Jet Streams - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the powerful winds that shape our weather patterns
What is a Jet Stream?
A jet stream is like a river of wind high up in the atmosphere! These powerful winds flow from west to east at speeds of 120-250 miles per hour, about 5-9 miles above the Earth's surface. They form where cold air masses meet warmer air masses, creating a steep temperature difference that makes the air move very fast.
Jet streams are important because they:
• Help move weather systems around the globe
• Influence where storms form and travel
• Affect how long weather patterns stay in one place
• Create boundaries between warm and cold air
Science Fact!
The fastest jet stream ever recorded was over Japan in 2019 with winds of 408 mph - that's faster than a speeding bullet train!
Types of Jet Streams

There are two main types of jet streams that affect our weather:
Polar Jet Stream
Found between 30°-60° latitude, usually 7-12 km high. It forms where cold polar air meets warmer mid-latitude air.
Subtropical Jet Stream
Located around 30° latitude, about 10-16 km high. It forms where warm tropical air meets cooler air to the north.
The polar jet stream is usually stronger and affects weather more in North America and Europe. Both jet streams can merge or split depending on the season and location.
Seasonal Changes!
Jet streams shift with the seasons - moving north in summer and south in winter as the Earth tilts toward or away from the Sun.
How Jet Streams Affect Weather
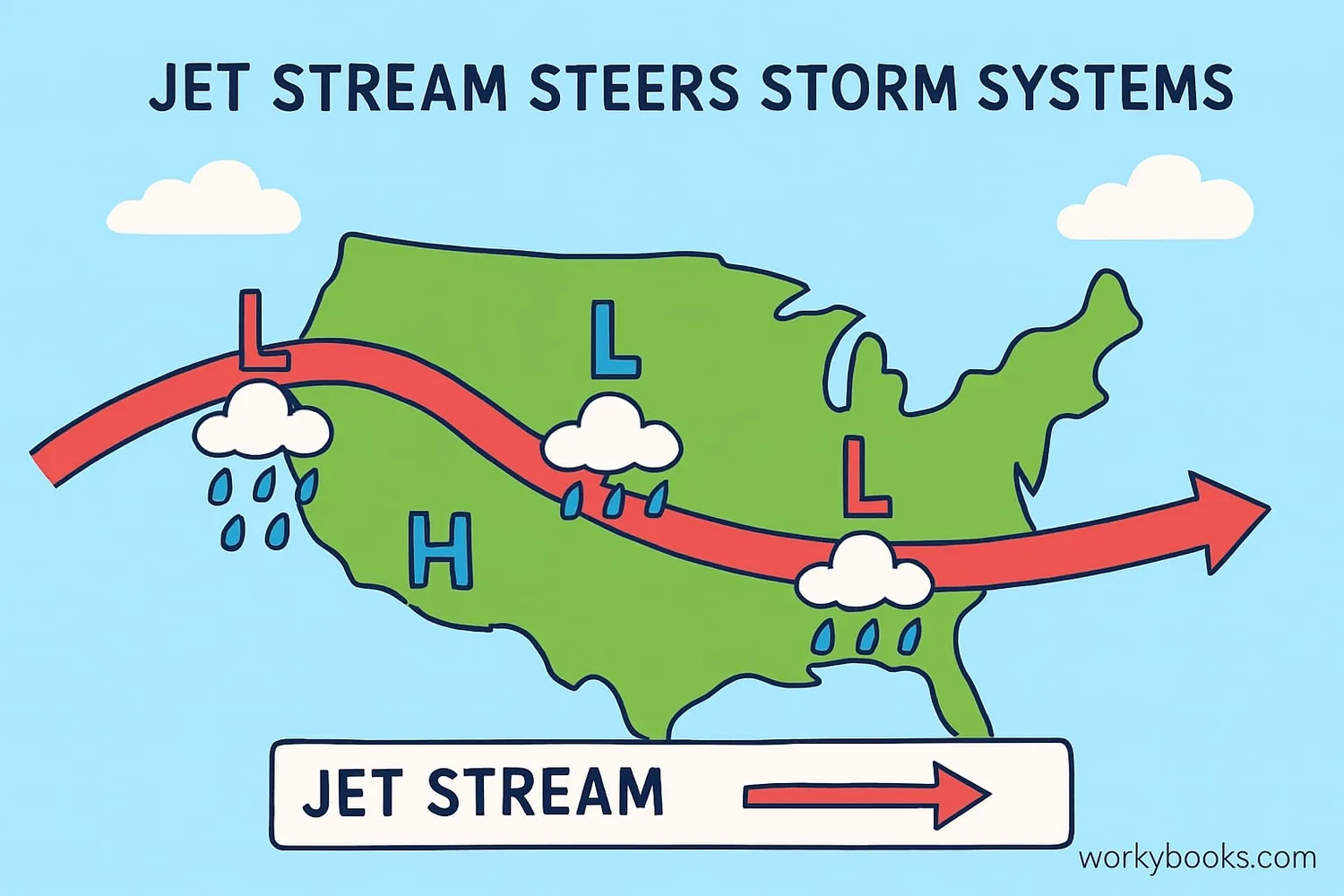
Jet streams are like weather directors that guide storms and air masses around our planet. Here's how they influence our daily weather:
Storm Steering
Jet streams push weather systems from west to east, determining where storms go
Temperature Boundaries
They create boundaries between warm southern air and cold northern air
Weather Duration
When a jet stream curves south, it can make weather patterns last longer
Severe Weather
Jet streams provide energy for powerful thunderstorms and hurricanes
When the jet stream dips south, it brings colder air with it. When it bulges north, warmer air follows. Meteorologists study jet streams to predict whether we'll have rainy, dry, cold, or warm weather!
Jet Streams and Aviation

Jet streams have a big impact on airplanes! Pilots carefully plan routes to either take advantage of these fast winds or avoid them:
Flying East
Planes flying east can "ride" the jet stream for a faster trip and fuel savings
Flying West
Planes flying west try to avoid jet streams because they create strong headwinds
Time Differences
A flight from NY to London can be 1 hour shorter than the return trip!
Commercial flights can save thousands of dollars in fuel by flying with the jet stream. However, flying through jet streams can cause turbulence, so pilots may adjust altitude to find smoother air.
Changing Jet Stream Patterns
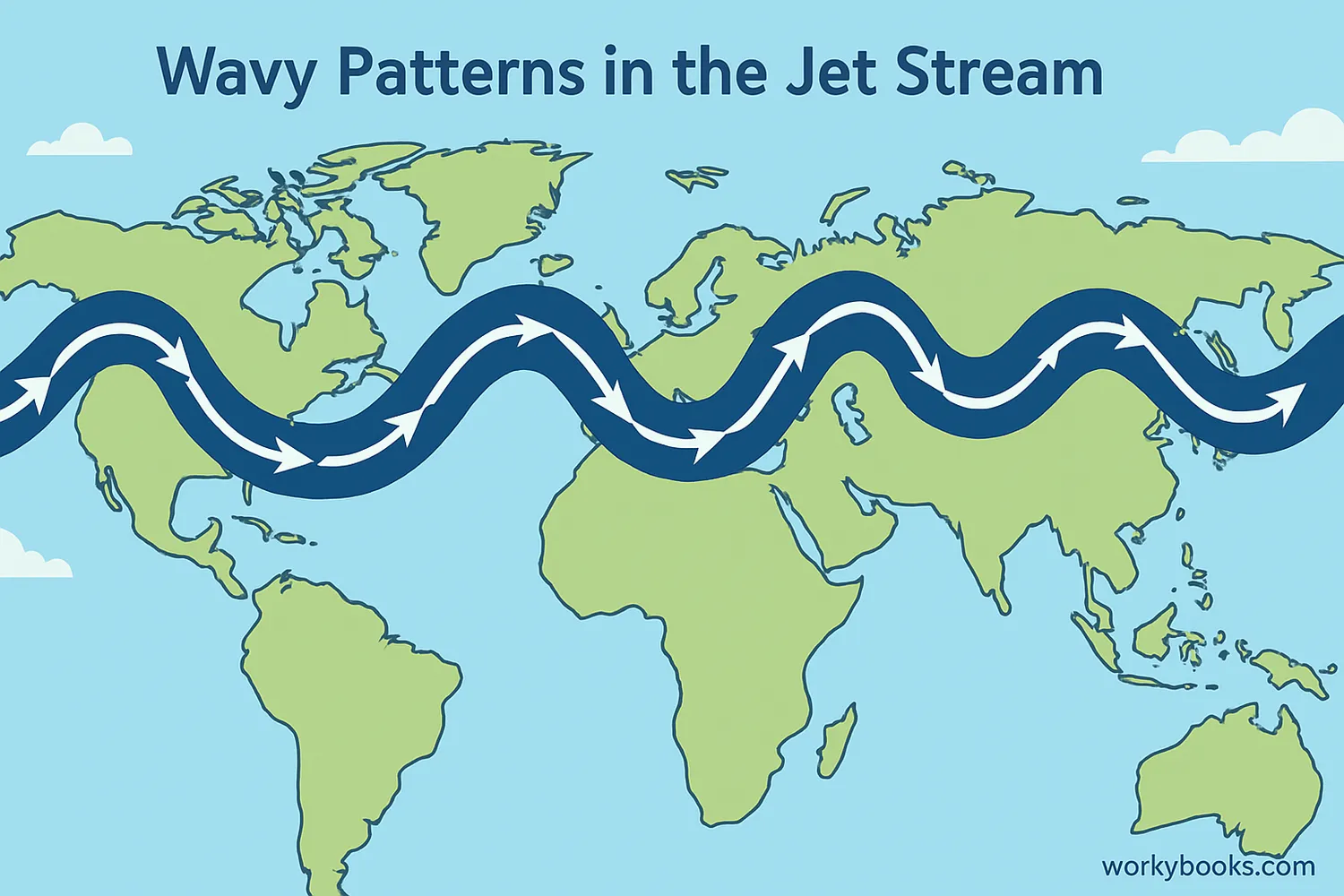
Jet streams don't always flow straight - they develop waves and curves that affect our weather for weeks or months:
Rossby Waves
Large north-south meanders in the jet stream that move slowly west to east
El Niño
Warms Pacific Ocean water, weakening and shifting the jet stream south
La Niña
Cools Pacific water, strengthening the jet stream and making it more active
When the jet stream develops large waves, it can cause "blocking patterns" that make weather stay in one place for a long time. This can lead to extended periods of rain, drought, heat, or cold in certain areas.
Scientists are studying how climate change might be affecting jet streams and making weather patterns more extreme.
Jet Stream Quiz
Test your knowledge about jet streams with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about jet streams:
Amazing Jet Stream Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about jet streams:
Discovery
Jet streams were discovered during World War II when bomber pilots noticed their ground speed was much faster than expected when flying eastward at high altitudes.
Speed Record
The fastest jet stream wind ever recorded was 408 mph over Japan in 2019. That's faster than the top speed of most race cars!
Flight Time Saver
Flying with the jet stream can save up to 2 hours on transatlantic flights from North America to Europe! The return trip against the jet stream takes longer.
Global Influence
Jet streams circle the entire planet! The polar jet stream can be over 7,000 miles long but only 100-300 miles wide and 1-3 miles thick.





