Algae - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how these tiny organisms create oxygen and support life on Earth!
What are Algae?

Algae are simple, plant-like organisms that live in water! They don't have roots, stems, or leaves like regular plants, but they contain chlorophyll which lets them perform photosynthesis - turning sunlight into energy.
Think of algae as nature's water gardens! They range from tiny single-celled phytoplankton to giant kelp forests. You can find them in oceans, lakes, rivers, and even in damp soil. Algae are super important because they produce much of Earth's oxygen!
Algae Fact!
Algae produce about 50-80% of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere through photosynthesis!
Types of Algae
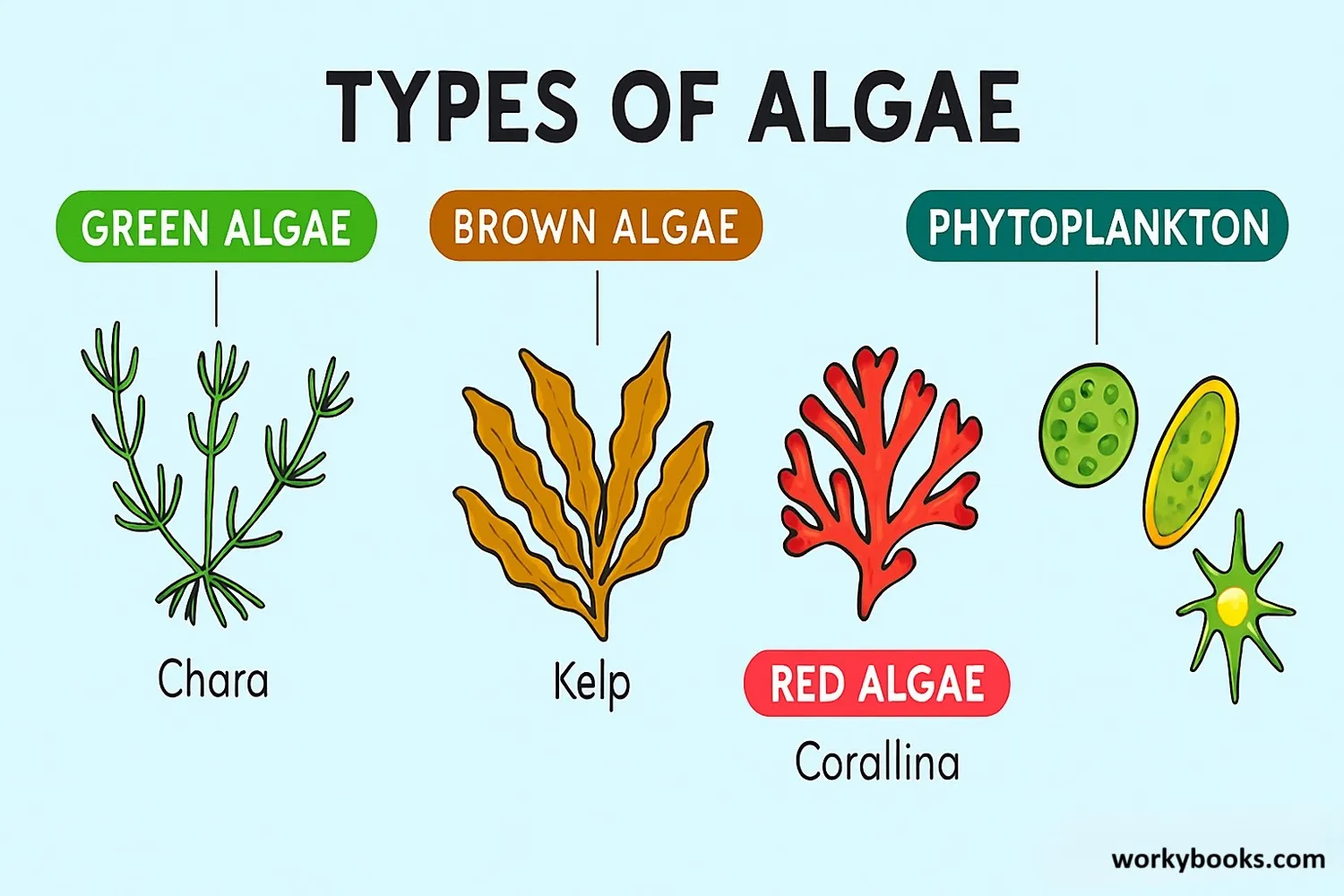
Algae come in many different shapes, sizes, and colors! Scientists group them based on their pigments and characteristics:
Green Algae
Most common in freshwater environments like ponds and lakes. They contain chlorophyll and give water a green appearance.
Brown Algae
Mainly found in marine environments. Includes kelp and rockweed that form underwater forests.
Red Algae
Mostly marine algae that can live in deeper water. Used to make nori for sushi!
Phytoplankton
Microscopic algae that float near the water's surface. The foundation of aquatic food chains.
Blue-Green Algae
Actually bacteria (cyanobacteria) but often grouped with algae. Can form blooms in nutrient-rich water.
Each type of algae has special adaptations that help it survive in different aquatic environments. Some float freely, while others attach to rocks or form large underwater forests.
Size Matters!
Algae range from microscopic phytoplankton (0.002 mm) to giant kelp that can grow over 150 feet long!
Why Algae are Important
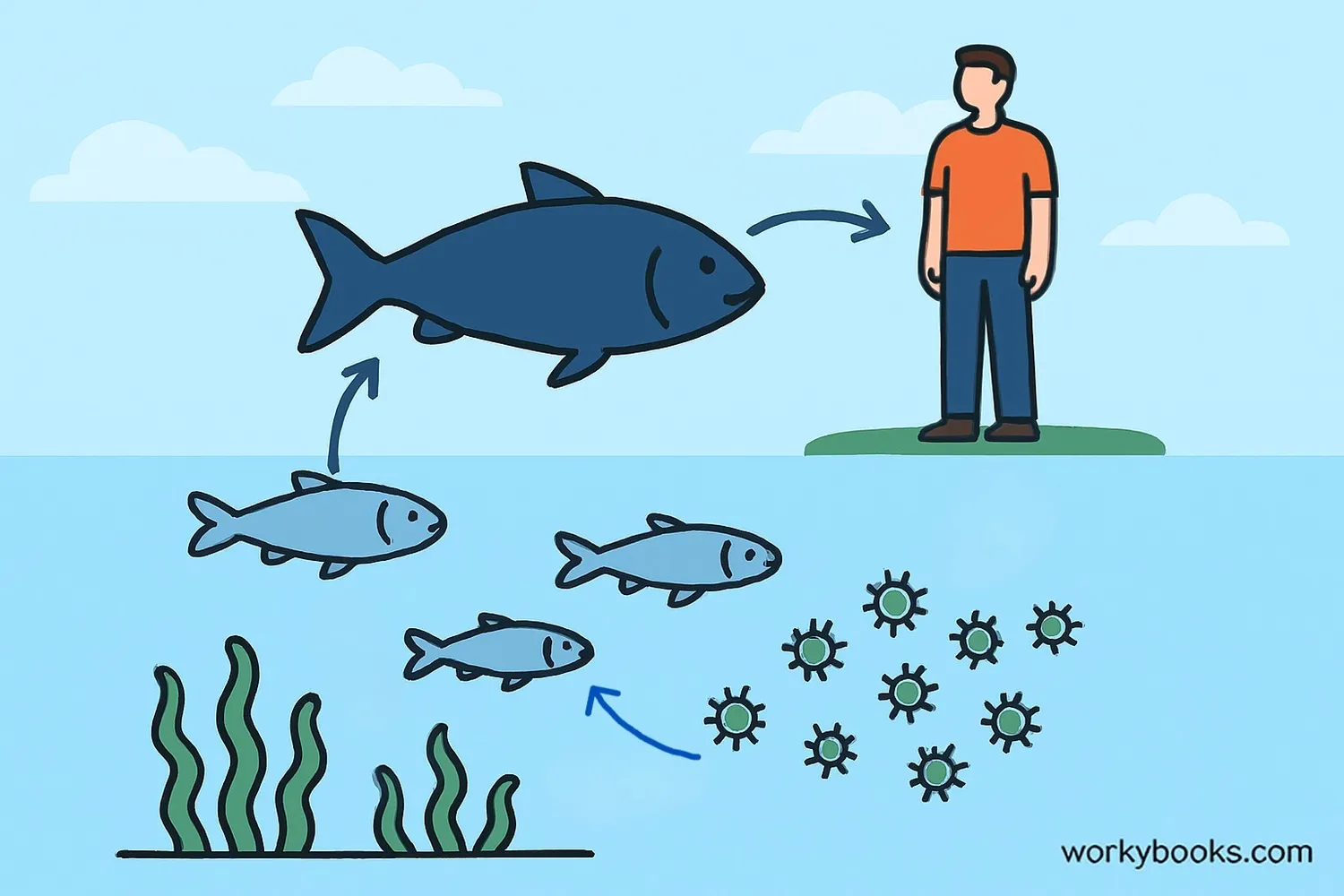
Algae might seem like simple organisms, but they play crucial roles in our world:
Oxygen Production
Through photosynthesis, algae produce most of Earth's oxygen - more than all land plants combined!
Food Source
Algae form the base of aquatic food chains, feeding everything from tiny zooplankton to whales.
Carbon Cycling
Algae absorb carbon dioxide and help regulate Earth's climate by storing carbon.
Humans also use algae in many ways:
• Food: Nori (sushi wraps), spirulina supplements
• Industry: Agar for science labs, carrageenan for food thickeners
• Environment: Biofuel production and wastewater treatment
• Biotechnology: Medicines, cosmetics, and nutritional products
Without algae, our planet would have less oxygen, fewer fish, and less stable ecosystems!
Algae Blooms

Sometimes algae grow very quickly, forming what we call "blooms." These can be harmful to aquatic ecosystems:
Causes
Excess nutrients from fertilizers, sewage, or pollution enter water systems.
Appearance
Blooms look like green paint or scum on water surfaces ("pond scum").
Effects
Can block sunlight, deplete oxygen, and release toxins that harm fish and humans.
Not all algae blooms are harmful, but some can create "dead zones" where fish can't survive. We can prevent harmful blooms by reducing pollution and protecting our waterways.
Red Tides
Some algae blooms cause "red tides" that make ocean water appear red or brown. These can release toxins that affect marine life and people.
Algae Quiz
Test your algae knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about algae:
Fun Algae Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about algae:
Ancient Organisms
Algae have been on Earth for over 1 billion years! Fossil evidence shows they were among the first organisms to perform photosynthesis.
Space Food
Astronauts eat algae in space! Spirulina is a nutrient-rich algae that's perfect for space travel because it grows quickly with minimal resources.
Oxygen Champions
Tiny algae called Prochlorococcus produce 20% of the oxygen in our atmosphere! There are about 3 billion billion billion of these algae in the ocean.
Algae Fuel
Some cars and planes now run on algae biofuel! Algae can produce oil that can be converted into renewable fuel, making them a promising energy source.





