Phylogeny - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how scientists map the evolutionary relationships between living things
What is Phylogeny?
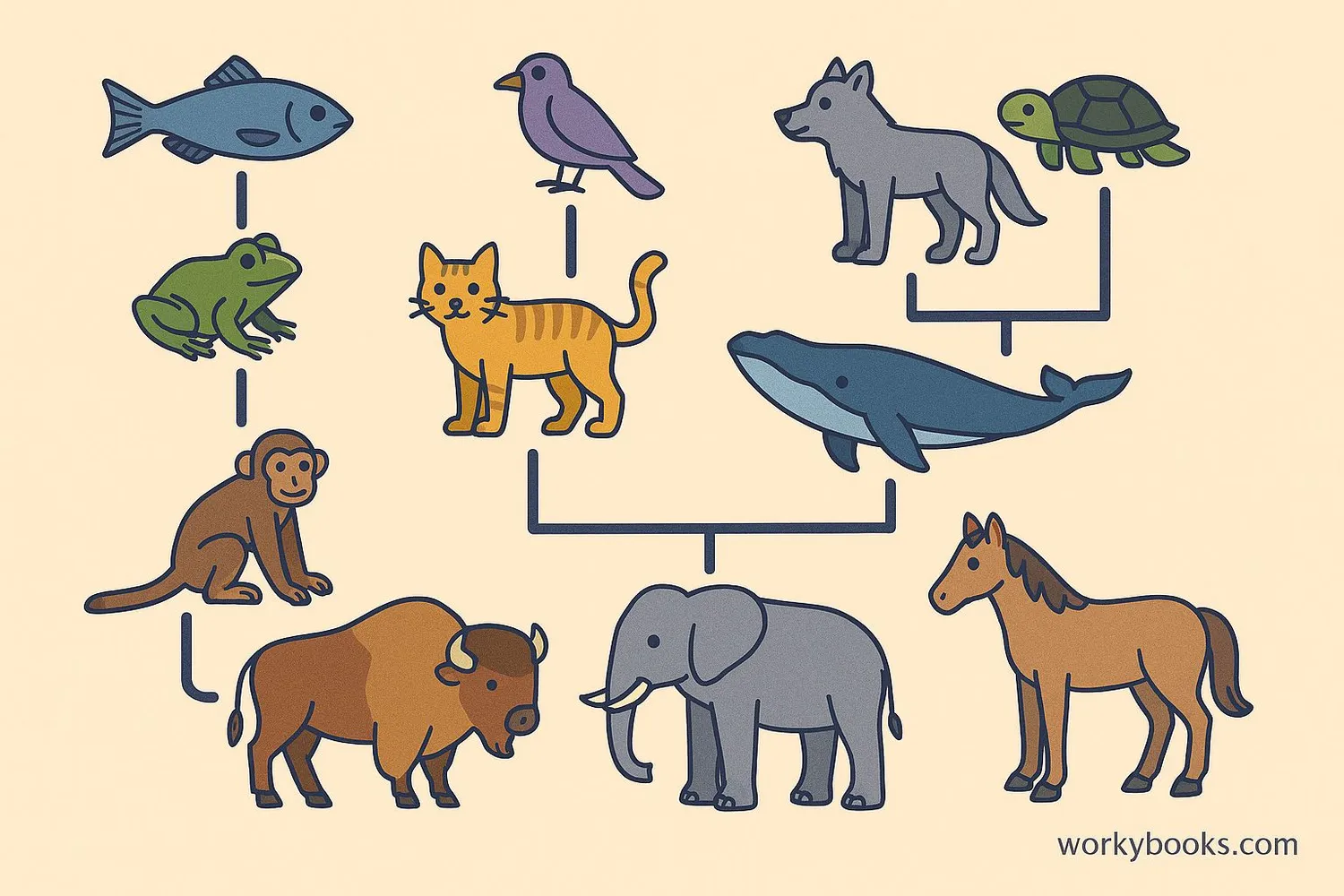
Phylogeny is the study of how different living things are related through evolution. It's like a family tree for species! Scientists use phylogeny to understand how organisms evolved from common ancestors over millions of years.
The word "phylogeny" comes from Greek words meaning "tribe" or "race" and "origin." Phylogeny helps scientists organize living things based on their evolutionary history rather than just how they look.
Definition
Phylogeny: The evolutionary history and relationships among species or groups of species.
Phylogenetic Trees
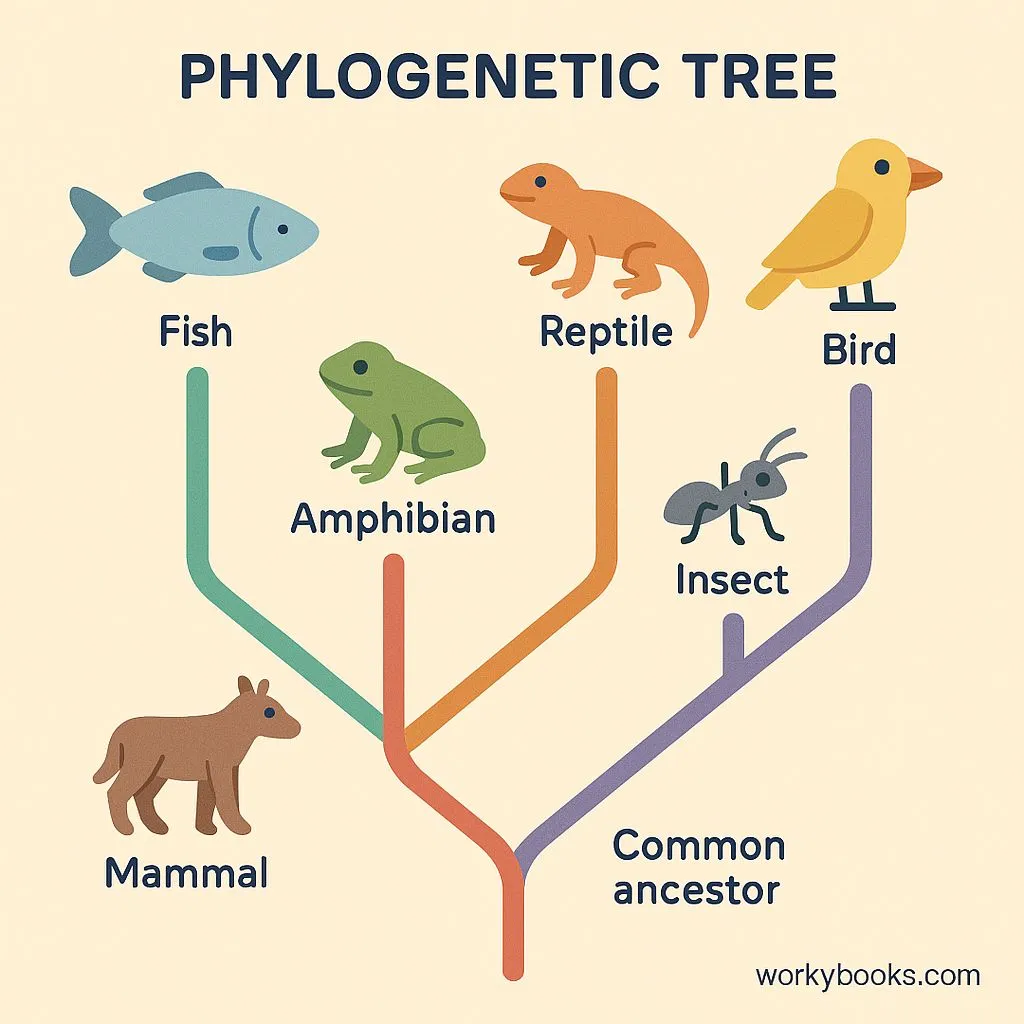
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships between different species. It looks like a tree with branches, where each branch point represents a common ancestor.
The main parts of a phylogenetic tree include:
Branches
Represent lineages evolving through time
Nodes
Points where branches split, representing common ancestors
Tips
End points representing living species or groups
Root
The common ancestor of all organisms in the tree
Phylogenetic trees help scientists understand how traits evolved and which species are most closely related. The closer two species are on the tree, the more recently they shared a common ancestor.
Molecular Phylogeny
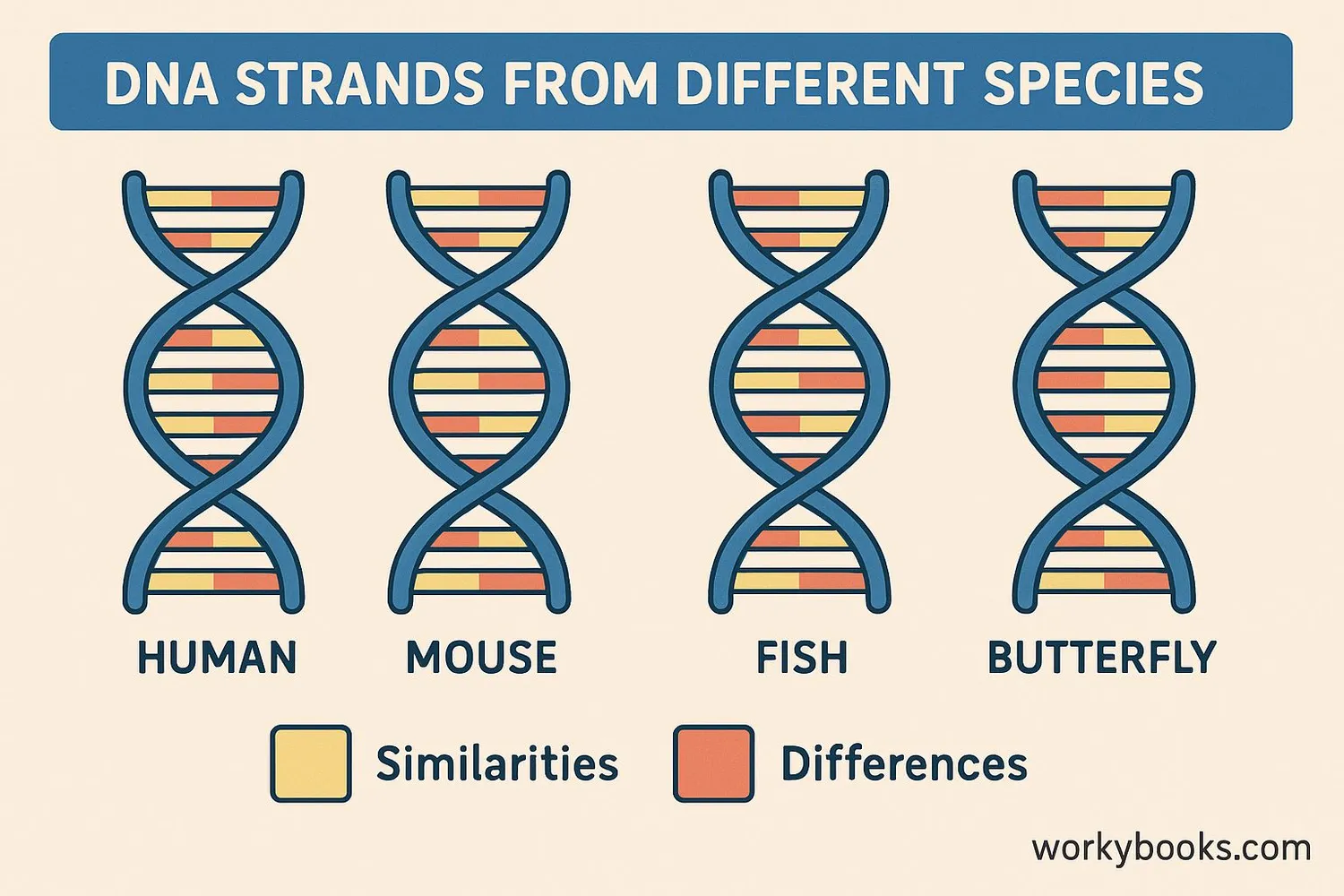
Molecular phylogeny uses DNA and protein sequences to study evolutionary relationships. By comparing genetic material from different organisms, scientists can determine how closely related they are.
Organisms with more similar DNA sequences are more closely related. Molecular phylogeny has revolutionized our understanding of evolutionary relationships because it provides objective data that isn't always obvious from physical appearance alone.
DNA Evidence
Humans share about 98.8% of our DNA with chimpanzees, showing we are closely related primates!
Human Phylogeny
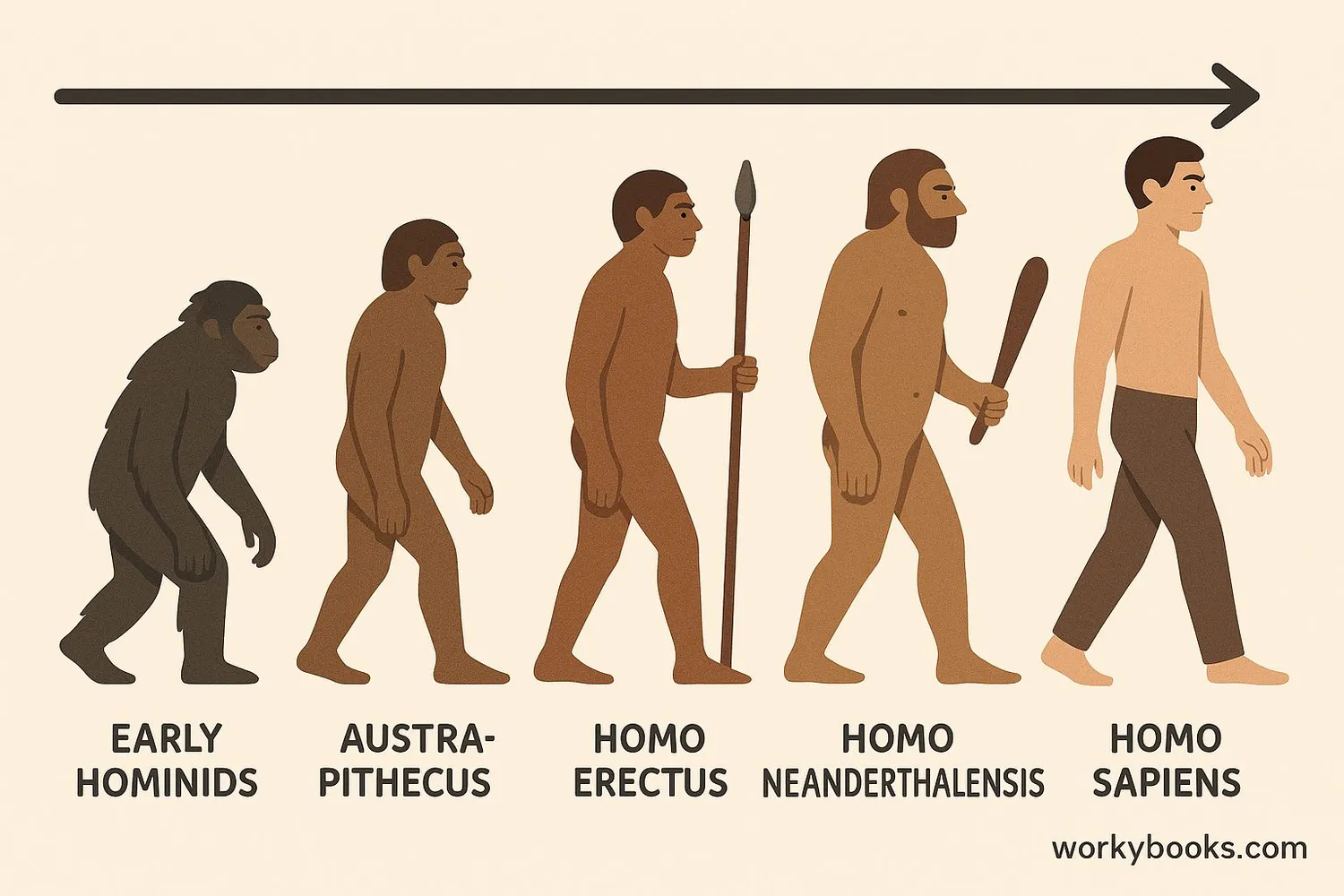
Human phylogeny studies our evolutionary history and relationships with other primates. Scientists have discovered that humans share a common ancestor with other great apes like chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans.
Key discoveries in human phylogeny include:
Fossil Evidence
Fossils show how early hominids walked upright and had developing brains
Genetic Studies
DNA analysis reveals our close relationship to other primates
Migration Patterns
Tracking how early humans migrated out of Africa to populate the world
Modern humans (Homo sapiens) appeared about 300,000 years ago in Africa. We are the only surviving species of the genus Homo, but we coexisted with other human species like Neanderthals until about 40,000 years ago.
Phylogeny Quiz
Test your knowledge about phylogeny with this quiz. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about phylogeny:
Interesting Phylogeny Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about phylogeny and evolutionary relationships:
Unexpected Relatives
Whales and hippos are closely related! DNA evidence shows that whales evolved from hoofed mammals, and their closest living relatives are hippopotamuses.
Shared DNA
Humans share about 60% of their DNA with bananas! This doesn't mean we're half banana, but that all living things share common genetic machinery from ancient ancestors.
Tree of Life
The phylogenetic "Tree of Life" includes all known organisms. The deepest split is between bacteria and archaea, with eukaryotes (including plants and animals) branching off later.
Molecular Clocks
Scientists use "molecular clocks" based on mutation rates in DNA to estimate when species diverged from common ancestors. This helps date evolutionary events.





