Analogous Structures - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how different animals develop similar solutions to life's challenges!
What Are Analogous Structures?
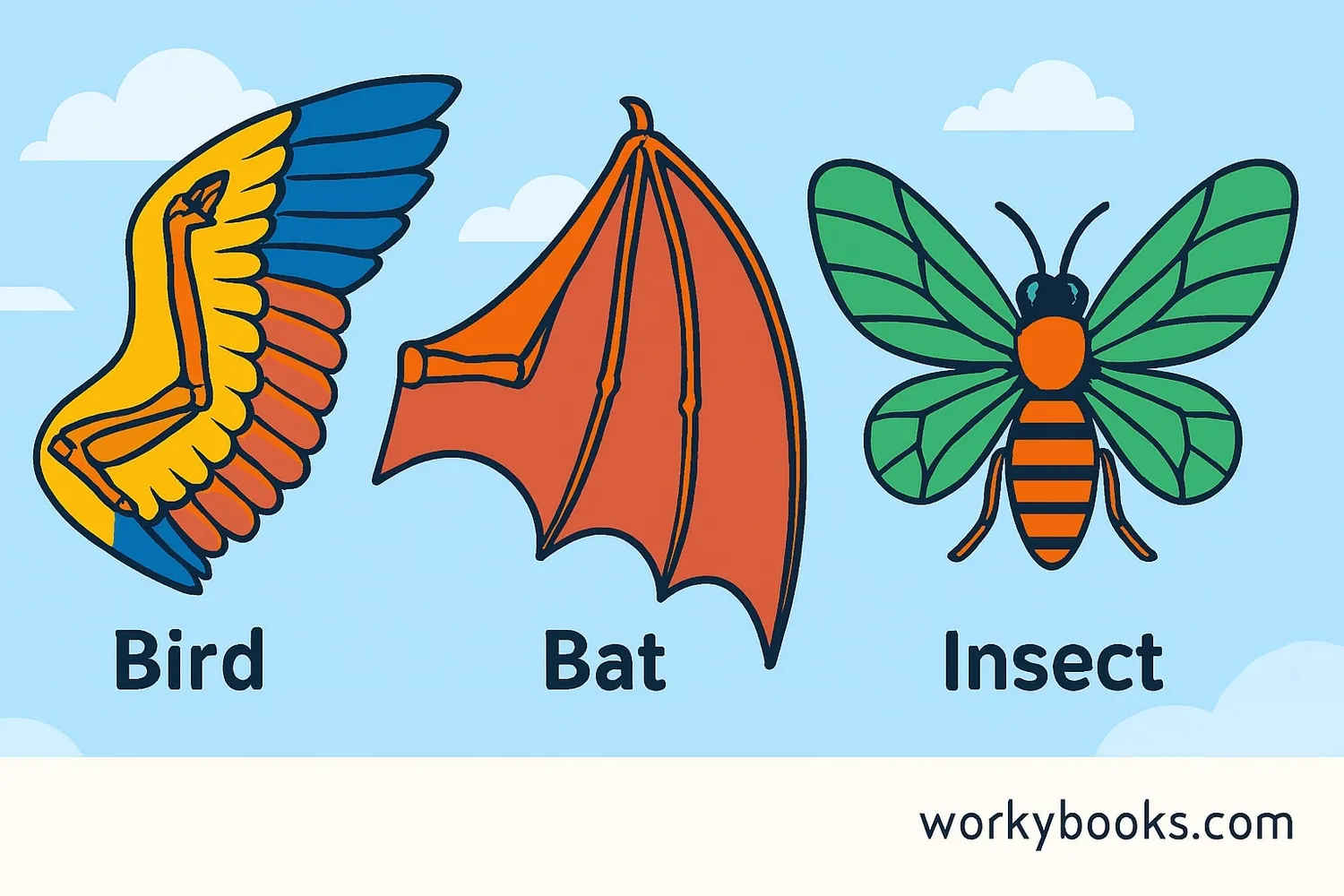
Analogous structures are body parts in different animals that have similar functions and may look alike, but they developed from different origins. These structures evolved independently to solve similar problems, not because the animals share a recent common ancestor.
Think of it like different inventors creating similar solutions to the same problem. For example, birds, bats, and insects all have wings for flying, but their wings developed in different ways and from different body parts. This is called convergent evolution - when unrelated species develop similar traits because they adapted to similar environments or lifestyles.
Key Point
Analogous structures have similar functions but different evolutionary origins. They develop through convergent evolution when unrelated species adapt to similar environments.
Examples of Analogous Structures
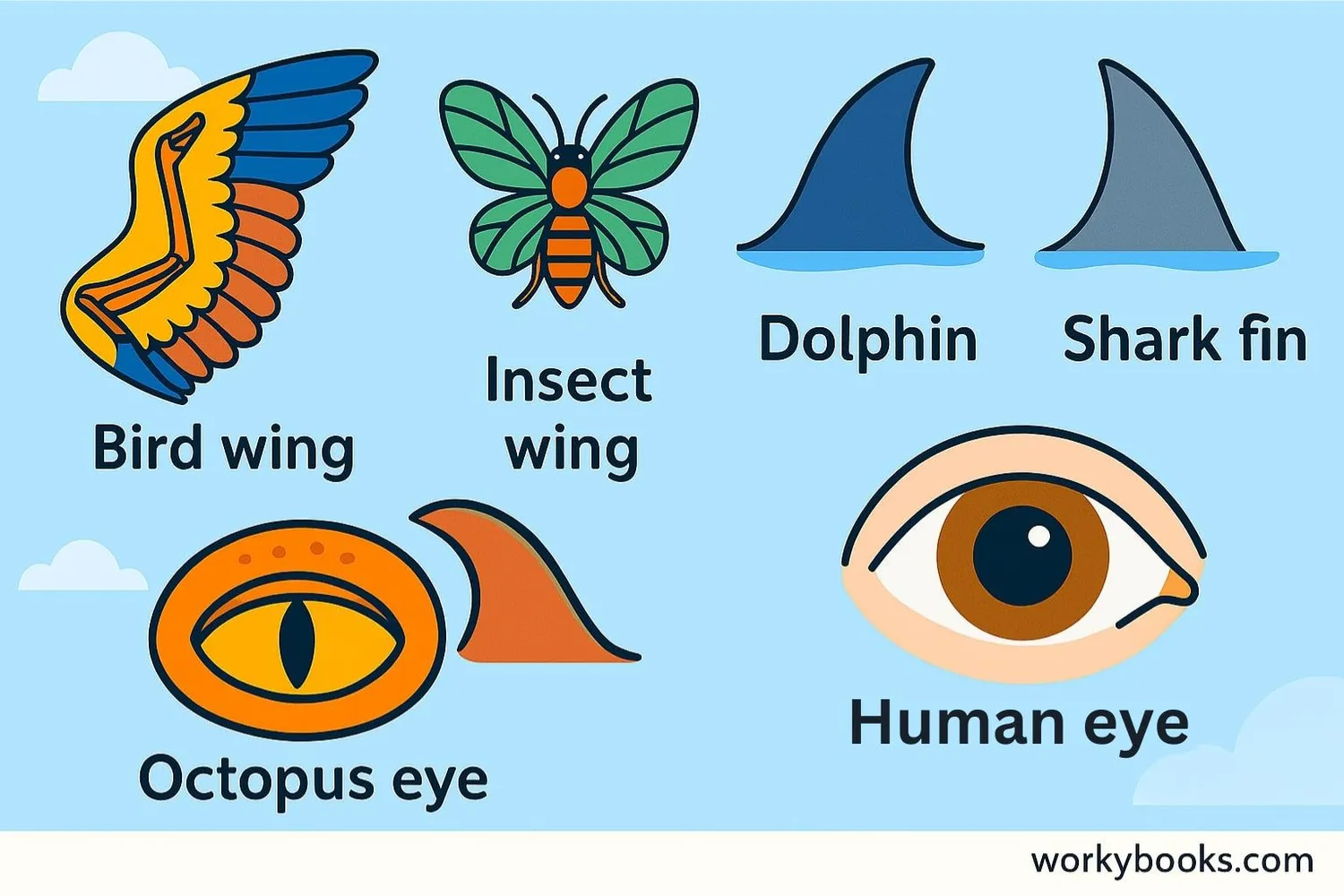
Nature is full of amazing examples of analogous structures. Here are some common ones:
Wings
Birds, bats, and insects all have wings for flying, but they developed from different body parts
Fins
Dolphins (mammals) and sharks (fish) both have fins for swimming but different skeletal structures
Eyes
Octopuses and mammals both have camera-like eyes but they evolved separately
Streamlined Bodies
Dolphins, sharks, and penguins all have streamlined bodies for efficient swimming
Digging Forelimbs
Moles (mammals) and mole crickets (insects) both have digging forelimbs but different structures
Each of these examples shows how different animals can arrive at similar solutions to life's challenges. Birds developed wings from their forelimbs, while insects developed wings from their exoskeleton. Despite looking similar and serving the same purpose, these structures have different evolutionary histories.
Analogous vs Homologous Structures
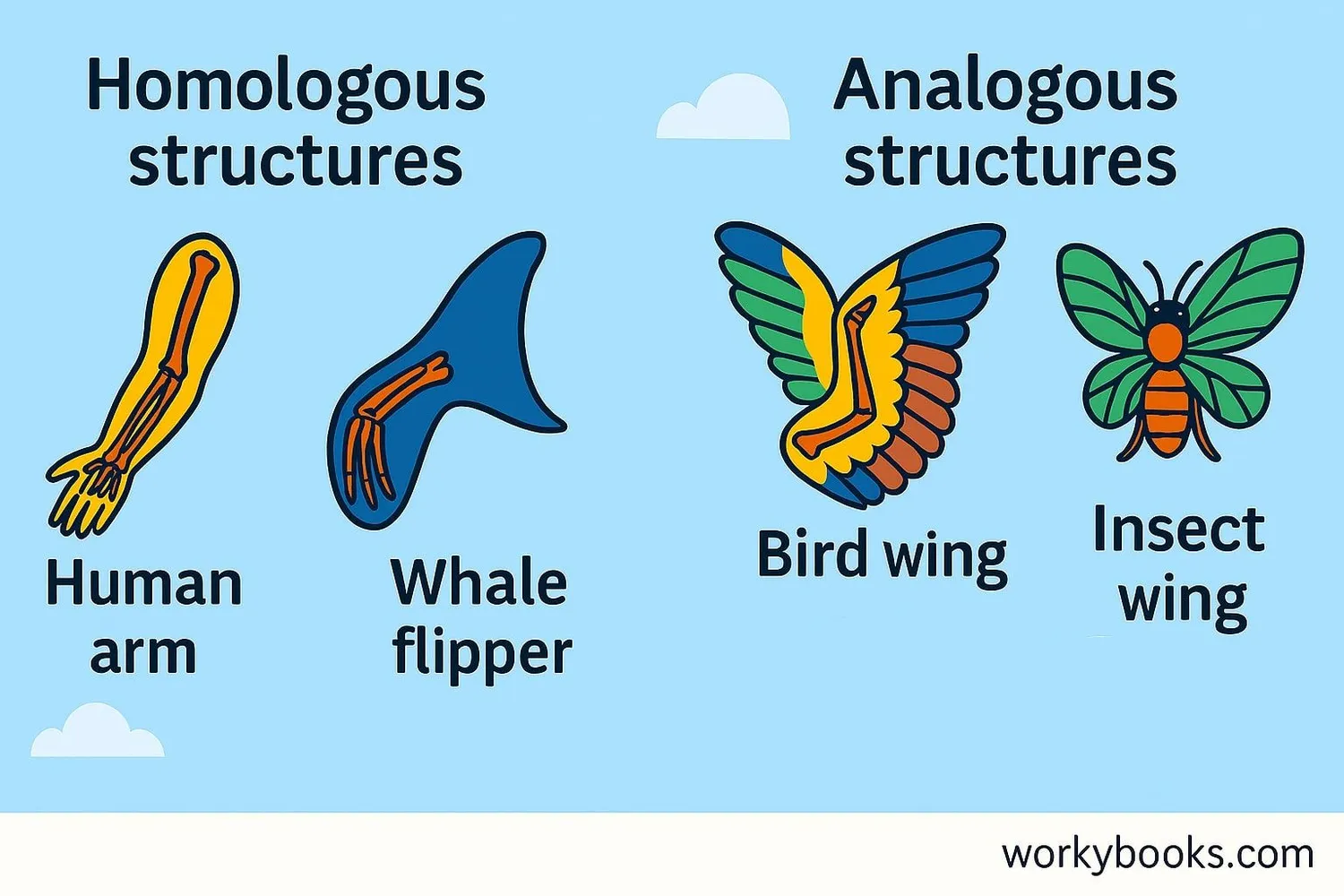
It's important to understand the difference between analogous structures and homologous structures:
| Feature | Analogous Structures | Homologous Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Similar function | May have different functions |
| Structure | Different internal structure | Similar internal structure |
| Evolution | Develop independently (convergent evolution) | Share common ancestor (divergent evolution) |
| Example | Wings of birds and insects | Arms of humans, flippers of whales, wings of bats |
| Evolutionary Relationship | Not closely related | Closely related |
Homologous structures like the human arm, whale flipper, and bat wing share a common underlying structure because these animals evolved from a common ancestor. Their limbs have the same basic bone structure but have adapted for different functions.
Analogous structures like bird wings and insect wings have similar functions (flying) but completely different structures because these animals do not share a recent common ancestor with wings. They developed flying abilities independently.
Remember This
Homologous = Same structure, different function (common ancestor)
Analogous = Different structure, similar function (no common ancestor)
Analogous Structures Quiz
Test your knowledge about analogous structures with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about analogous structures:
Fun Trivia About Analogous Structures
Discover some amazing facts about analogous structures in nature!
Evolutionary Time
Camera-type eyes (like human eyes and octopus eyes) evolved independently at least seven different times in evolutionary history! This shows how valuable good vision is for survival.
Flying Solutions
There are four completely different ways animals have evolved to fly: insects with exoskeleton wings, birds with feather wings, bats with skin wings, and pterosaurs with membrane wings.
Plant Parallels
In the deserts of North America (cacti) and Africa (euphorbias), unrelated plants developed similar succulent stems, spines, and water storage tissues to survive dry conditions.
Streamlined for Success
Dolphins (mammals), penguins (birds), and sharks (fish) all evolved streamlined body shapes for efficient swimming, despite their different classifications and evolutionary histories.





