Infrasound - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how sounds too low for humans to hear play an important role in nature and science
What is Infrasound?
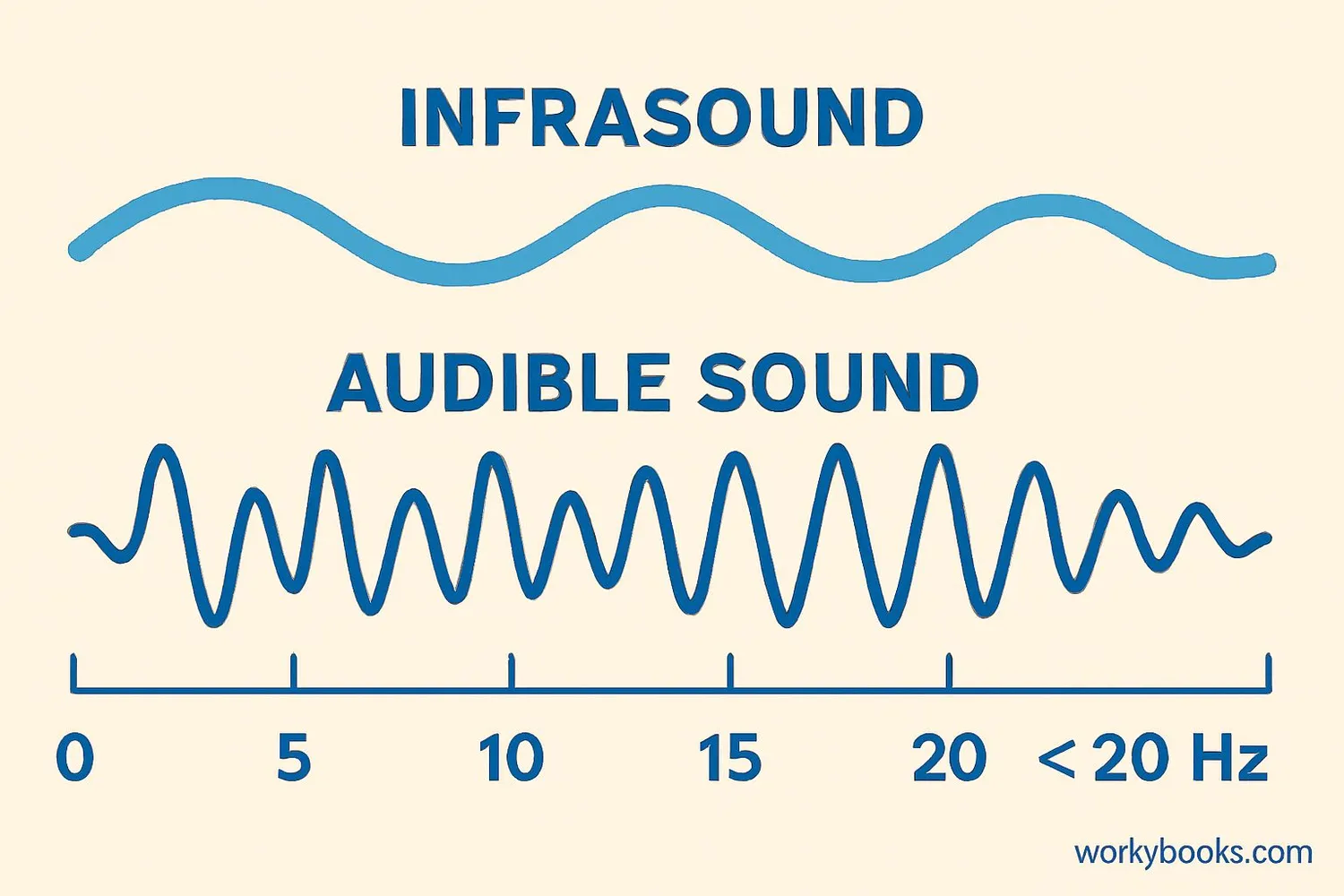
Infrasound is sound that has a frequency too low for humans to hear! While humans can typically hear sounds between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz, infrasound refers to sounds below 20 Hz.
Think of sound waves like waves in the ocean. Some waves are close together (high frequency), and some are far apart (low frequency). Infrasound waves are like very gentle, long waves that travel great distances without losing much energy. Even though we can't hear these sounds, they're all around us in nature!
Sound Fact!
Many animals can detect infrasound that humans cannot hear, including elephants, whales, and giraffes!
How Infrasound Works
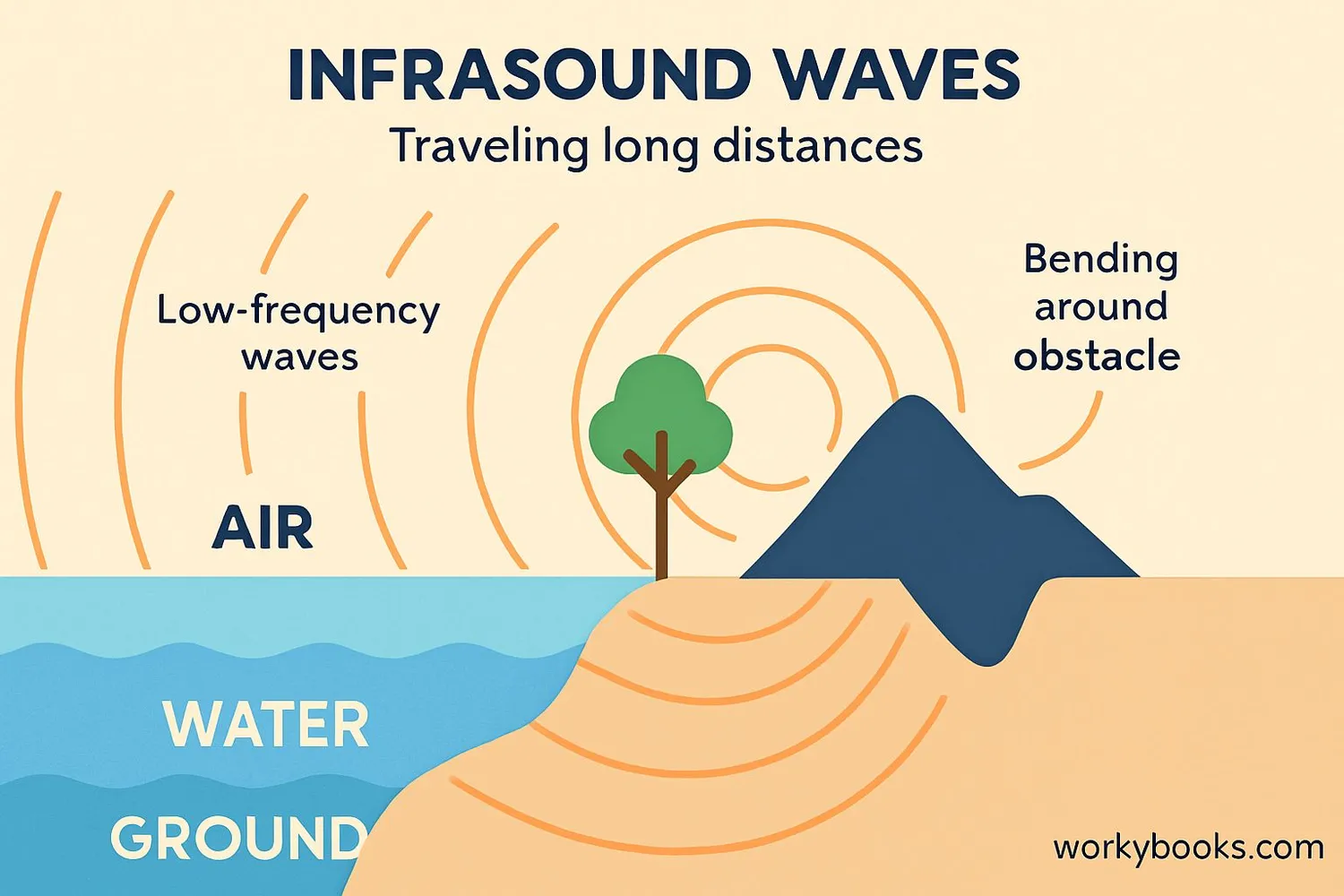
Infrasound works differently from the sounds we normally hear. Because of its very low frequency, infrasound has some special properties:
Long Waves
Infrasound waves can be miles long from peak to peak
Travels Far
These waves can travel thousands of miles without much energy loss
Bends Around Objects
Infrasound can curve around hills and buildings
Penetrates Materials
It can move through walls, water, and even the ground
These special properties make infrasound useful for many applications. Scientists use special microphones called infrasonic microphones to detect these low-frequency sounds that are created by natural events like earthquakes, volcanoes, and thunderstorms, as well as human activities.
Detection Fact!
The International Monitoring System uses infrasound detectors to verify compliance with the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty, as nuclear explosions create distinctive infrasound signatures.
Why Infrasound is Important

Infrasound plays important roles in nature, science, and technology:
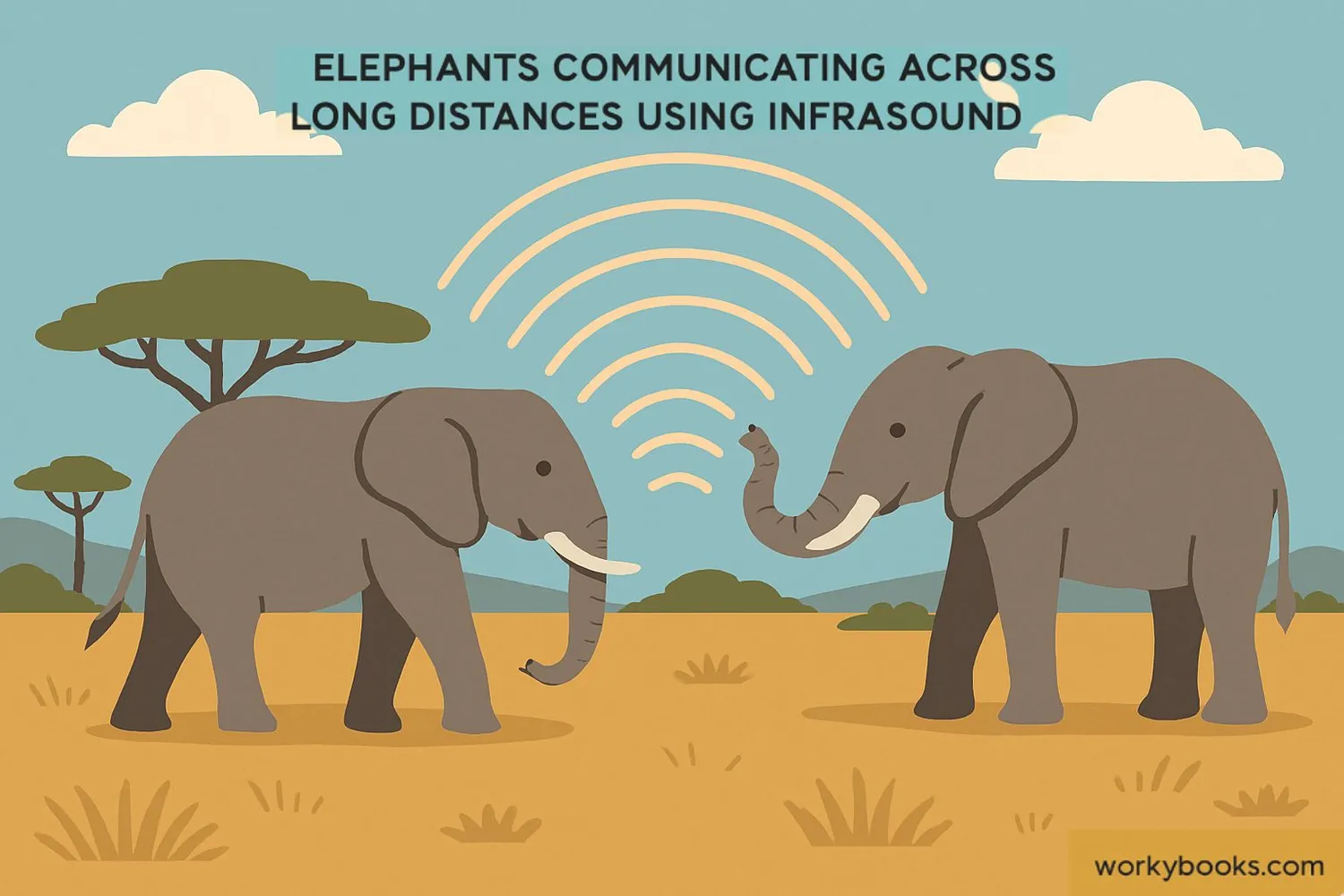
Animal Communication
Elephants, whales, and other animals use infrasound to communicate over long distances
Natural Disaster Detection
Scientists use infrasound to detect volcanoes, earthquakes, and meteors
Weather Monitoring
Infrasound helps track severe weather systems like tornadoes
Without the study of infrasound, we would miss important information about:
• Animal behavior and communication patterns
• Early warnings for natural disasters
• Weather pattern changes and severe storm development
• Monitoring for nuclear weapons testing
The study of infrasound helps scientists understand our world better and can even help keep people safe by providing early warnings for dangerous events!
Infrasound Quiz
Test your knowledge about infrasound with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about infrasound:
Fun Infrasound Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about infrasound!
Elephant Communication
Elephants can detect infrasound through their feet! They sense vibrations in the ground through special nerve endings in their foot pads and can communicate with other elephants up to 6 miles away.
Volcanic Predictions
Scientists can sometimes predict volcanic eruptions by monitoring infrasound. Changes in the infrasound patterns coming from a volcano can indicate rising magma and possible eruption days or weeks in advance.
Storm Detection
Meteorologists use infrasound to detect severe weather. Tornadoes produce distinctive infrasound signatures that can be detected before the tornado becomes visible, providing earlier warnings to communities.
Meteor Tracking
When meteors enter Earth's atmosphere, they create powerful shockwaves that generate infrasound. Scientists use this to track meteor paths and even locate meteorites that have fallen to Earth.





