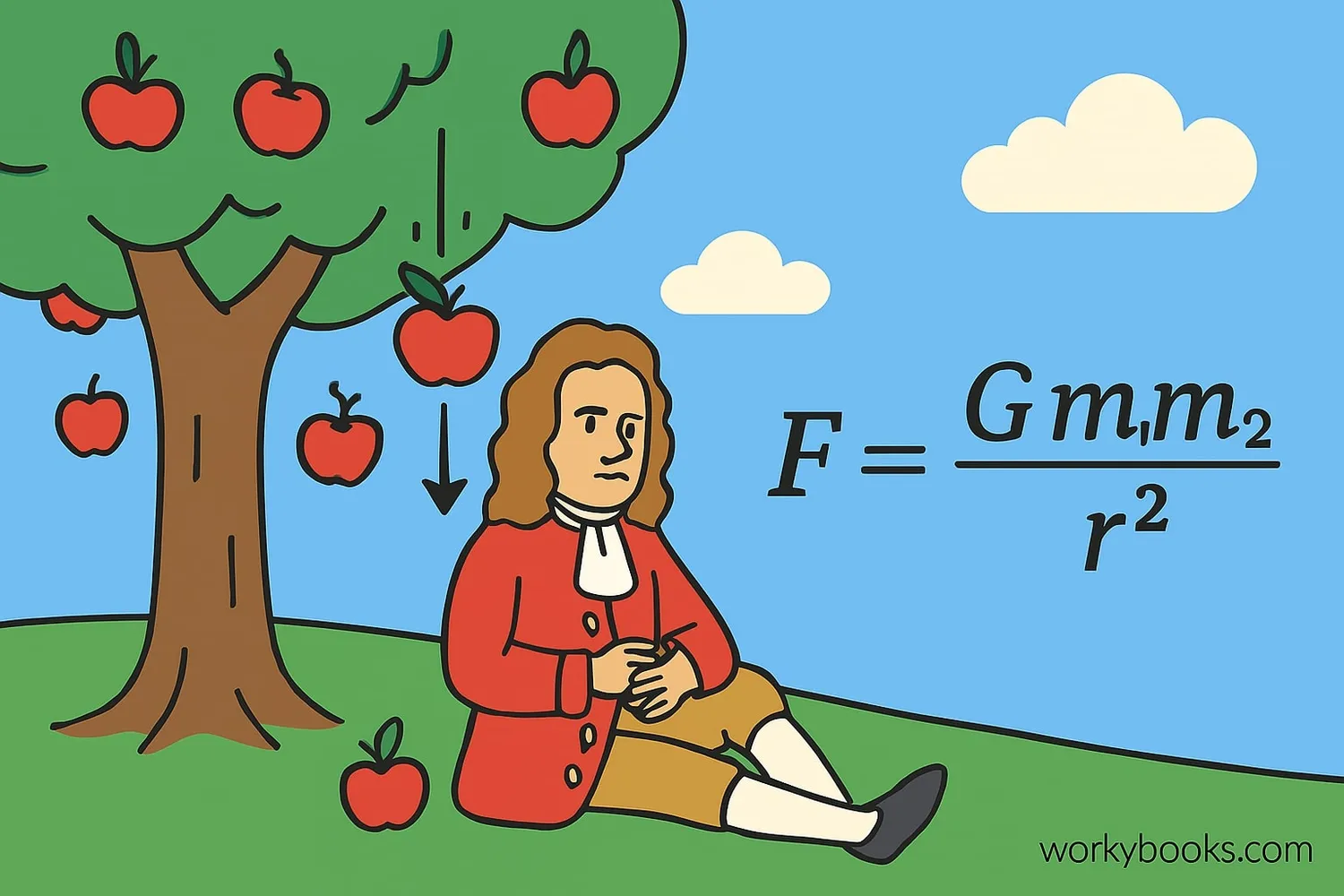
In 1687, Sir Isaac Newton published his law of universal gravitation. He realized that the same force that makes an apple fall also keeps the moon in orbit around Earth!
Newton's law states that every mass attracts every other mass with a force proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This is expressed as:
F = G(m₁m₂)/r²
Where F is the gravitational force, G is the gravitational constant, m₁ and m₂ are the masses, and r is the distance between them.
Universal Gravitational Constant
G is approximately 6.67430 × 10⁻¹¹ m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻². This tiny number explains why we don't feel the gravity between everyday objects!
Kepler's Laws
Newton used Kepler's laws of planetary motion to develop his theory of gravity
Inverse Square Law
Gravity weakens with the square of distance - double the distance, gravity becomes 4x weaker
Celestial Motion
Newton's laws explained the orbits of planets and comets with remarkable accuracy
Einstein's Theory of Relativity
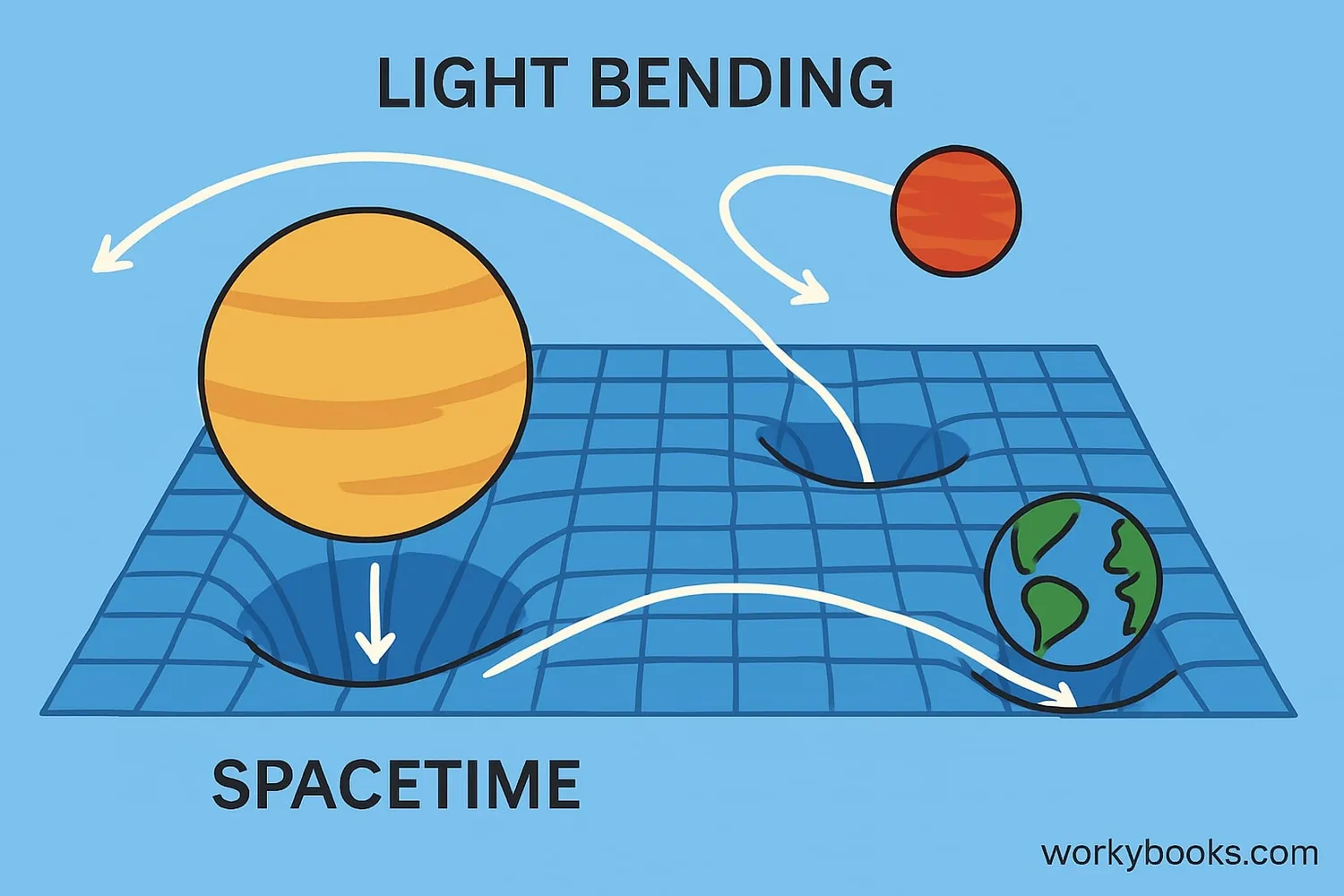
In 1915, Albert Einstein revolutionized our understanding of gravity with his general theory of relativity. Instead of thinking of gravity as a force, Einstein described it as the curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy.
Imagine spacetime as a trampoline. When you place a heavy object like a bowling ball on it, the fabric curves. Smaller objects like marbles will roll toward the bowling ball - not because of a mysterious force, but because of the curved surface!
This theory explained phenomena that Newton's laws couldn't, like the precise orbit of Mercury and how light bends around massive objects.
Principle of Equivalence
Einstein realized that the effects of gravity are indistinguishable from acceleration - a cornerstone of general relativity.
Black Holes
Regions where spacetime is so curved that nothing, not even light, can escape
Gravitational Waves
Ripples in spacetime caused by massive accelerating objects, like colliding black holes
Time Dilation
Time passes slower in stronger gravitational fields - proven by atomic clocks!
Gravity Quiz
Test your gravity knowledge with this fun quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about gravity:
Gravity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about gravity!
Supermassive Black Holes
The supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy has a mass of 4 million suns! Its gravity shapes the orbits of all nearby stars.
Jupiter's Gravity
Jupiter's strong gravity acts as a cosmic vacuum cleaner, protecting Earth by pulling in dangerous comets and asteroids.
Gravitational Waves
When scientists first detected gravitational waves in 2015, they measured a distortion 1/1000th the width of a proton!
Plants and Gravity
Plants use gravity to know which way to grow! Special cells called statocytes help roots grow downward and stems grow upward.





