Metalloids - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the elements with dual personalities between metals and nonmetals!
What Are Metalloids?
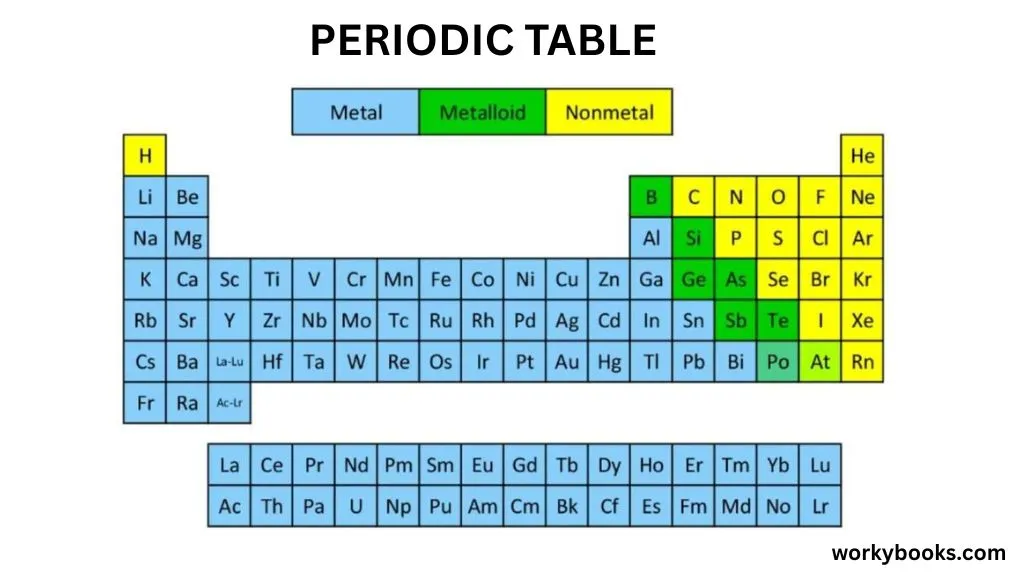
Metalloids are special elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals. They're like the "middle children" of the periodic table, positioned between the metals on the left and the nonmetals on the right.
Think of metalloids as having a dual personality! Sometimes they act like metals (they can conduct electricity), and sometimes they act like nonmetals (they can be brittle). This makes them incredibly useful for technology like computers and electronics.
Did You Know?
There are typically 7 elements classified as metalloids: boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium.
Properties of Metalloids
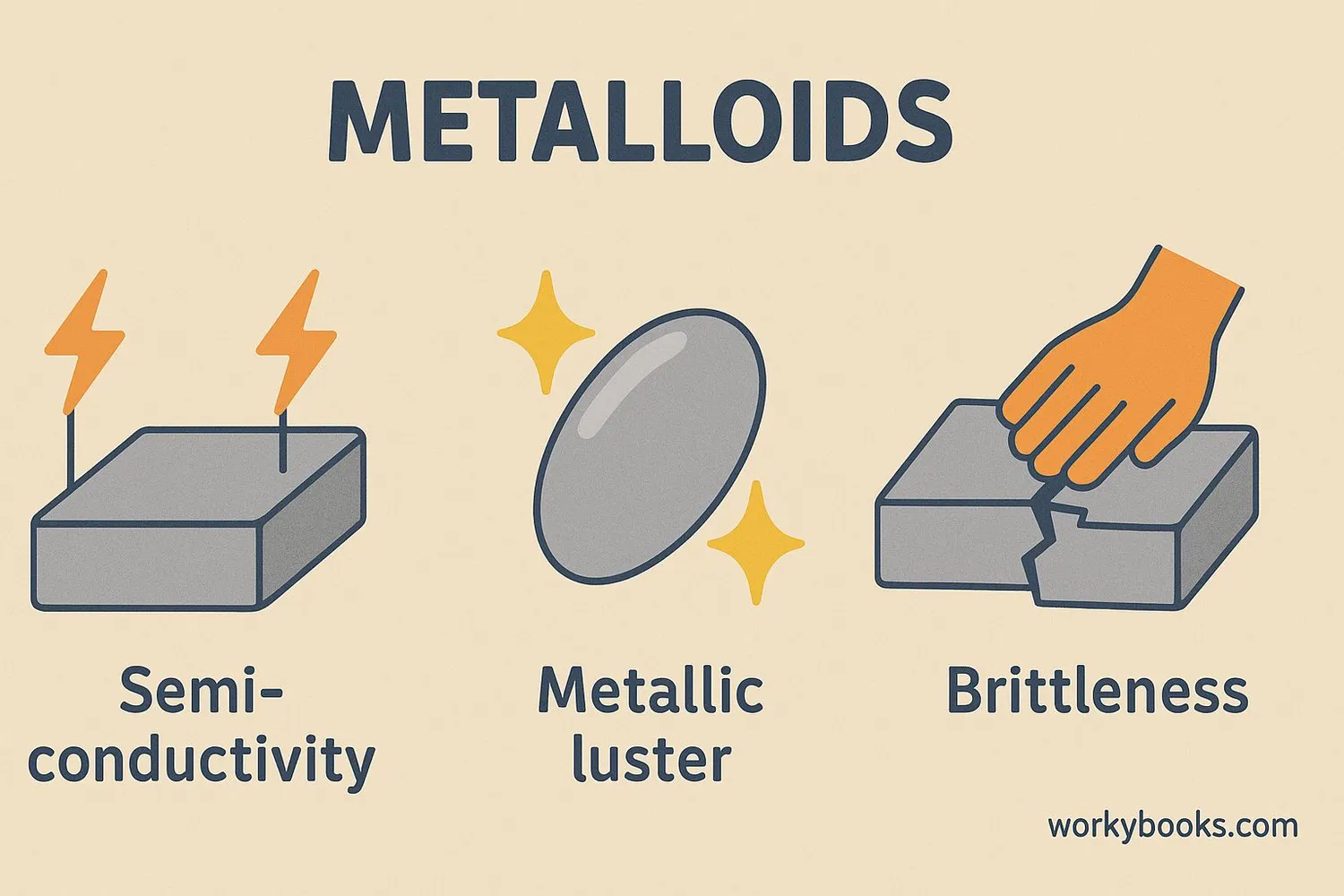
Metalloids have fascinating properties that make them unique. Here are their key characteristics:
Semi-Conductivity
They can conduct electricity, but not as well as metals
Metallic Luster
They often have a shiny appearance like metals
Brittleness
They tend to be brittle and break easily like nonmetals
Varied Reactivity
Their chemical behavior falls between metals and nonmetals
Intermediate Form
They can form alloys with metals or covalent bonds with nonmetals
The most important property of metalloids is their semi-conductivity. This means they can conduct electricity under certain conditions but not others. This special property makes them perfect for use in electronic devices like computers and smartphones.
Changing Behavior!
The conductivity of metalloids can change with temperature, light, or impurities. This is why they're so useful in technology!
Metalloids Examples
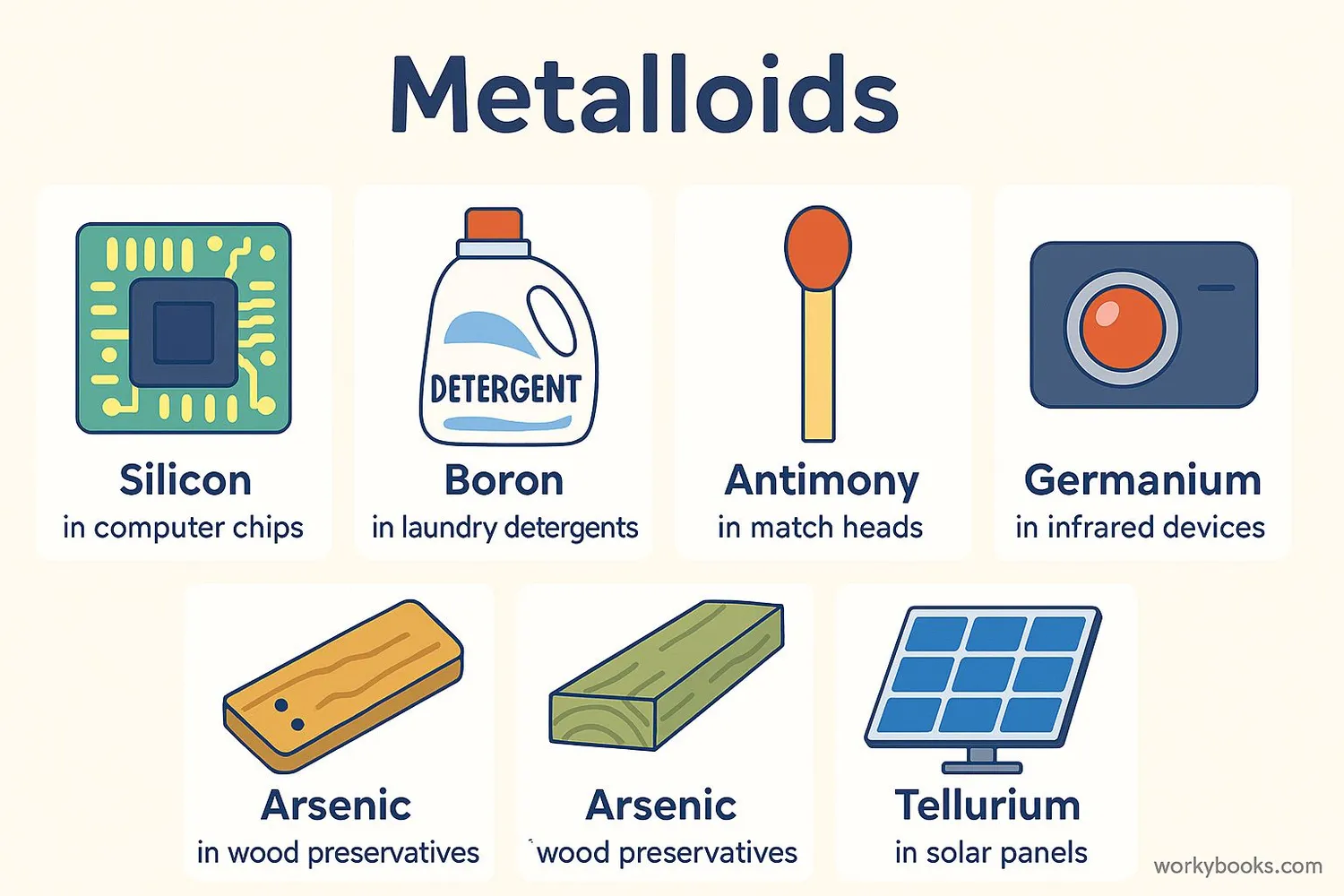
Let's look at some common metalloids and where we find them:
Silicon (Si)
The most famous metalloid! Used in computer chips, solar cells, and glass
Boron (B)
Found in laundry detergents, eye drops, and as a flame retardant
Antimony (Sb)
Used in flame-proofing materials, matches, and batteries
Arsenic (As)
Used in wood preservatives (though it's toxic in large amounts)
Tellurium (Te)
Used in solar panels, memory chips, and as an alloy with copper
Germanium (Ge)
Used in fiber optics, infrared devices, and camera lenses
These elements might have complicated names, but they play important roles in our everyday lives! From the computer or phone you're using right now to the detergent that cleans your clothes, metalloids are all around us.
Uses of Metalloids
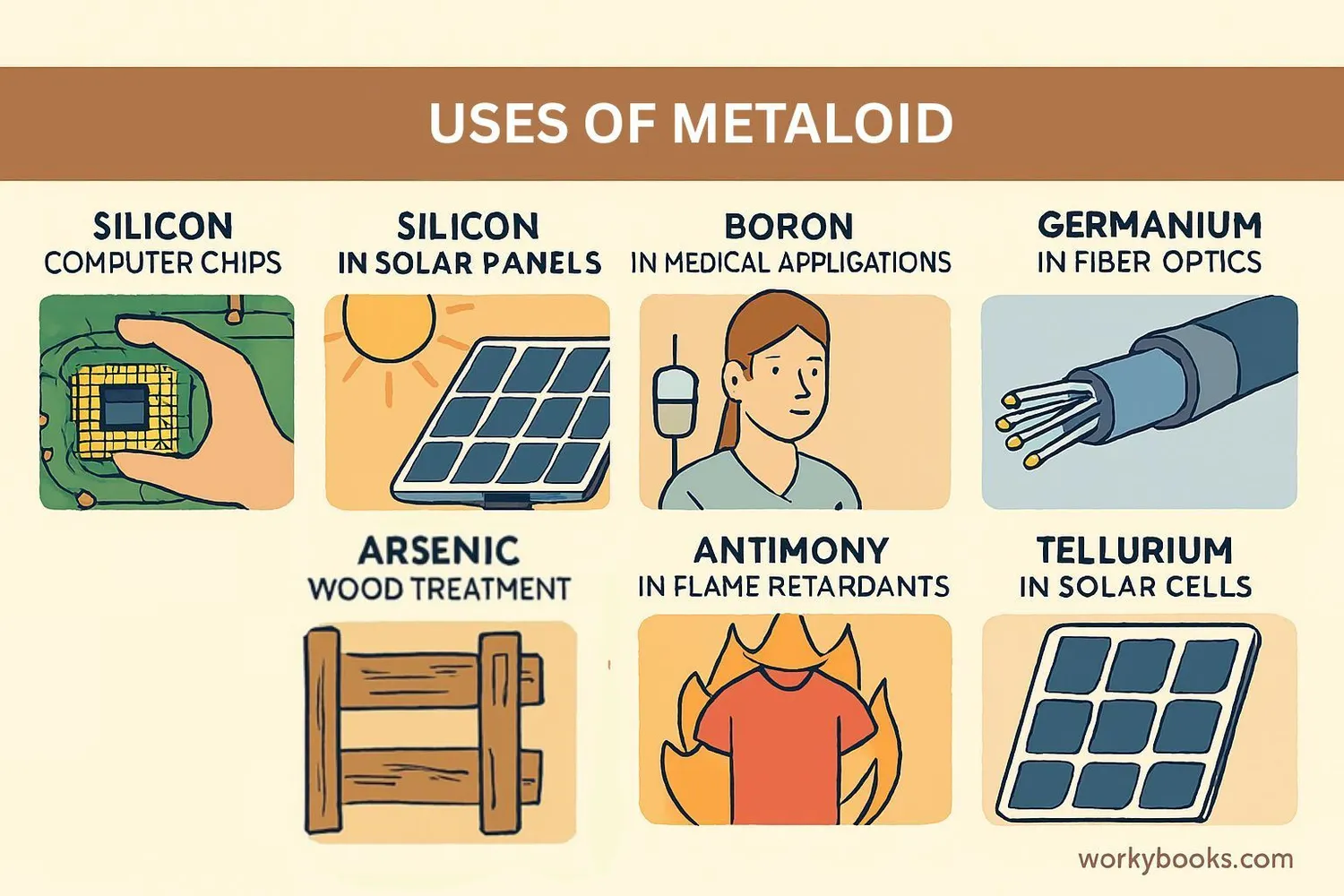
Metalloids are incredibly useful because of their special properties. Here are some of their most important applications:
Electronics
Silicon and germanium are used to make computer chips, transistors, and diodes
Solar Energy
Silicon is used in solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity
Medicine
Boron compounds are used in eye drops and antiseptics
Flame Retardants
Antimony compounds help make materials flame-resistant
Glass Production
Boron is used to make heat-resistant glass like Pyrex
Batteries
Tellurium is used in some types of batteries and memory chips
Without metalloids, we wouldn't have modern computers, smartphones, or solar panels. Their special semi-conducting properties make them essential for the technology we use every day. The next time you use a electronic device, remember that metalloids are working hard inside!
Silicon Valley!
California's famous "Silicon Valley" got its name from the silicon used in computer chips. This shows how important metalloids are to technology!
Metalloids Quiz
Test your knowledge about metalloids with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about metalloids:
Fun Metalloids Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about metalloids!
Silicon Abundance
Silicon is the second most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up about 28% of it by weight. Only oxygen is more abundant!
Boron Strength
Boron is added to steel to make it stronger. Just a tiny amount (0.001% to 0.003%) can double the strength of the steel!
Germanium Discovery
Germanium was one of the elements whose existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev before it was actually discovered. He called it "eka-silicon."
Tellurium Name
Tellurium gets its name from the Latin word "tellus," which means Earth. It was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth in 1798.





