Cells - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the building blocks of life and how they work
What is a Cell?
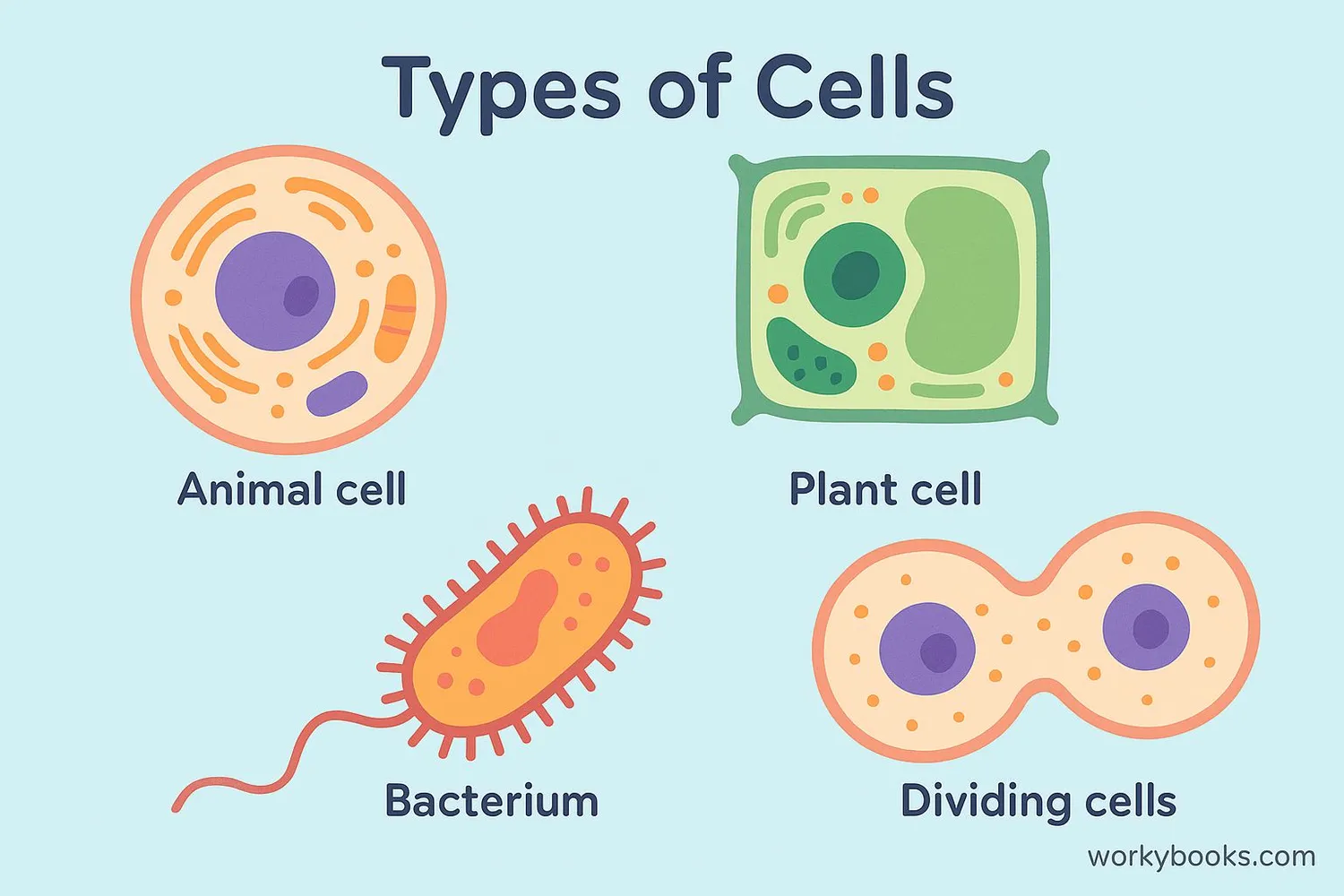
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. Just like bricks build houses, cells build your body. Every plant, animal, fungus, and microorganism is made of cells - from the tallest tree to the tiniest bacteria!
The word "cell" comes from the Latin word "cella," meaning "small room." This name was given by scientist Robert Hooke in 1665 when he looked at cork through a microscope and saw tiny compartments that reminded him of monks' rooms.
Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see most of them. The average human body contains about 37 trillion cells! Each cell has a special job to do - some carry oxygen, some fight germs, and some send messages through your body.
Did You Know?
The smallest known cells are bacteria called mycoplasma. They are so small that 10,000 could fit on the tip of a pencil!
Parts of a Cell
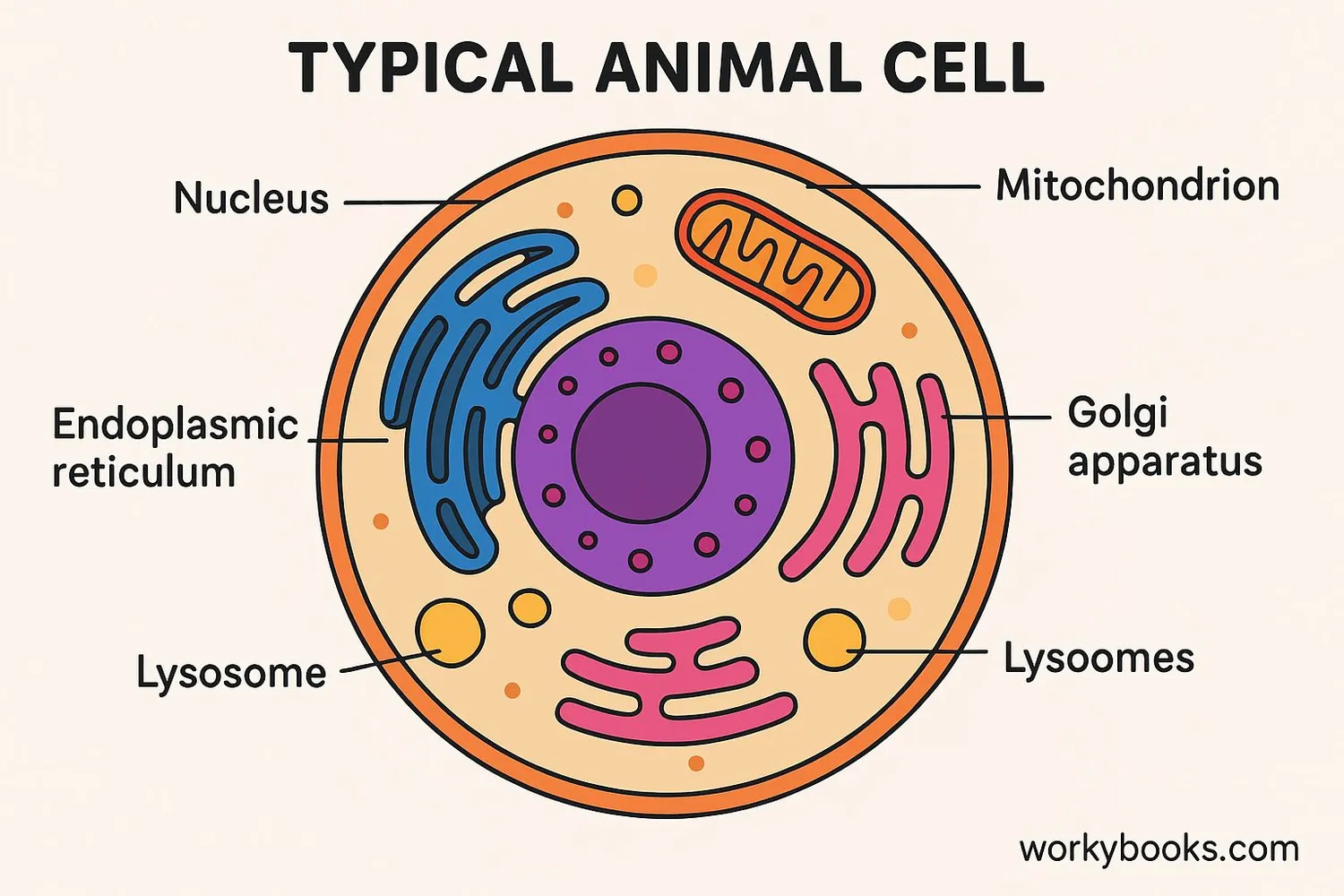
Cells contain special parts called organelles (like tiny organs) that each have important jobs. Here are the main parts found in most animal and plant cells:
| Organelle | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Controls what enters and leaves the cell | Like a security guard at the door |
| Cytoplasm | Jelly-like substance that holds organelles | Like the air inside a building |
| Nucleus | Controls the cell and contains DNA | Like the brain of the cell |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy for the cell | Like the cell's power plant |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Transports materials within the cell | Like a highway system |
| Golgi Apparatus | Packages and ships materials | Like a post office |
| Ribosomes | Makes proteins | Like a factory |
| Lysosomes | Breaks down waste materials | Like a recycling center |
Plant Cells Have Extra Parts!
Plant cells have three special structures that animal cells don't have: cell walls for support, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large vacuoles for storage.
Types of Cells
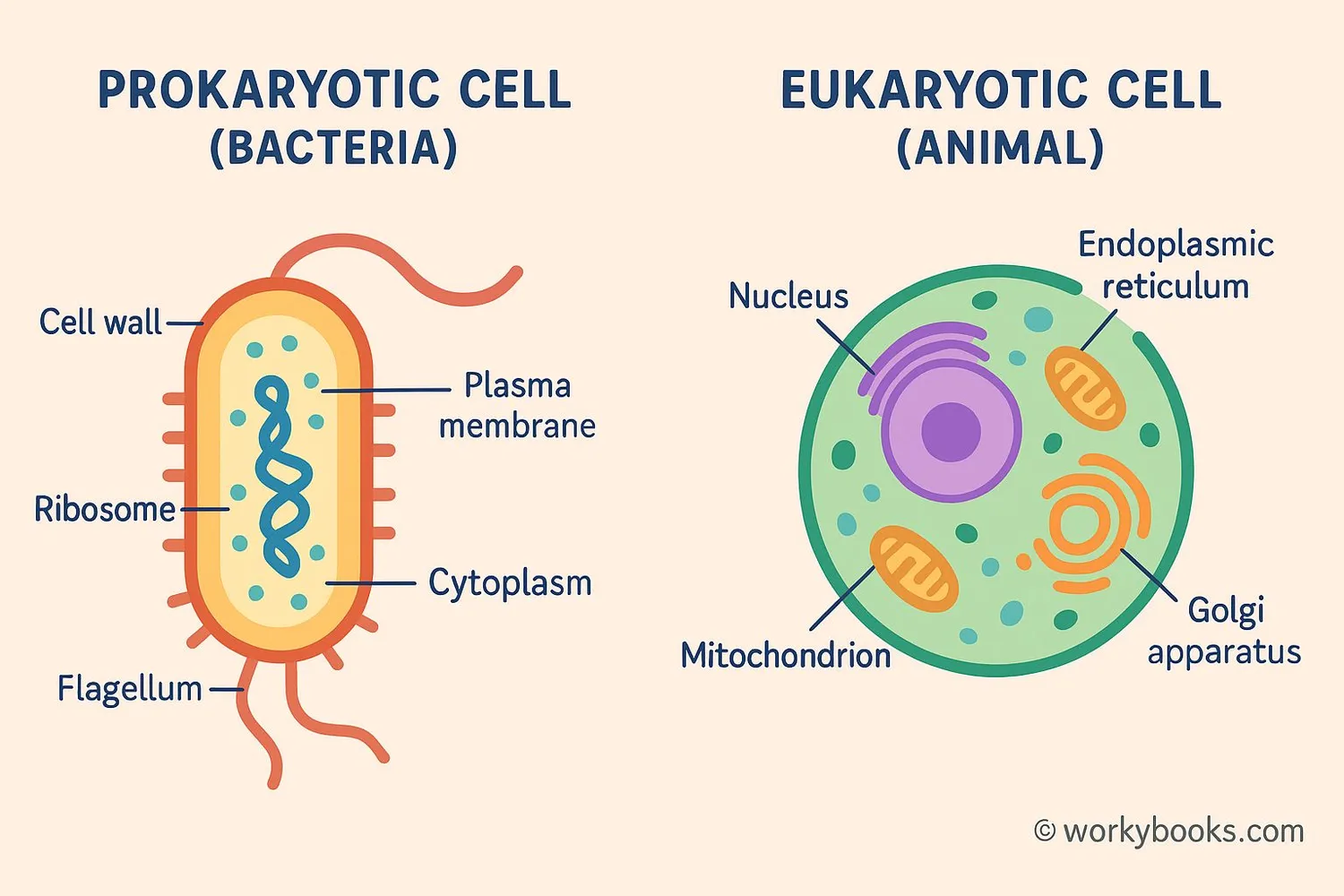
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The key difference is that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Prokaryotic Cells
• No nucleus
• Simple structure
• Small size
• Bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
• Have a nucleus
• Complex organelles
• Larger size
• Animals, plants, fungi
Examples:
• Prokaryotic cells: Bacteria like E. coli or Streptococcus
• Eukaryotic cells: Human skin cells, plant leaf cells, mushroom cells
Eukaryotic cells are like a big city with specialized buildings (organelles), while prokaryotic cells are like a small village where everything happens in one place.
Cell Theory
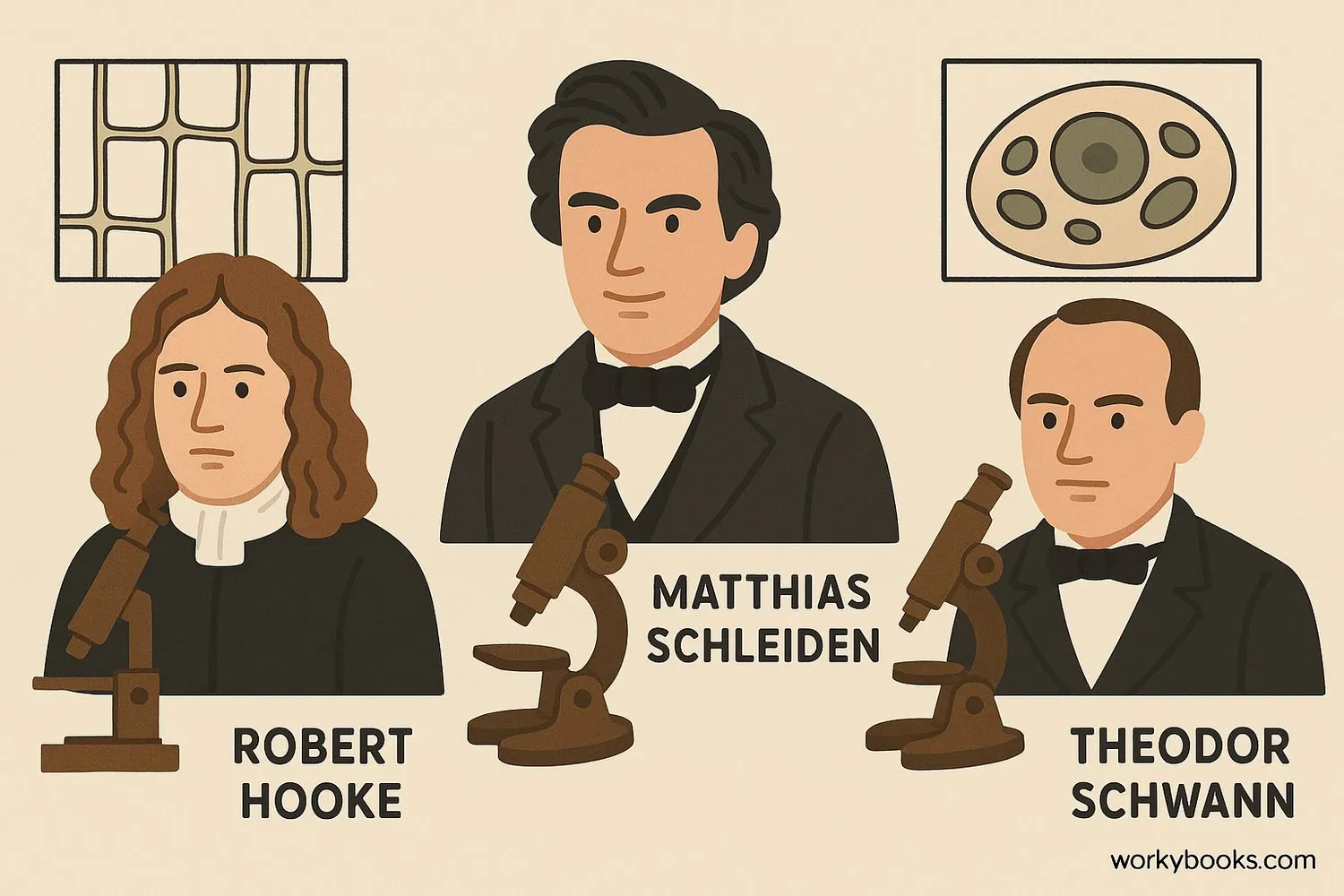
The Cell Theory is one of the fundamental principles of biology. Developed in the mid-1800s, it has three main ideas:
All living things are made of cells
From tiny bacteria to giant whales, all life is cellular
Cells are the basic units of structure and function
Cells are the smallest living units that perform life functions
New cells come from existing cells
Cells reproduce through cell division
These principles were established through the work of scientists like Matthias Schleiden (plants), Theodor Schwann (animals), and Rudolf Virchow (cell reproduction). Today, we know that cells contain DNA that passes genetic information to new cells during division.
Modern Addition
Some scientists add a fourth principle: Cells contain DNA passed to daughter cells, and energy flow occurs within cells.
Cell Biology Quiz
Test your knowledge about cells with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about cells:
Amazing Cell Facts
Discover some fascinating trivia about cells:
Size Matters
If you lined up all the cells in your body end to end, they would stretch around the Earth over 47 times! That's about 2 million kilometers of cells.
Constant Renewal
Your body creates about 300 million new cells every minute! Your skin cells completely replace themselves every 2-4 weeks.
Bacterial Dominance
There are more bacterial cells in your body than human cells! Most are harmless or helpful, especially those in your digestive system.
Nerve Speed
Nerve cells can transmit signals at speeds up to 120 meters per second. That's faster than a race car!




