Velocity - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how speed and direction work together in motion!
What is Velocity?
Velocity is a measurement of how fast something is moving AND in what direction. It's different from speed because velocity includes direction, while speed is just how fast something moves.
Think of velocity like giving someone directions: "Walk 3 miles per hour toward the school" is velocity, while "Walk 3 miles per hour" is just speed. Scientists call velocity a vector quantity because it has both size (the speed) and direction.
Key Point
Velocity = Speed + Direction. Changing either the speed or the direction changes the velocity!
Speed vs. Velocity
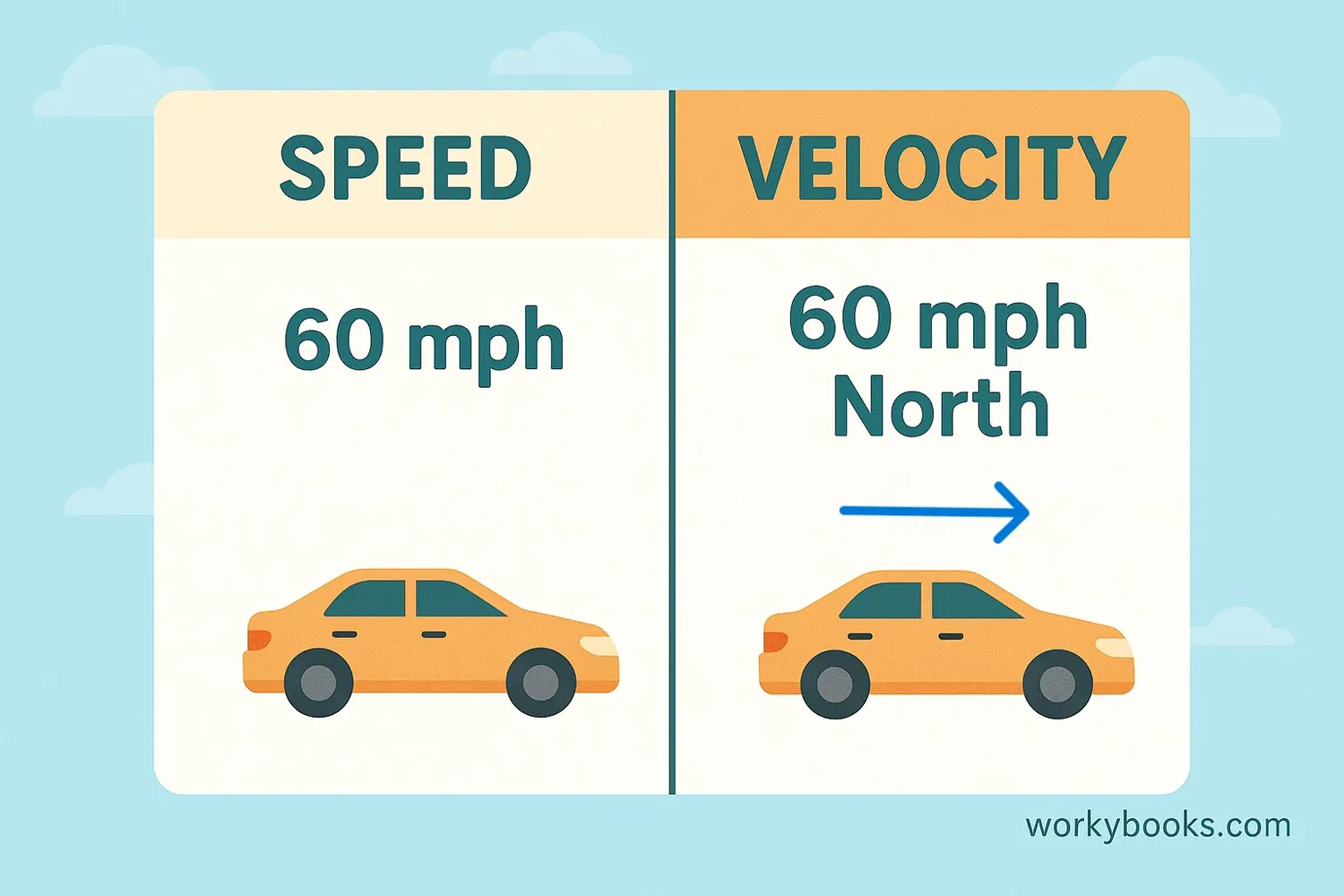
While speed and velocity are related, they're not the same thing. Here's the key difference:
Speed
How fast an object is moving (just a number)
Example: 50 km/h
Velocity
How fast AND in what direction
Example: 50 km/h North
Speed is called a scalar quantity because it only has magnitude (size). Velocity is a vector quantity because it has both magnitude and direction.
This means an object can have constant speed but changing velocity if it changes direction. For example, a car driving in circles at a steady 30 mph has constant speed but changing velocity because its direction keeps changing.
Calculating Velocity
To calculate velocity, we use this formula:
Velocity = Displacement ÷ Time
Displacement is different from distance. Distance is how far something has traveled, while displacement is the change in position from start to finish, including direction.
Measure Displacement
Find the change in position with direction (e.g., 50 meters East)
Measure Time
Determine how long it took (e.g., 10 seconds)
Calculate
Divide displacement by time (50 m East ÷ 10 s = 5 m/s East)
Remember: Velocity must always include units and direction. Common units for velocity include meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or miles per hour (mph).
Example Calculation
If a bicycle moves 300 meters North in 60 seconds, its velocity is 300 m North ÷ 60 s = 5 m/s North.
Real World Examples

We encounter velocity every day in many situations. Here are some common examples:
Driving a Car
When you say "I'm driving 65 mph North on the highway," you're describing velocity.
Weather Forecasts
Meteorologists report wind velocity, such as "15 mph from the West."
Sports
A baseball pitcher throws a fastball with velocity of 95 mph toward home plate.
Other examples include:
• A bird migrating south at 25 mph
• A rocket launching upward at 7,000 m/s
• A swimmer moving at 2 m/s toward the wall
• A hurricane moving northwest at 10 mph
In each case, both the speed and direction are important for understanding the complete picture of motion.
Velocity Quiz
Test your velocity knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about velocity:
Fun Velocity Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about velocity!
Earth's Motion
You're moving right now! Earth rotates at about 1,000 mph at the equator, and orbits the sun at about 67,000 mph. But we don't feel it because velocity is relative.
Fastest Animal
The peregrine falcon is the fastest animal when diving. It can reach velocities of over 240 mph when swooping down on prey from great heights!
Space Velocity
The Parker Solar Probe is the fastest human-made object, reaching velocities of 430,000 mph as it orbits close to the Sun. That's fast enough to travel from New York to Tokyo in under a minute!
Sports Speeds
In sports, velocity is crucial! A professional tennis serve can reach 150 mph, a baseball pitch can exceed 100 mph, and a badminton shuttlecock can travel over 200 mph.





