The Notochord - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the important structure that supports developing animals
What is a Notochord?
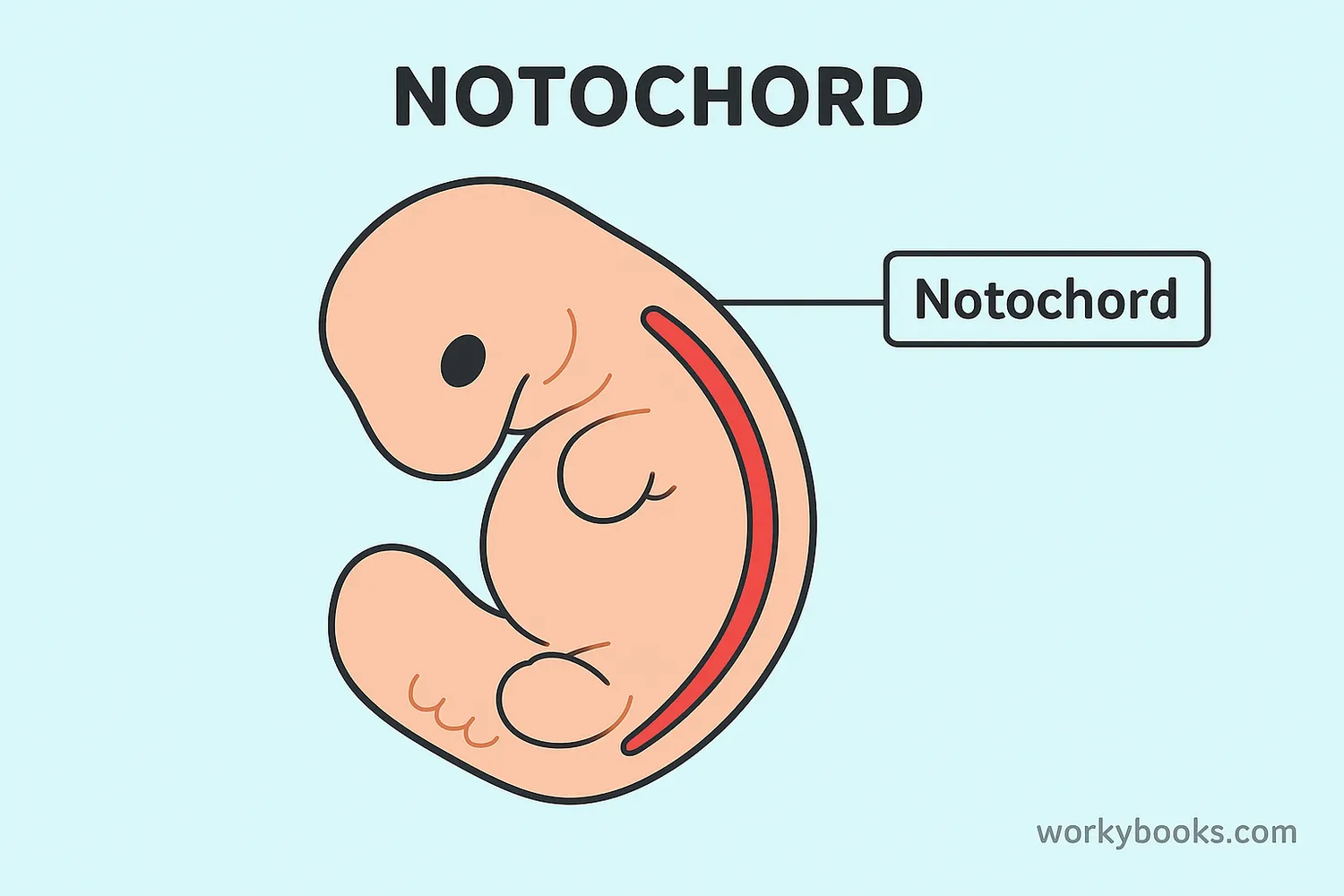
A notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped structure that forms in the early development of all chordate animals. This includes vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals (including humans)!
The notochord serves as the first "backbone" in developing embryos. It's made of special cells and is surrounded by a tough protective sheath. Think of it as nature's first attempt at creating a supportive structure for animals to grow around!
Did You Know?
The word "notochord" comes from Greek words meaning "back" and "string" or "cord" - literally a "back cord"!
Notochord Functions
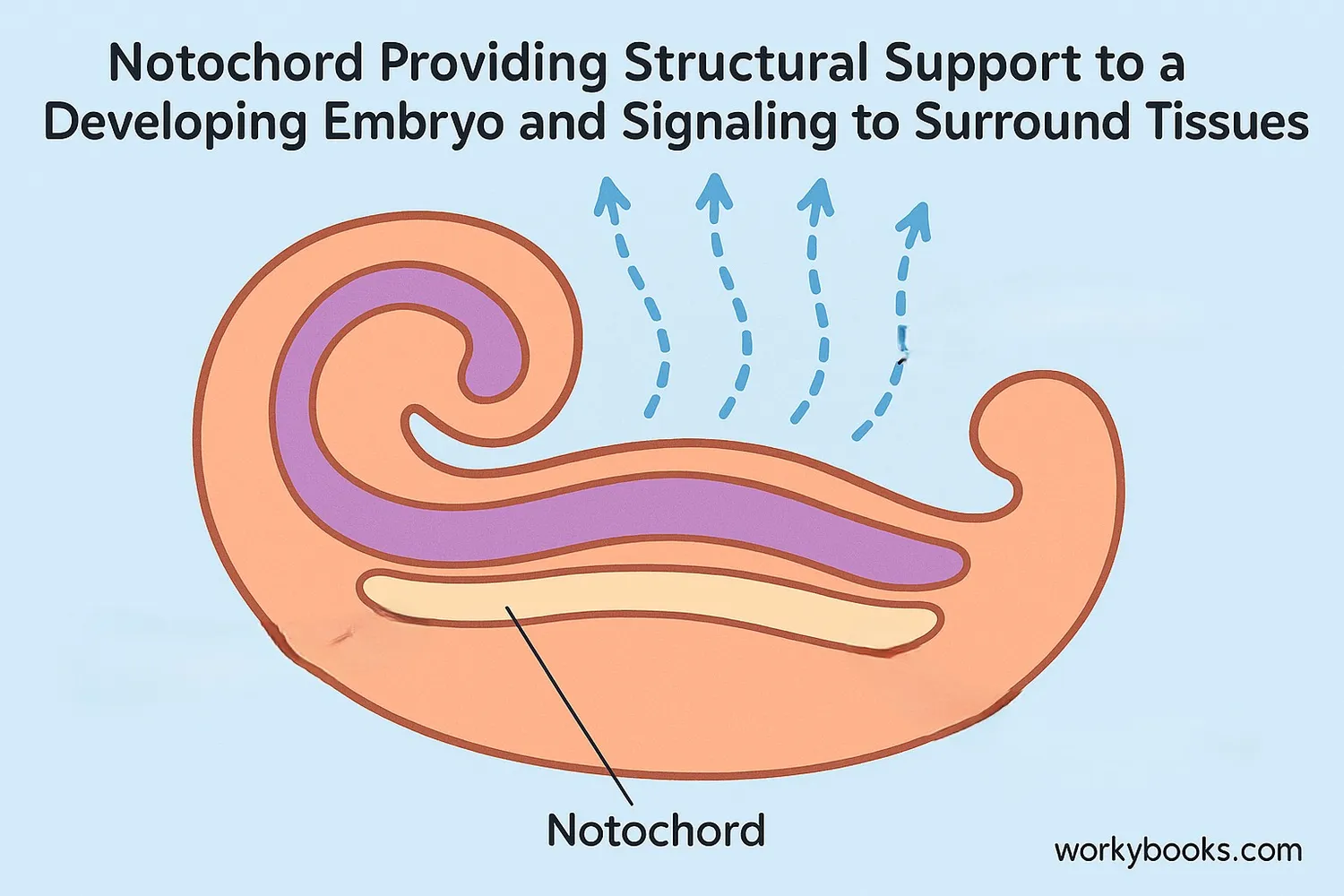
The notochord has several important jobs during animal development:
Structural Support
Provides the first skeletal support for the developing embryo
Development Guide
Helps establish the body plan and axis of the embryo
Signaling Center
Releases chemicals that guide development of nearby tissues
Neural Development
Induces formation of the neural tube which becomes the brain and spinal cord
The notochord is like a construction foreman at a building site - it doesn't just provide support itself, but also gives instructions to other developing tissues about how and where to form!
Notochord Development
The notochord forms very early in embryonic development through a process called gastrulation. Here's how it develops:
Formation
Special cells called chordamesoderm form the notochord
Elongation
The notochord elongates along what will become the back
Signaling
It signals nearby tissues to form the neural tube
Vertebra Formation
In vertebrates, it helps pattern the developing vertebrae
Transformation
In most vertebrates, it becomes part of the intervertebral discs
In humans and other vertebrates, most of the notochord disappears as the bony vertebrae form around it. But parts of it remain as the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs between our vertebrae!
Notochord vs. Nerve Cord
While the notochord is a supportive structure, the nerve cord (which becomes the spinal cord) is part of the nervous system. The notochord actually helps induce formation of the nerve cord!
Notochord in Vertebrates
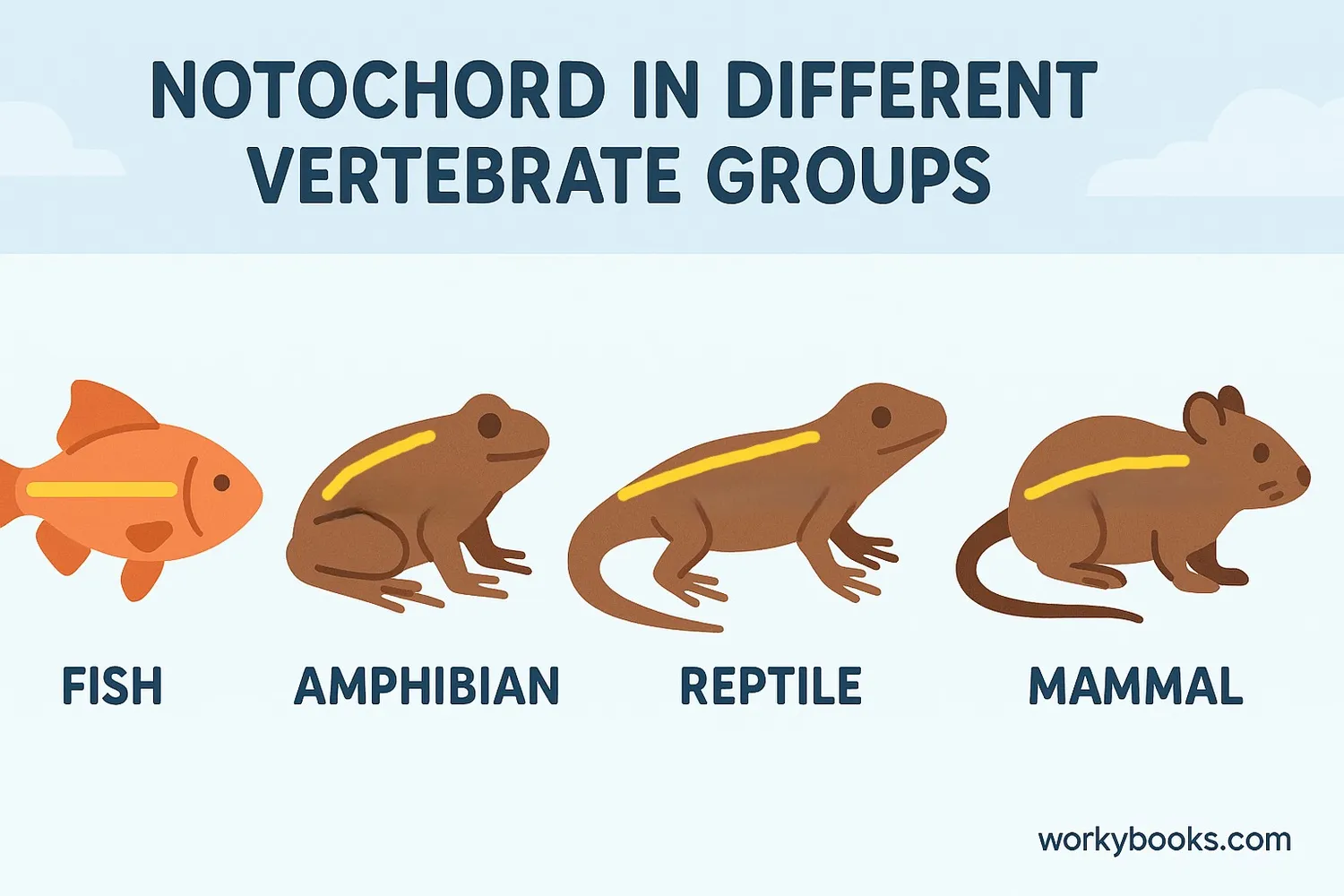
The notochord plays different roles in various vertebrate groups:
Fish
Some fish retain a functional notochord into adulthood
Amphibians
The notochord is largely replaced by vertebrae
Birds & Mammals
The notochord becomes part of intervertebral discs
In some primitive fish like lampreys and hagfish, the notochord remains as the main supportive structure throughout life. In more advanced vertebrates, it's mostly replaced by bony vertebrae during development, but remnants persist in our spines as the soft, gel-like centers of discs between vertebrae.
These remnants are important for flexibility and shock absorption in our spines. When people have a "slipped disc," it's actually the notochord-derived material that has bulged out!
Notochord Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of the notochord with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the notochord:
Interesting Notochord Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about the notochord!
Evolutionary Importance
The notochord is a defining feature of chordates, the animal group that includes vertebrates. It represents a major evolutionary advancement in animal body plans.
Medical Significance
Rare tumors called chordomas can develop from notochord remnants, usually at the base of the skull or bottom of the spine. These affect only about 1 in a million people each year.
Research Model
Scientists study simple animals like lancelets that keep their notochord into adulthood to understand how more complex vertebrates develop.
Ancient Structure
The notochord has been around for over 500 million years! Fossil evidence shows that early chordates like Pikaia from the Cambrian period had a notochord.





