Diploid - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Understanding chromosome pairs in living things
What is Diploid?
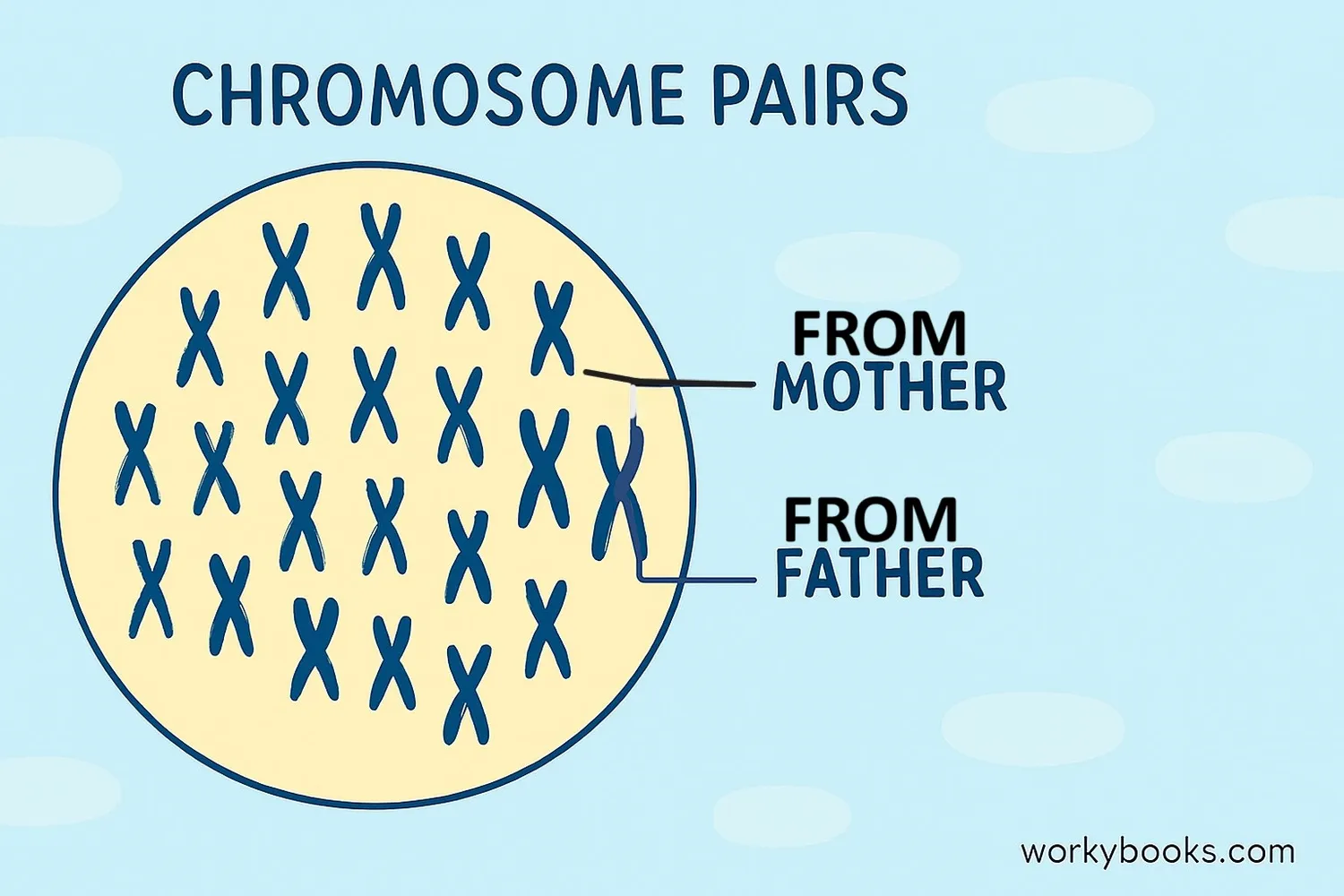
Diploid is a term used in biology to describe cells that have two complete sets of chromosomes. One set comes from the mother, and the other set comes from the father.
Think of chromosomes as instruction books that tell your body how to grow and work. In diploid organisms like humans, you get two copies of each instruction book - one from each parent. This is why you might have your mother's eyes and your father's smile!
In humans, diploid cells contain 46 chromosomes organized into 23 pairs. Each pair has one chromosome from the mother and one from the father.
Did You Know?
Almost all animals and many plants are diploid organisms. This means most of their cells contain paired chromosomes.
Diploid vs Haploid
While diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, haploid cells have only one set. Understanding the difference between these two types of cells is important in biology.
| Feature | Diploid Cells | Haploid Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Number of chromosome sets | Two sets (2n) | One set (n) |
| Number in humans | 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) | 23 chromosomes (no pairs) |
| Cell division process | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Examples | Skin cells, muscle cells, blood cells | Sperm cells, egg cells |
| Function | Growth, repair, and maintenance of the body | Sexual reproduction |
When diploid and haploid cells combine during fertilization, they create a new diploid cell with a complete set of paired chromosomes. This is how children inherit traits from both parents!
Diploid Cells in Our Bodies
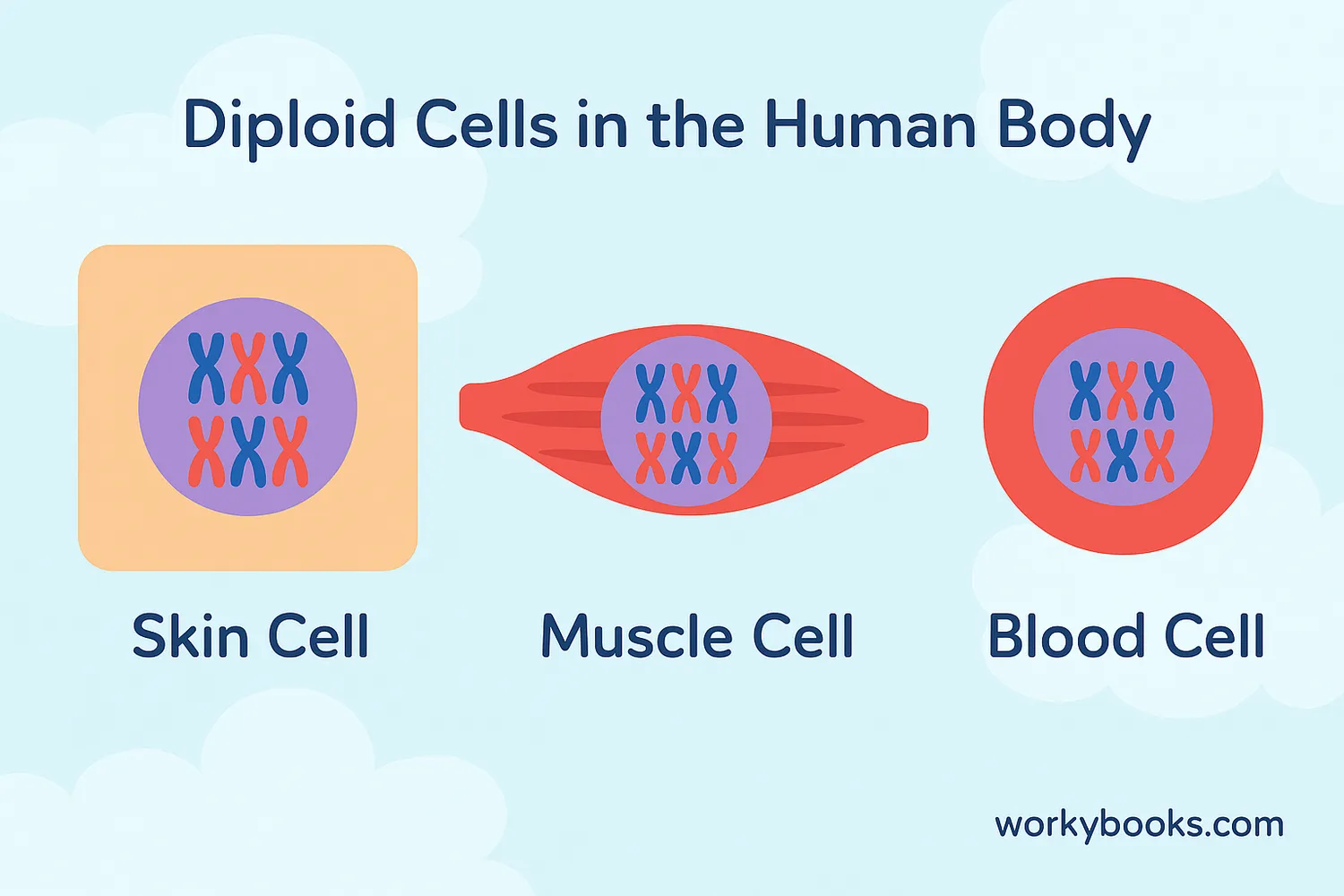
Most cells in your body are diploid cells. These cells work together to help you grow, heal, and stay healthy. Let's look at some examples:
Skin Cells
These diploid cells protect your body and help you feel touch
Muscle Cells
Diploid cells that help you move and pump blood
Blood Cells
Red and white blood cells are diploid (except red blood cells which lose their nucleus)
Diploid cells reproduce through a process called mitosis, where one cell divides to create two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.
This is different from haploid cells (like sperm and egg cells), which are created through meiosis and have only half the number of chromosomes.
Cell Fact!
The only human cells that are not diploid are gametes (sperm and egg cells), which are haploid.
Diploid Cells Quiz
Test your knowledge about diploid cells with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about diploid cells:
Interesting Diploid Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about diploid cells and chromosomes!
Chromosome Count
Humans have 46 chromosomes, but that's not the highest count! The adder's tongue fern has 1,260 chromosomes per cell - the most of any known organism!
Animal Variations
Different animals have different numbers of chromosomes. Dogs have 78, goldfish have 100, and kangaroos have 16 chromosomes in their diploid cells!
Discovery History
The term "diploid" was first used in 1905 by German scientist Eduard Strasburger. He was studying how chromosomes behave during cell division in plants.
Plant Life Cycles
Plants have both diploid and haploid generations. The diploid generation produces spores, which grow into haploid plants that then produce gametes.





