Mitochondrion: The Cell's Powerhouse - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how tiny organelles create energy for all living things
What is a Mitochondrion?
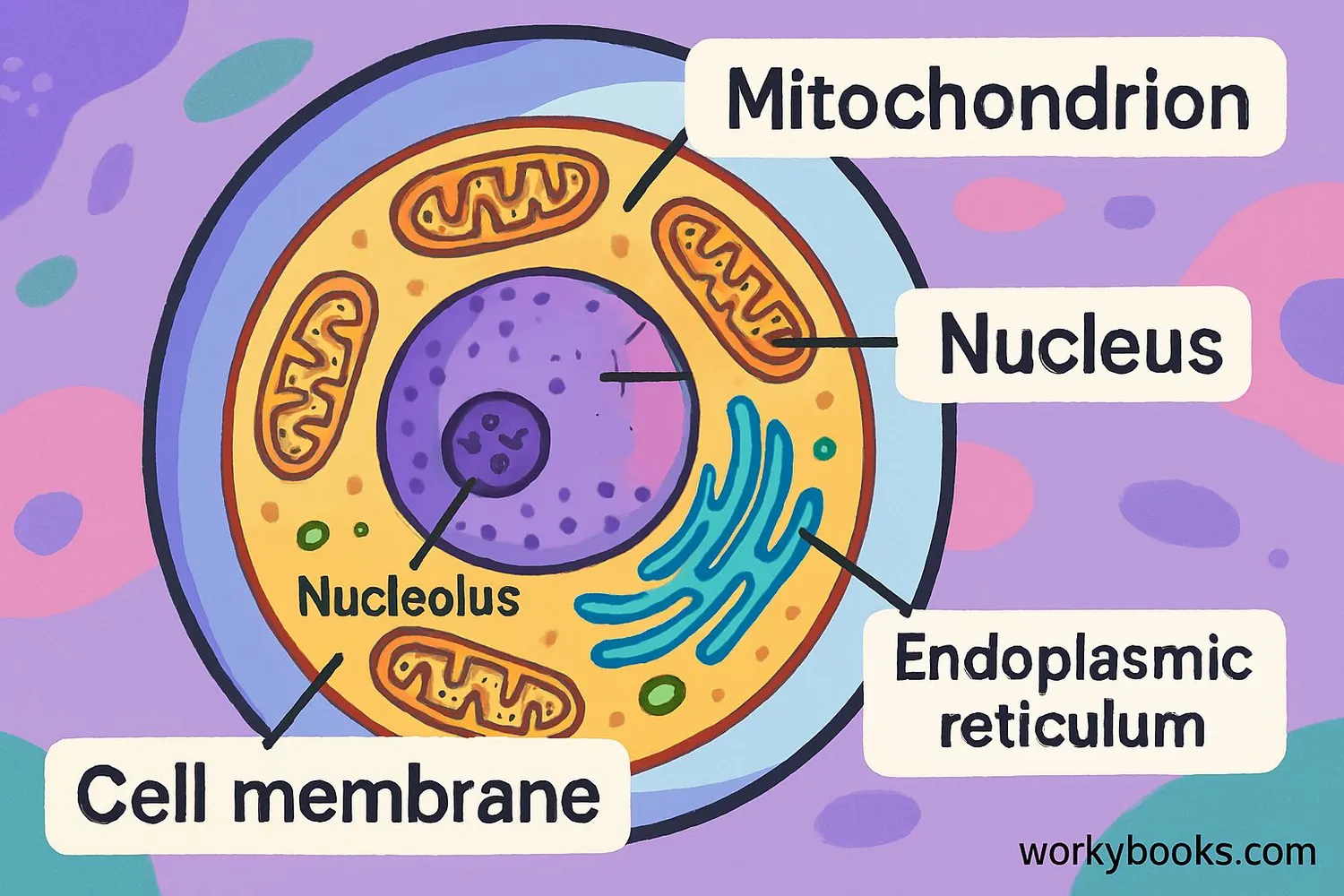
Mitochondria (pronounced my-toh-KON-dree-uh) are tiny but mighty structures inside your cells that act like power plants! Their main job is to create energy that your cells need to function.
Think of mitochondria as the cellular powerhouse - they take the food you eat and the oxygen you breathe and transform them into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency of the cell. Without mitochondria, your cells wouldn't have the energy to do anything!
Did You Know?
Mitochondria have their own DNA! This suggests they were once independent bacteria that moved into cells billions of years ago.
Mitochondrion Structure
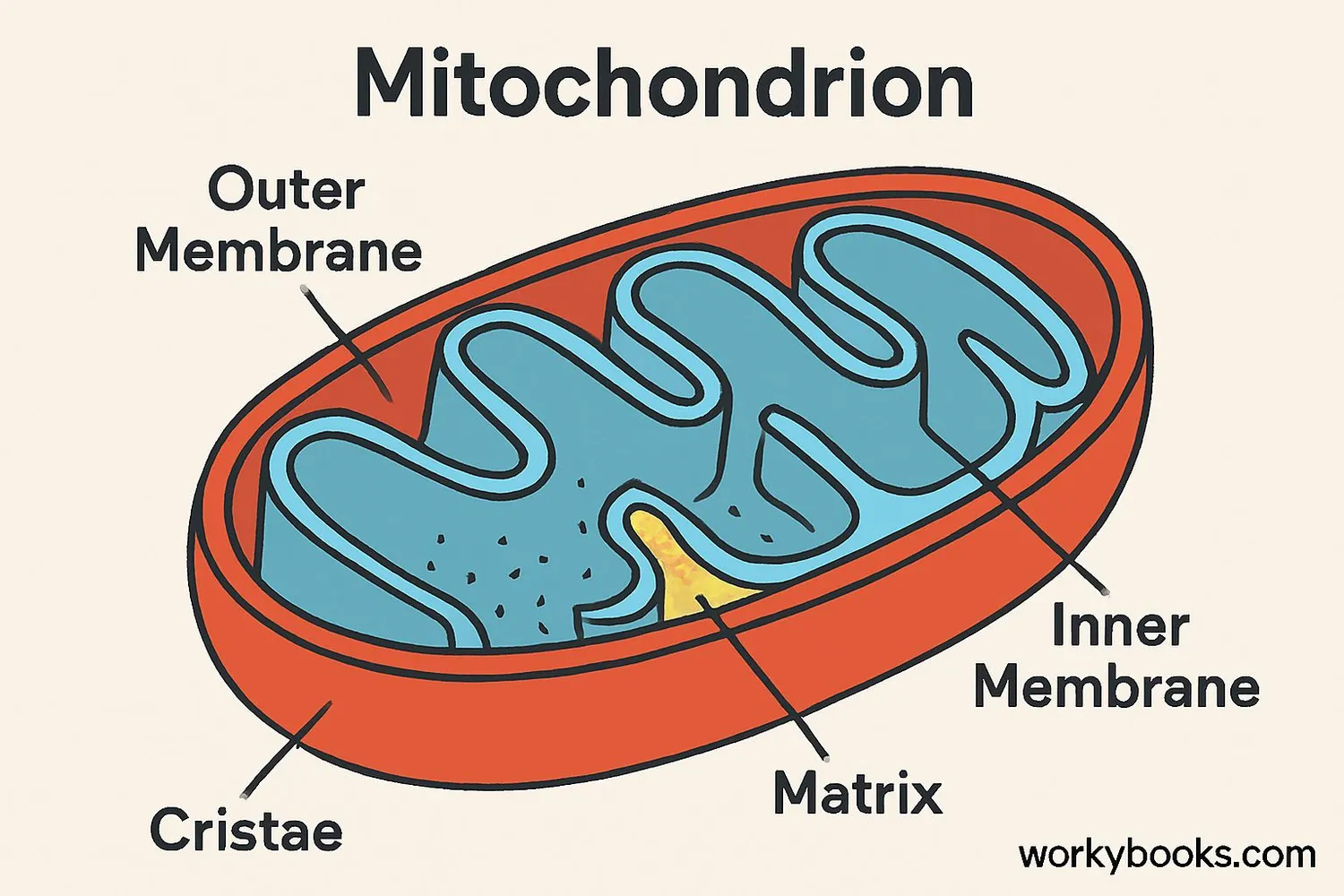
Mitochondria have a special structure that makes them perfect for energy production. Let's look at the key parts:
Outer Membrane
The protective outer layer that surrounds the mitochondrion
Inner Membrane
Folded into cristae to increase surface area for energy production
Cristae
Folds that provide space for chemical reactions
Matrix
Fluid-filled space inside where some reactions occur
Mitochondrial DNA
Genetic material separate from the cell's nucleus
The folded inner membrane (cristae) creates more space for the chemical reactions that produce ATP. This is similar to how crumpling a piece of paper gives you more writing surface in a small area!
Size Matters!
Mitochondria are tiny - about 0.5 to 1 micrometer long. You could fit 1,000 mitochondria across the width of a pencil tip!
Energy Production
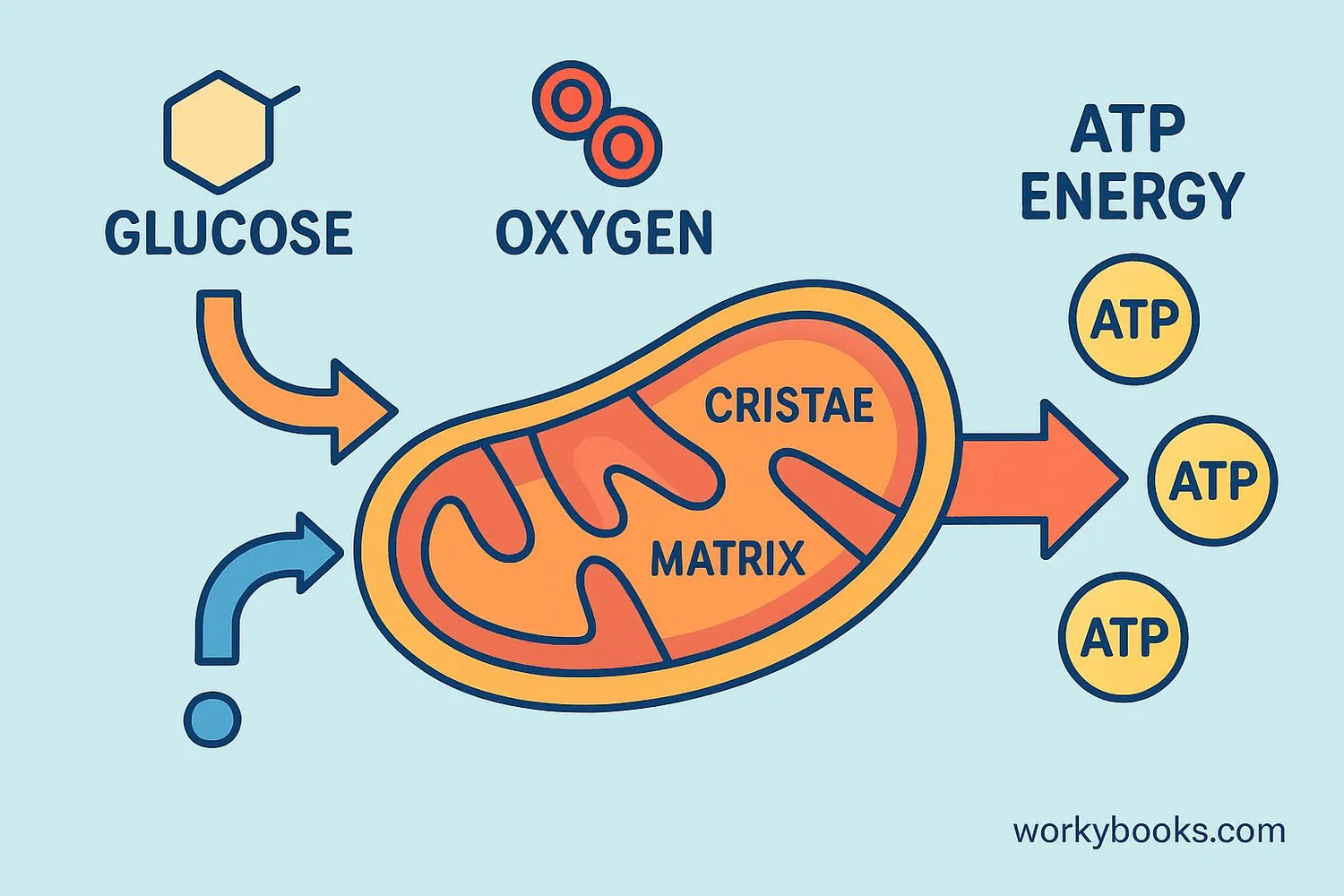
Mitochondria produce energy through a process called cellular respiration. This happens in three main stages:
1. Glycolysis
Glucose from food is broken down in the cell's cytoplasm
2. Krebs Cycle
Further breakdown in the mitochondrial matrix
3. Electron Transport
Energy production along the cristae membranes
The energy production process is called oxidative phosphorylation. Oxygen is essential for this process - that's why we need to breathe! The chemical reaction looks like this:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP)
Which means: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
ATP Production
One glucose molecule can produce up to 36 ATP molecules! Mitochondria in a typical cell produce about 10 million ATP molecules every second!
Health & Function
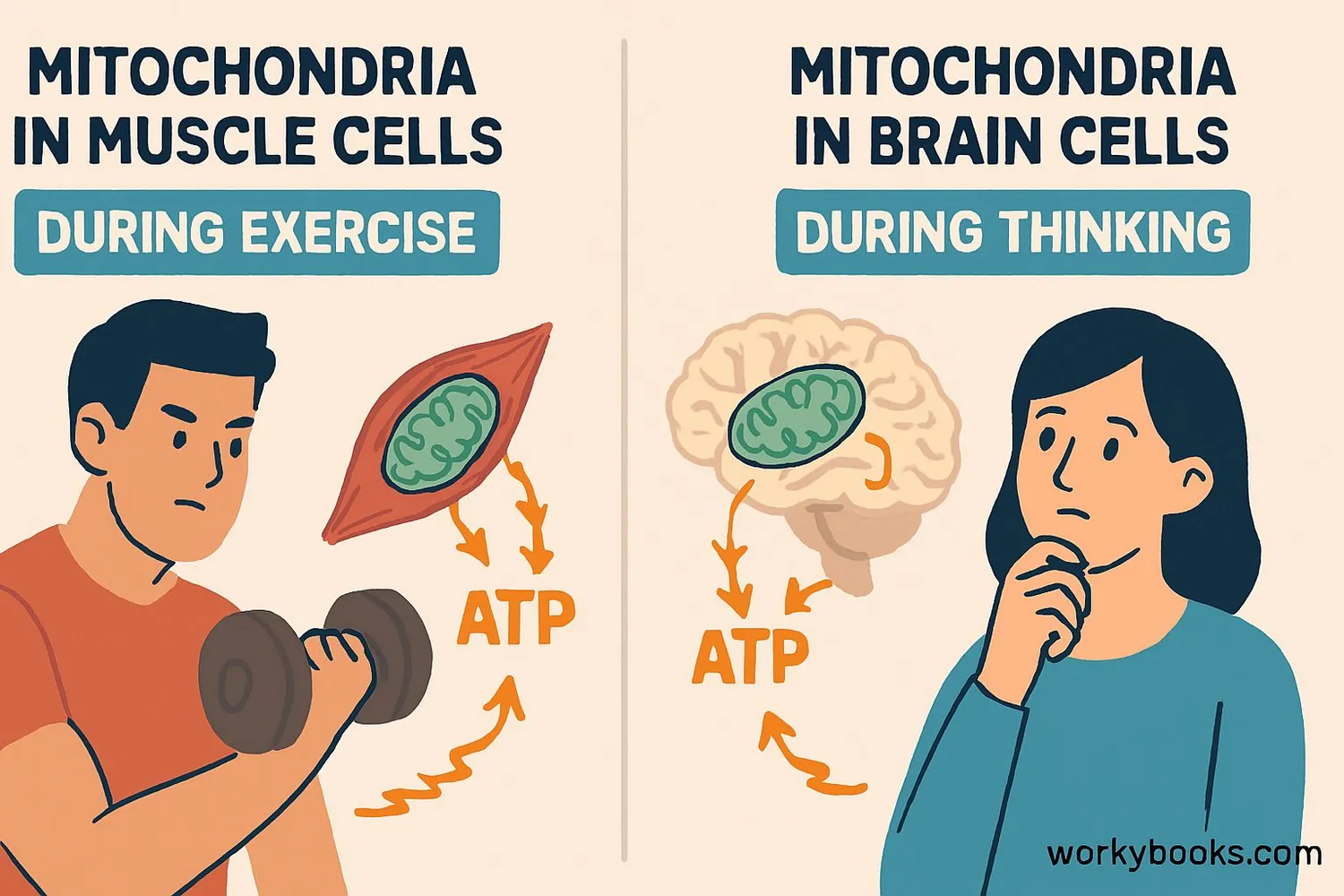
Mitochondria are crucial for our health and vitality. Here's why:
Muscle Power
Muscle cells have thousands of mitochondria to power movement
Brain Function
Neurons need constant energy for thinking and signaling
Body Heat
Mitochondria help generate warmth to maintain body temperature
When mitochondria don't work properly, it can lead to:
• Fatigue and muscle weakness
• Neurological problems
• Growth issues in children
• Various mitochondrial diseases
Keeping your mitochondria healthy involves regular exercise, a balanced diet, and good sleep!
Mitochondrion Knowledge Quiz
Test your knowledge with this 5-question quiz! Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about mitochondria:
Fascinating Mitochondrion Facts
Discover amazing facts about these cellular powerhouses:
Energy Production
A single cell can contain anywhere from a few hundred to over 2,000 mitochondria, depending on its energy needs!
Ancient Origins
Mitochondria were once free-living bacteria! About 1.5 billion years ago, they formed a partnership with larger cells in a process called endosymbiosis.
Unique DNA
Mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from your mother! This makes it useful for tracing maternal ancestry through genetic testing.
Size Variation
Mitochondria can change shape, move around the cell, and even fuse together or split apart depending on the cell's energy needs!





