Helium - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the lightest noble gas - where it's found, its properties, and amazing uses!
What is Helium?

Helium is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe, after hydrogen.
Helium is a noble gas, which means it doesn't easily react with other elements. At room temperature, helium is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that is much lighter than air. This is why helium balloons float upward!
Helium was first discovered in 1868 during a solar eclipse when astronomers noticed a yellow line in the sun's spectrum that didn't match any known element. That's how it got its name from the Greek word "helios," meaning sun.
Did You Know?
Helium is the only element that was discovered in space before it was found on Earth!
Properties of Helium
Helium has some unique properties that make it special:
Lightweight
Helium is the second lightest element, after hydrogen
Inert Gas
It doesn't react with other elements under normal conditions
Low Boiling Point
Helium becomes liquid at -268.9°C (-452°F)
High Thermal Conductivity
It conducts heat very efficiently
Non-Flammable
Helium is safe to use as it doesn't burn
One of helium's most amazing properties is that it remains liquid even at temperatures close to absolute zero (-273.15°C or -459.67°F). All other elements freeze solid at these extremely cold temperatures.
Superfluid Property
When cooled to extremely low temperatures, helium becomes a superfluid that can flow without friction, climb up walls, and escape through tiny holes that normal liquids can't pass through!
Uses of Helium
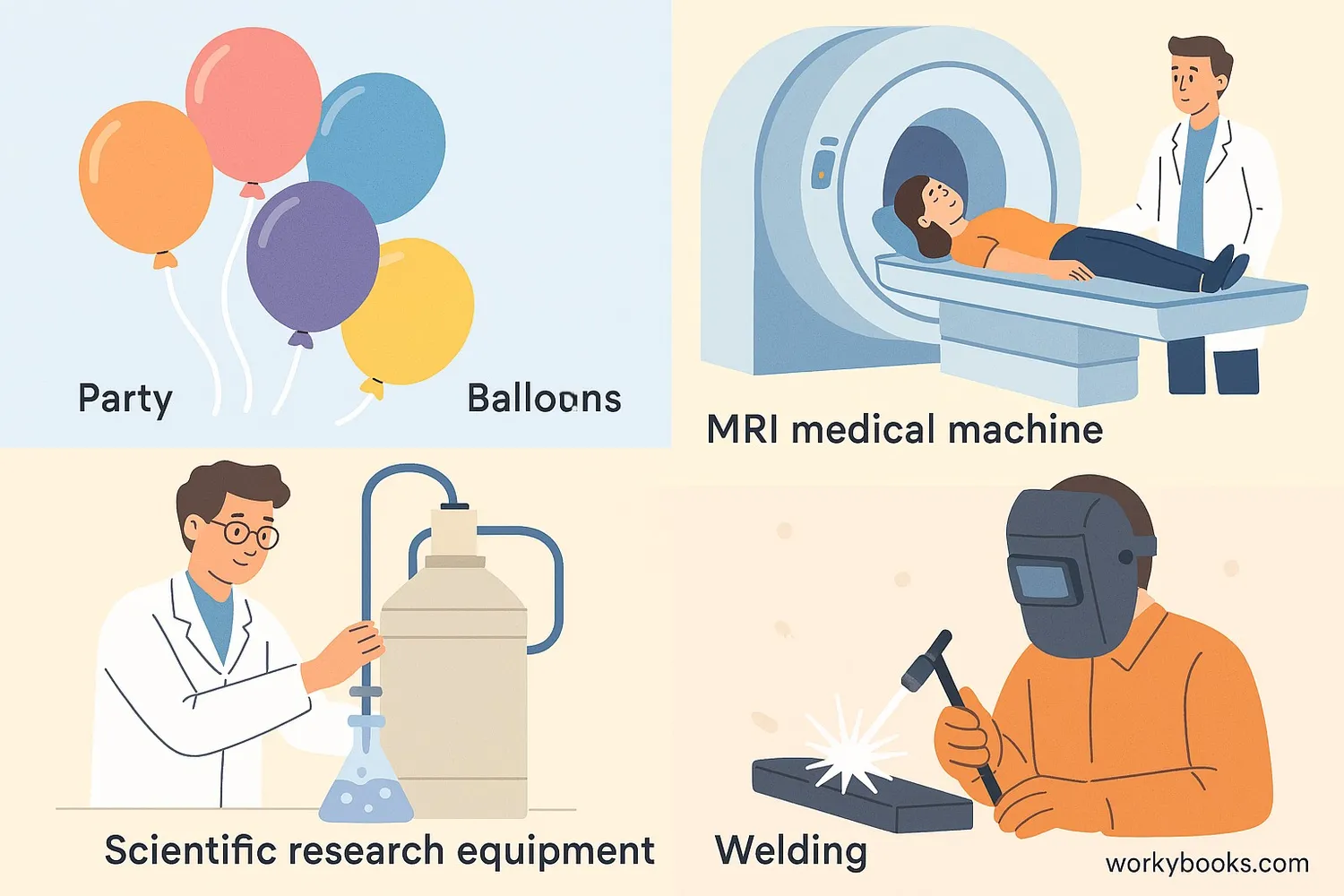
While most people know helium for filling party balloons, it has many important scientific, medical, and industrial uses:
Medical Imaging
Cooling magnets in MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines
Scientific Research
Used in cryogenics to achieve extremely low temperatures
Welding
Creates inert atmosphere for arc welding
Space Exploration
Pressurizing rocket fuel tanks
Deep Sea Diving
Mixed with oxygen for breathing at great depths
Helium is also used to detect leaks in high-vacuum equipment and air-conditioning systems because it diffuses through solids much faster than other gases. In the technology industry, helium is used in the manufacturing of semiconductor chips.
Helium on the Periodic Table
Helium Element Facts
Symbol: He
Atomic Number: 2 (means it has 2 protons)
Atomic Weight: 4.0026
Element Category: Noble gas
Phase at Room Temperature: Gas
Melting Point: -272.2°C (-458°F) at pressure
Boiling Point: -268.9°C (-452°F)
Discovery: 1868 by Pierre Janssen and Norman Lockyer
On the periodic table, helium is in group 18, which is the group of noble gases. These elements have a full outer electron shell, making them very stable and unreactive.
Despite being the second element, helium is placed on the far right of the periodic table because of its chemical properties. It's the first element in the noble gas group, which also includes neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon.
Electron Configuration
Helium has two electrons that completely fill its first and only electron shell. This stable electron configuration is why helium doesn't readily form compounds with other elements.
Helium Quiz
Test your helium knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about helium:
Fun Helium Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about helium!
Cosmic Abundance
About 24% of all the normal matter in the universe is helium! It was mostly created during the Big Bang and in stars through nuclear fusion.
Coldest Element
Liquid helium is the coldest substance on Earth! It can reach temperatures close to absolute zero (-273°C or -459°F), the theoretically coldest possible temperature.
U.S. Reserve
The United States created the National Helium Reserve in 1925 to supply helium for airships. This reserve held over 1 billion cubic meters of helium at its peak!
Balloon Facts
A standard helium balloon can lift about 14 grams. That's why you need many balloons to lift heavier objects - it would take about 5,000 balloons to lift a person!





