The Cell Membrane - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the protective barrier that controls what enters and leaves every cell
What is the Cell Membrane?
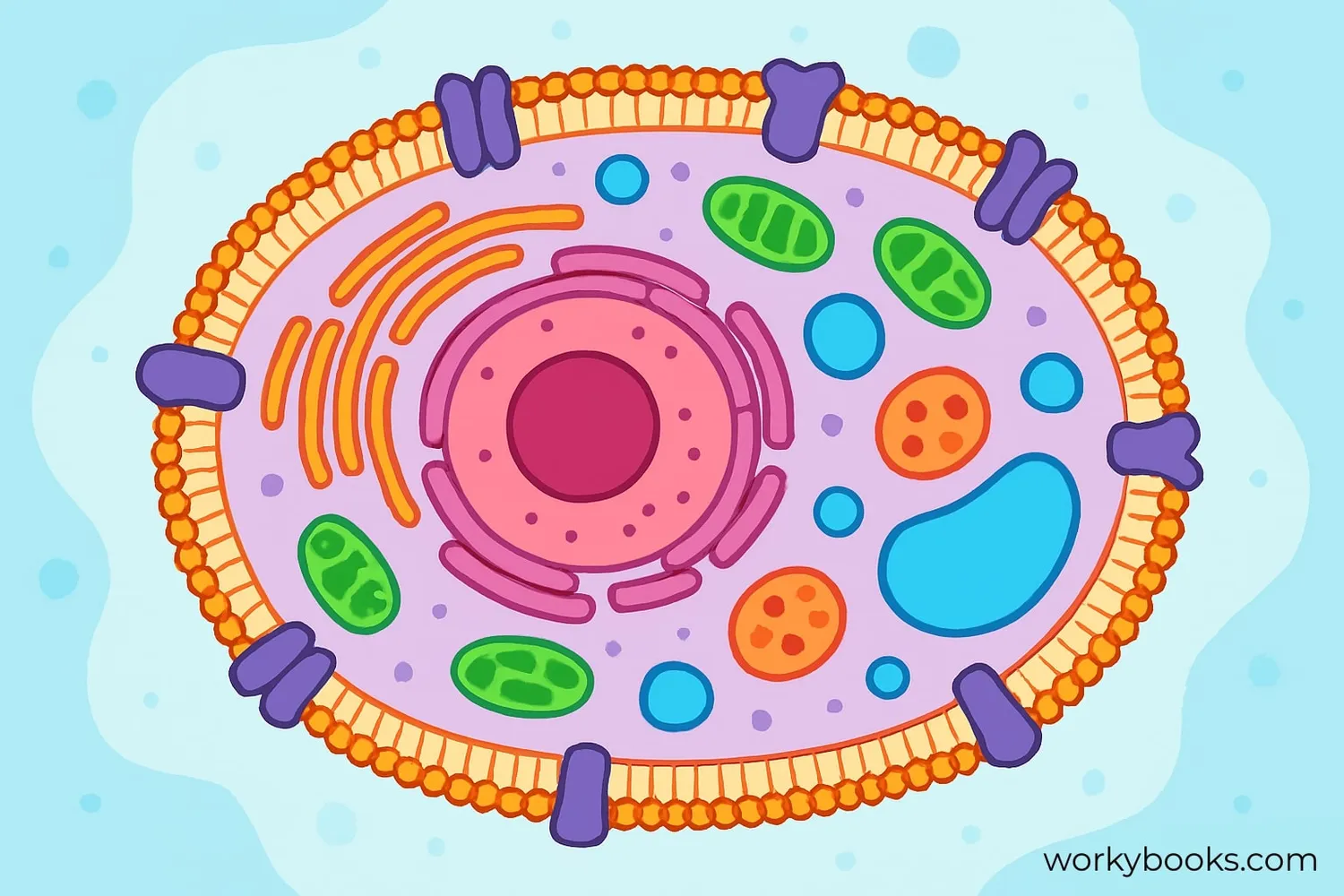
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is like a protective gatekeeper for every cell. It surrounds the cell and controls what enters and leaves, much like the walls and doors of a castle.
Think of it as the cell's security system! It decides which nutrients can come in, which waste products can go out, and keeps harmful things outside. Without a cell membrane, the cell would spill its contents and couldn't survive.
Cell Analogy
Imagine your school building. The walls and doors are like the cell membrane - they protect what's inside, control who comes in and out, and separate the inside from the outside world.
Structure of the Cell Membrane
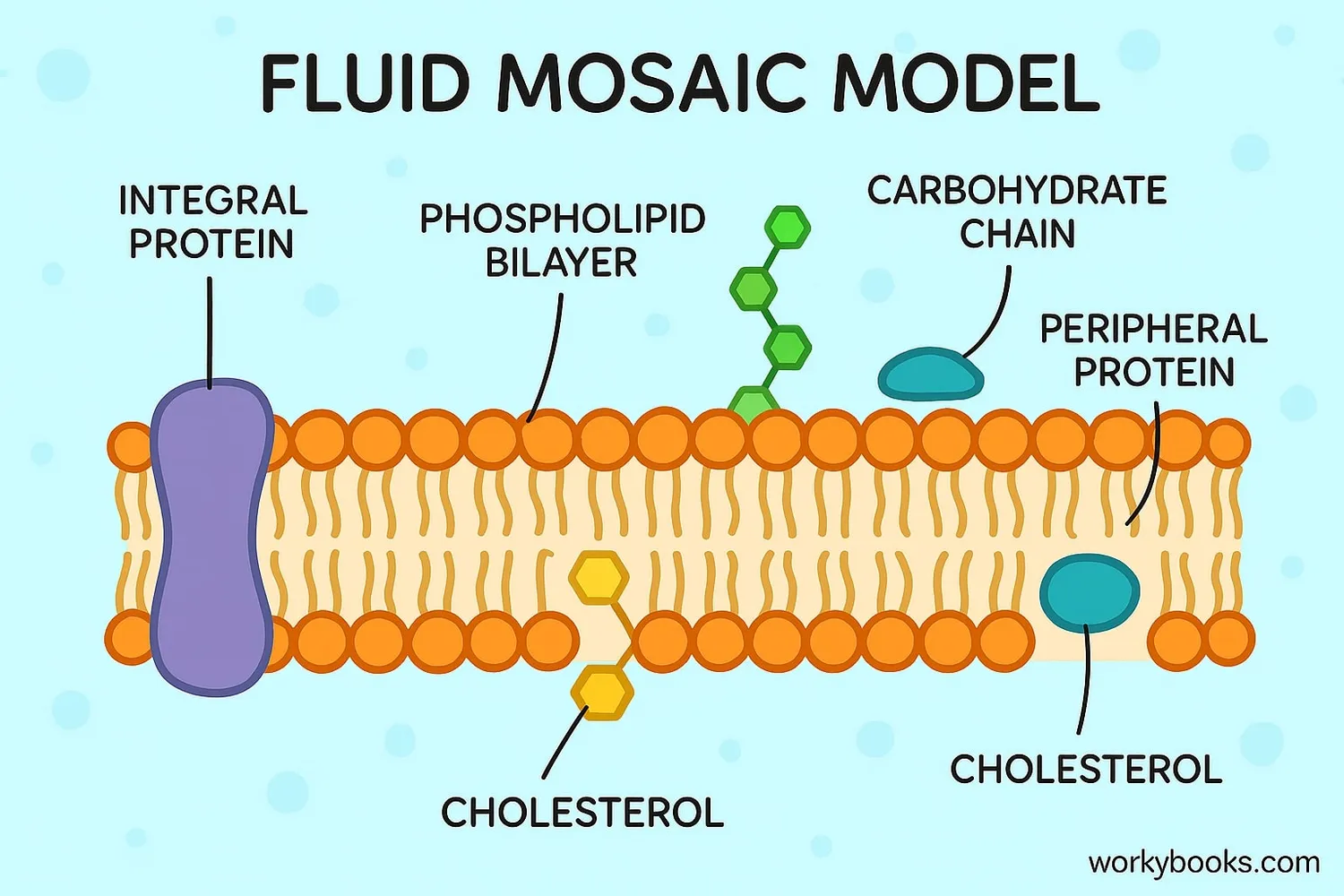
Scientists call the cell membrane structure the Fluid Mosaic Model. This fancy name describes how the membrane is made of many different parts that can move around freely, like boats floating on a lake.
Lipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipid molecules form the foundation
Proteins
Embedded proteins act as gates, channels and receptors
Cholesterol
Keeps the membrane flexible but stable
Carbohydrates
Act as identification tags for the cell
The lipid bilayer is made of molecules with a water-loving head and water-hating tail. They arrange themselves with heads facing the watery outside and inside of the cell, and tails facing each other in the middle.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
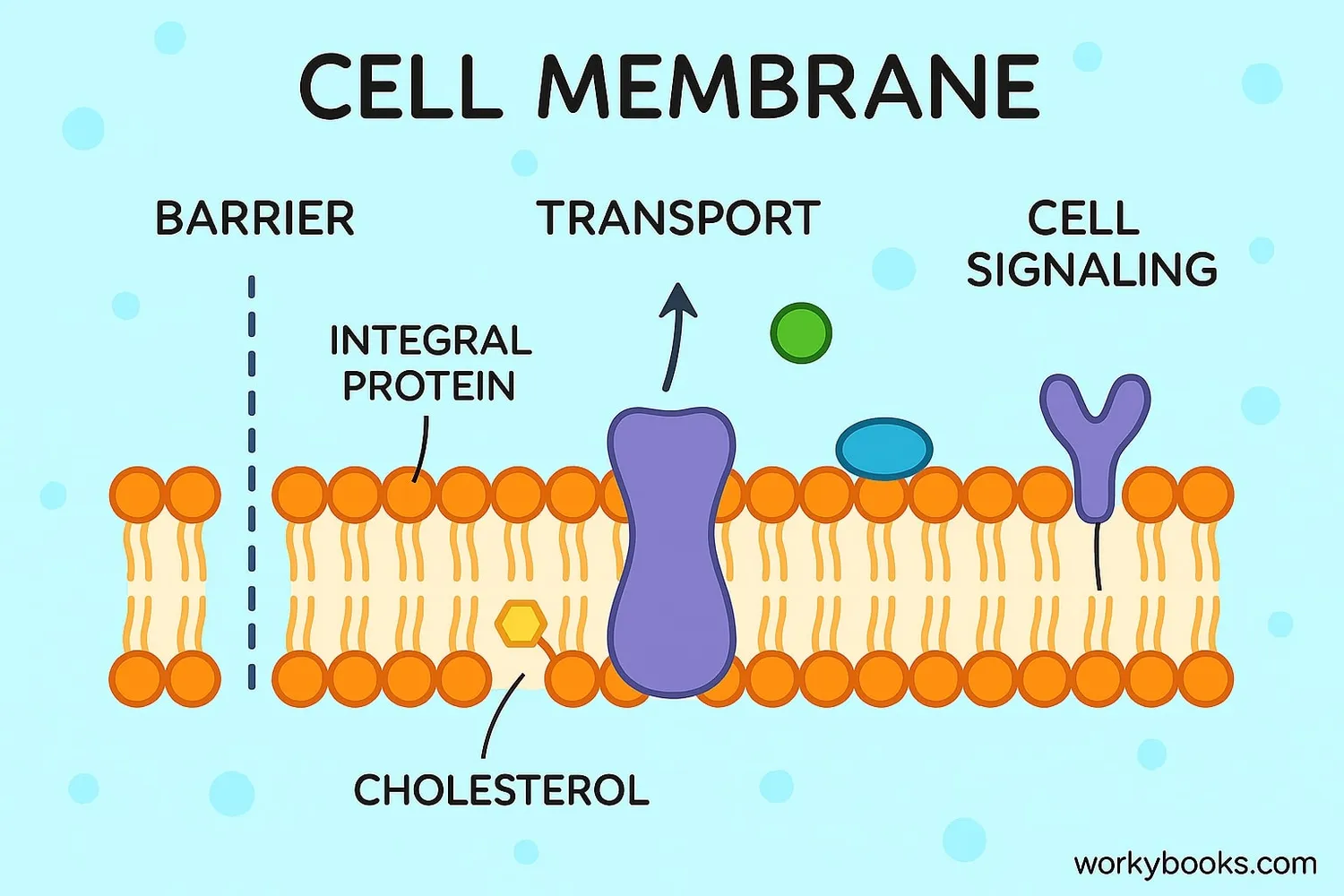
The cell membrane has several important jobs that keep the cell alive and functioning:
Protective Barrier
Separates the inside of the cell from the outside environment
Transport Control
Regulates what enters and exits the cell
Cell Communication
Receives signals from other cells and the environment
The membrane uses different methods to transport materials:
• Passive transport: Molecules move without energy (like diffusion)
• Active transport: Cells use energy to move molecules
• Endocytosis: Bringing large particles inside
• Exocytosis: Expelling large particles outside
Components of the Cell Membrane
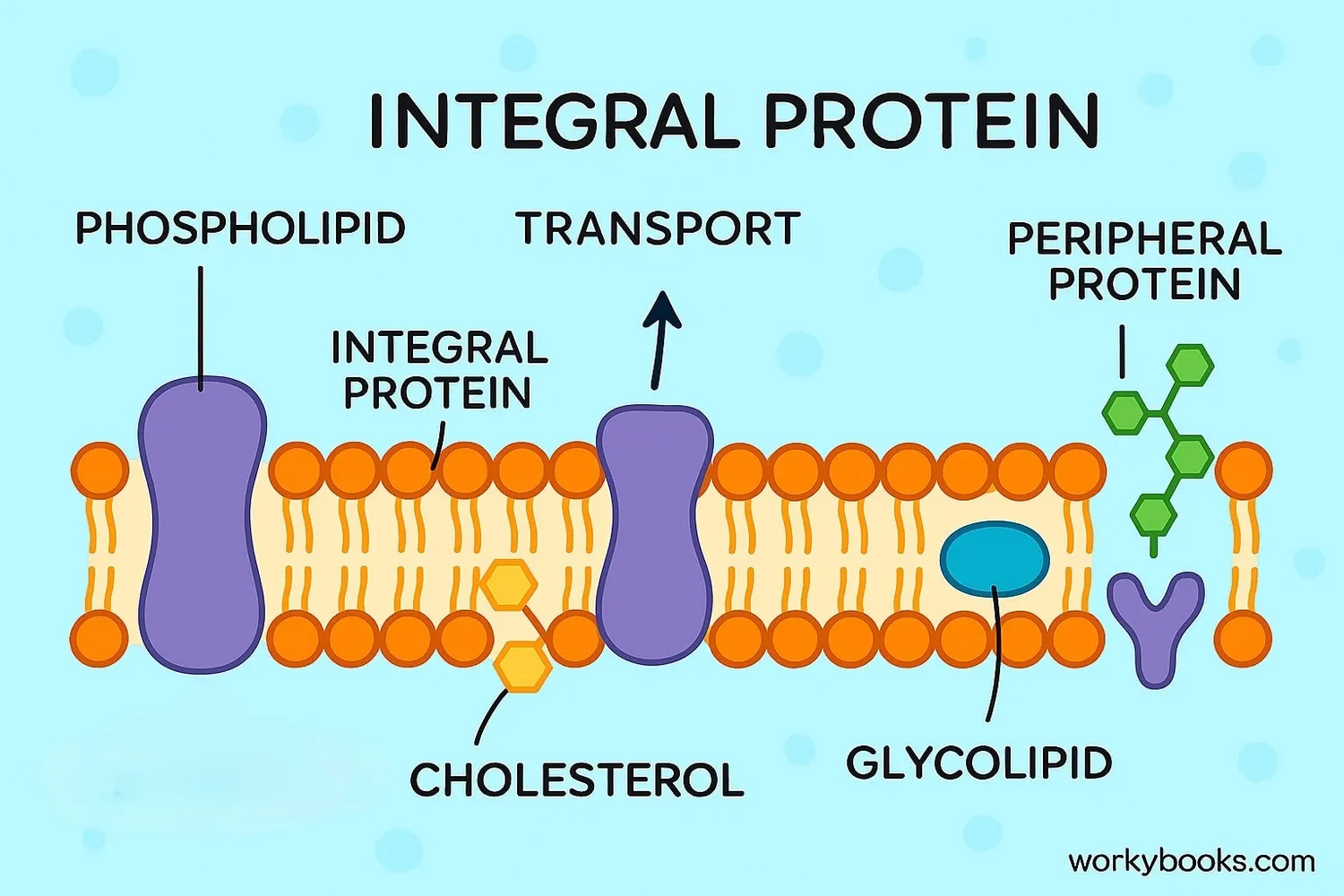
The cell membrane is made of several key components that work together:
Phospholipids
Form the double-layer foundation with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
Proteins
Transport molecules, act as receptors, and provide structural support
Cholesterol
Maintains membrane fluidity and stability
Carbohydrates
Help with cell recognition and communication
The specific arrangement and combination of these components give the membrane its unique properties of being both flexible and strong, selective yet permeable.
Cell Membrane Quiz
Test your knowledge about the cell membrane with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the cell membrane:
Fun Cell Membrane Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about cell membranes!
Huge Surface Area
If you spread out all the cell membranes in your body, they would cover an area of about 2,000 square meters - that's larger than half a basketball court!
Ancient Origins
Cell membranes first formed about 3.8 billion years ago, creating the first cells and making life on Earth possible!
Medical Importance
Many medicines work by interacting with proteins in cell membranes. Understanding membranes helps scientists develop better treatments for diseases.
Constant Renewal
Your body replaces the molecules in your cell membranes constantly. A typical phospholipid molecule only lasts about 2 weeks before being replaced!





