Crystal Science - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how crystals form and grow in nature and science
What is Crystallization?
Crystallization is the process where solid crystals form from a liquid or gas. It happens when atoms or molecules arrange themselves in a repeating, organized pattern. This creates beautiful geometric shapes with flat surfaces and sharp edges.
Think of crystallization like building with LEGO blocks - when you arrange them in a pattern, you create a structure. In crystallization, molecules arrange themselves in specific patterns to form crystals. This process happens in nature to create snowflakes, gemstones, and salt crystals!
Did You Know?
Every snowflake is a unique crystal! Their six-sided patterns form when water vapor freezes in clouds.
The Crystallization Process
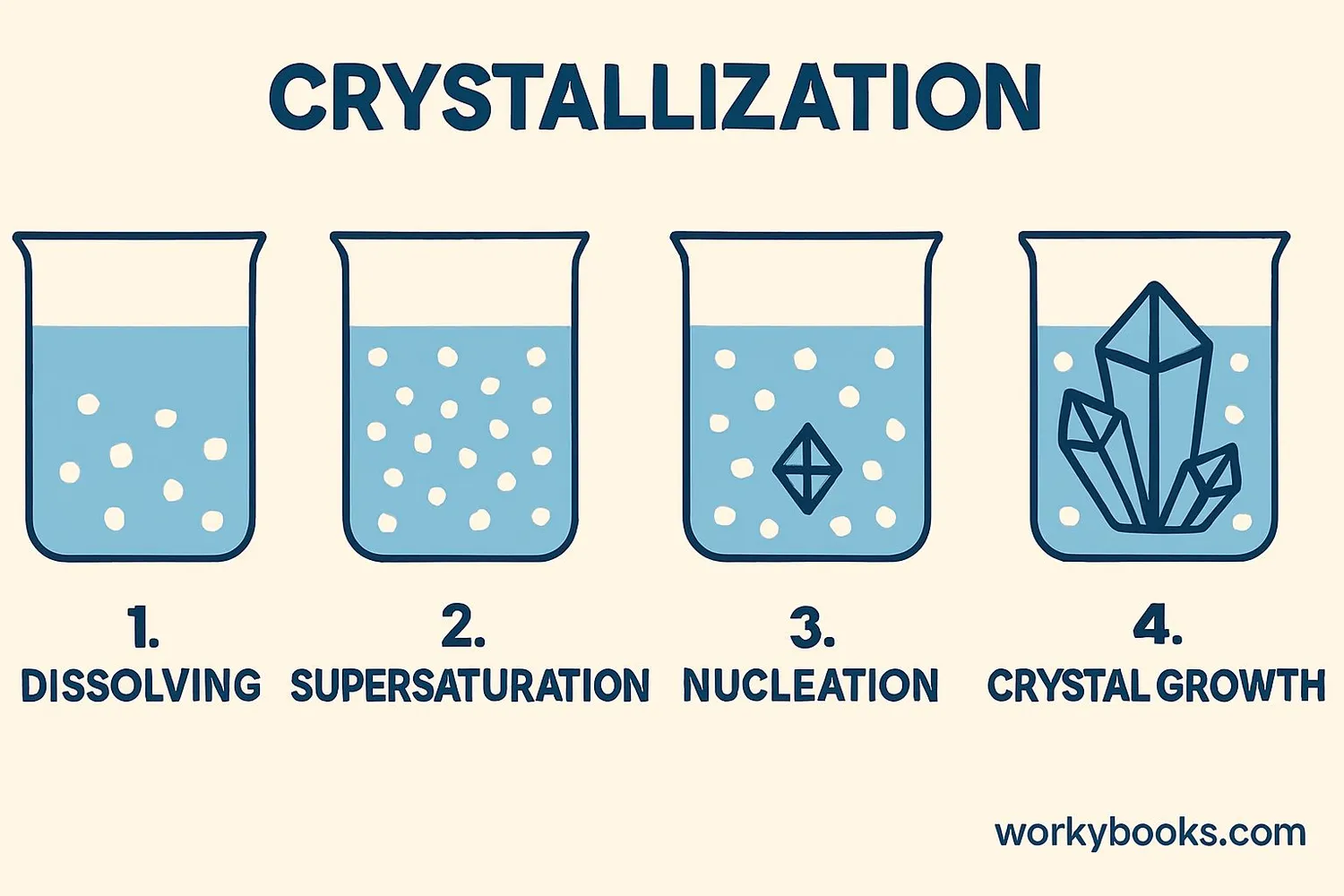
Crystallization happens in four main steps. Let's explore how crystals form from a solution:
Dissolving
A solid dissolves in a liquid to make a solution
Supersaturation
More solid is added than can dissolve
Nucleation
Molecules start to form tiny crystal seeds
Crystal Growth
Molecules arrange onto the seeds to grow crystals
The key to crystal formation is supersaturation. When a solution has more dissolved material than it can normally hold, the extra material comes out of solution and forms crystals. Temperature changes often trigger crystallization - like when warm saltwater cools and salt crystals form.
Crystal Fact!
Crystals grow in specific shapes based on how their molecules arrange. Table salt forms perfect cubes because sodium and chlorine atoms arrange in a cube pattern!
Examples of Crystallization
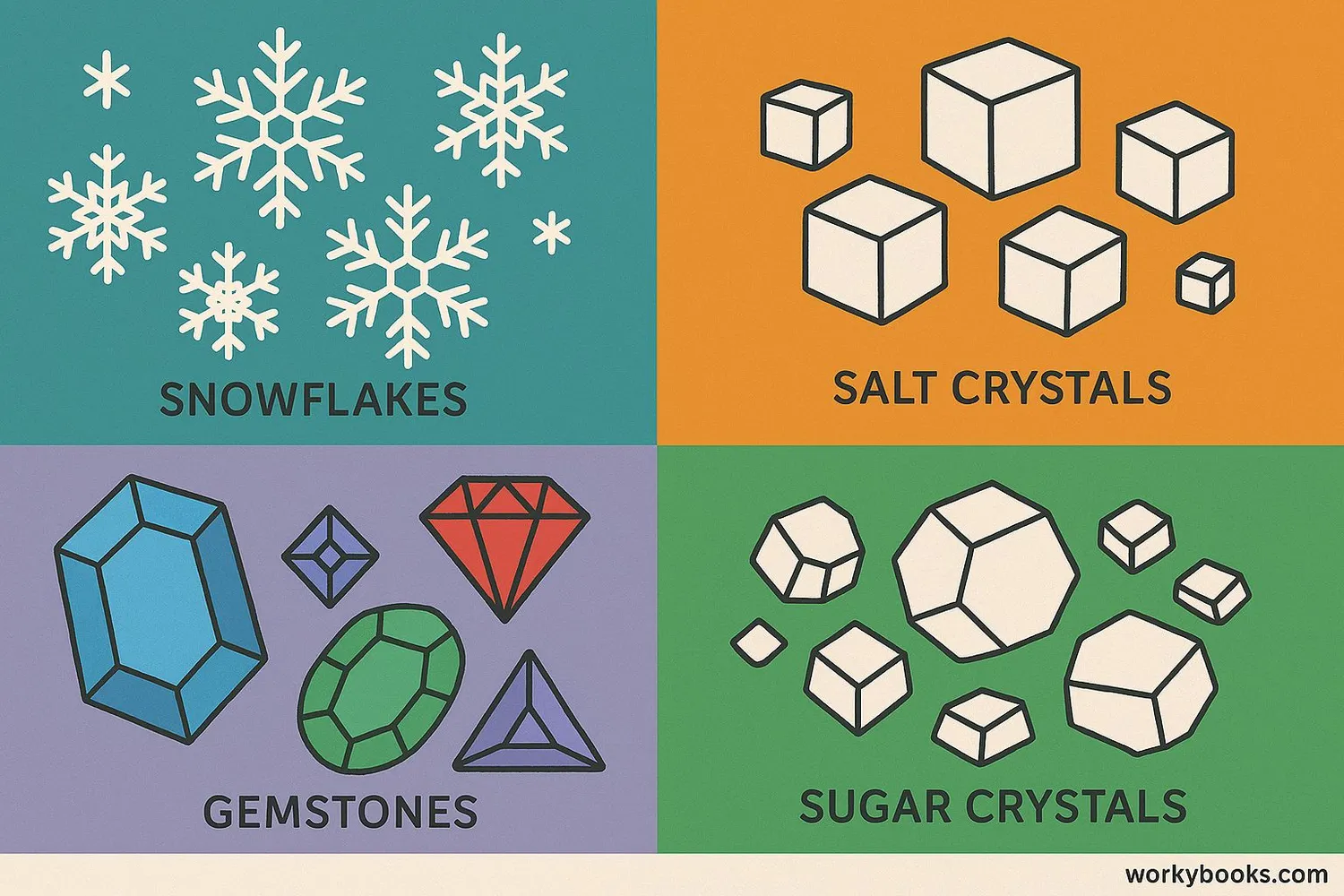
Crystallization happens all around us! Here are some common examples:
Snowflakes
Water vapor crystallizes into ice in clouds
Salt Crystals
Form when seawater evaporates in salt ponds
Sugar Crystals
Grow when sugar syrup cools and crystallizes
Gemstones
Form when minerals crystallize deep in the Earth
Honey Crystallization
Natural honey forms sugar crystals over time
Frost on Windows
Water vapor crystallizes on cold surfaces
These examples show how crystallization occurs in different ways - from evaporation (salt), cooling (sugar), freezing (snow), and pressure (gemstones). Each material forms crystals with unique shapes and properties!
Fractional Crystallization
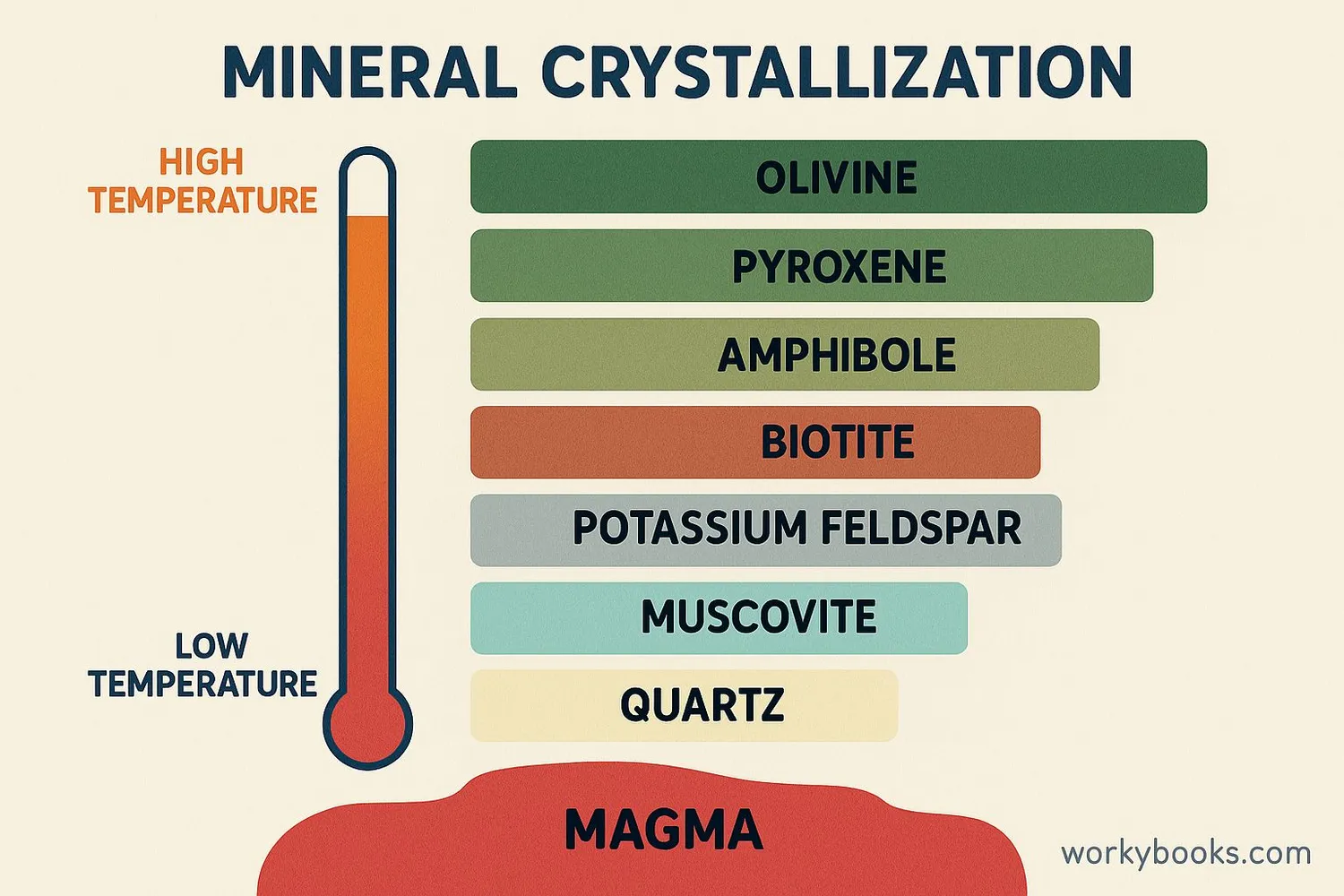
Fractional crystallization is a special process that separates mixtures based on crystallization. It works because different substances crystallize at different temperatures.
Here's how it works:
1. A mixture is melted to form a liquid
2. The liquid is slowly cooled
3. The substance with the highest melting point crystallizes first
4. Crystals are removed
5. The remaining liquid cools further, and the next substance crystallizes
This process is important in:
• Geology: Forms different rock types as magma cools
• Chemistry: Purifies chemicals and separates mixtures
• Food industry: Separates components like fats from oils
Rock Formation!
Granite forms through fractional crystallization! As magma cools, different minerals crystallize at different temperatures to create this speckled rock.
How to Grow Crystals
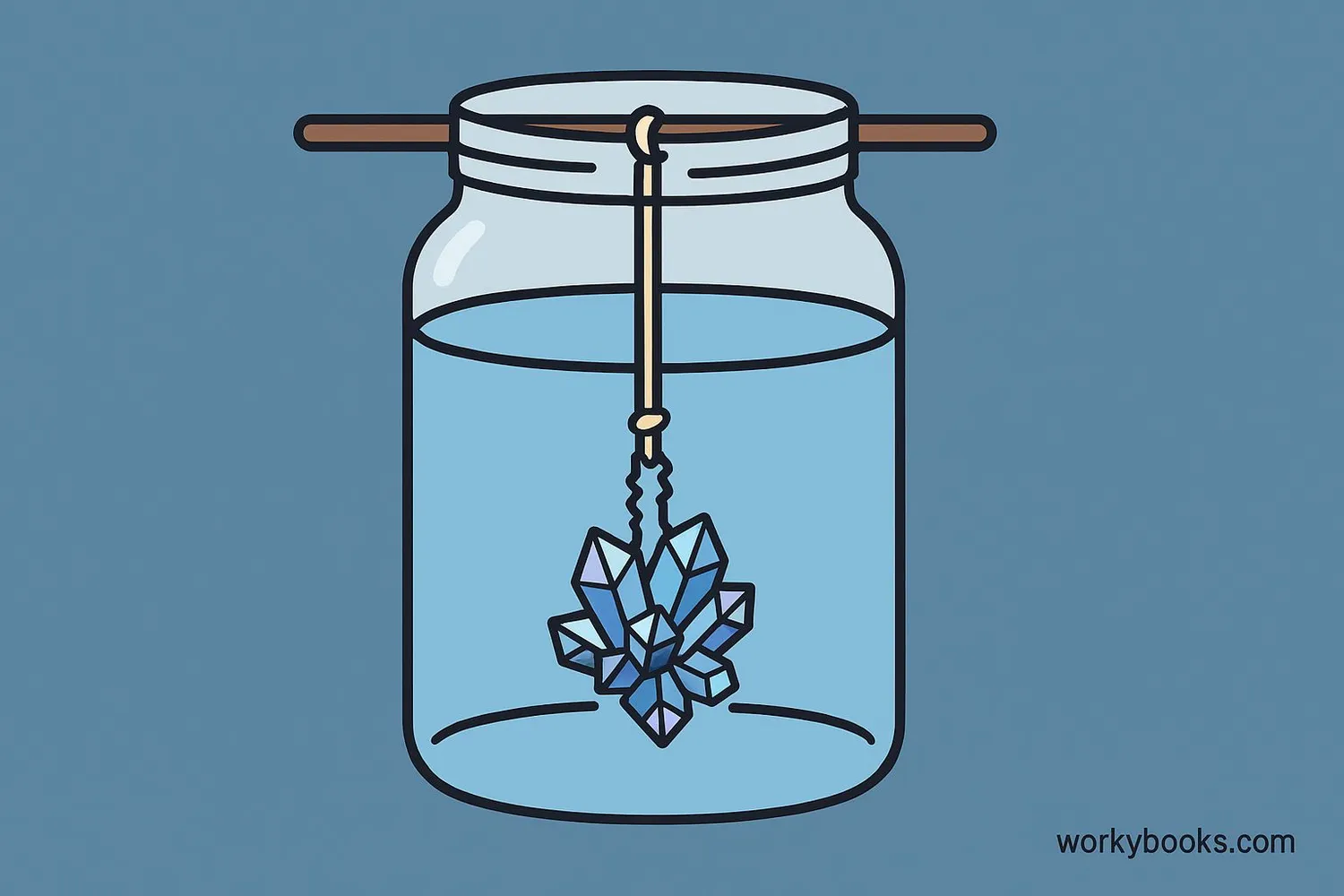

You can grow your own crystals at home! Here's a simple experiment using salt or sugar:
Crystal Growing Experiment
- Make a supersaturated solution: Heat water and add salt or sugar until no more dissolves
- Prepare your growing surface: Tie a string to a pencil and suspend it in the solution
- Cool slowly: Place the jar where it won't be disturbed
- Wait: Crystals will start forming on the string in 1-7 days
- Observe: Examine your crystals with a magnifying glass
Tips for success:
• Use distilled water for clearer crystals
• Add food coloring to make colored crystals
• For faster growth, place the jar in the refrigerator after it cools
• Try different materials: salt, sugar, borax, or Epsom salts
Safety First!
Always have an adult help with hot water. Borax crystals are beautiful but borax should not be ingested.
Crystallization Quiz
Test your crystallization knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about crystallization:
Fun Crystallization Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about crystallization!
Giant Crystals
The largest natural crystals on Earth are in Mexico's Cave of Crystals. Some selenite crystals are over 36 feet long and weigh 55 tons!
Crystal Technology
Silicon crystals are used to make computer chips! These ultra-pure crystals are "grown" in special laboratories for the electronics industry.
Unique Snowflakes
Every snowflake is unique because each forms under slightly different temperature and humidity conditions as it falls through the atmosphere.
Ancient Crystals
The oldest known crystals on Earth are zircon crystals from Australia, dating back 4.4 billion years - almost as old as Earth itself!





