Sympathetic Nervous System - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn how your body's emergency response system works
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System?
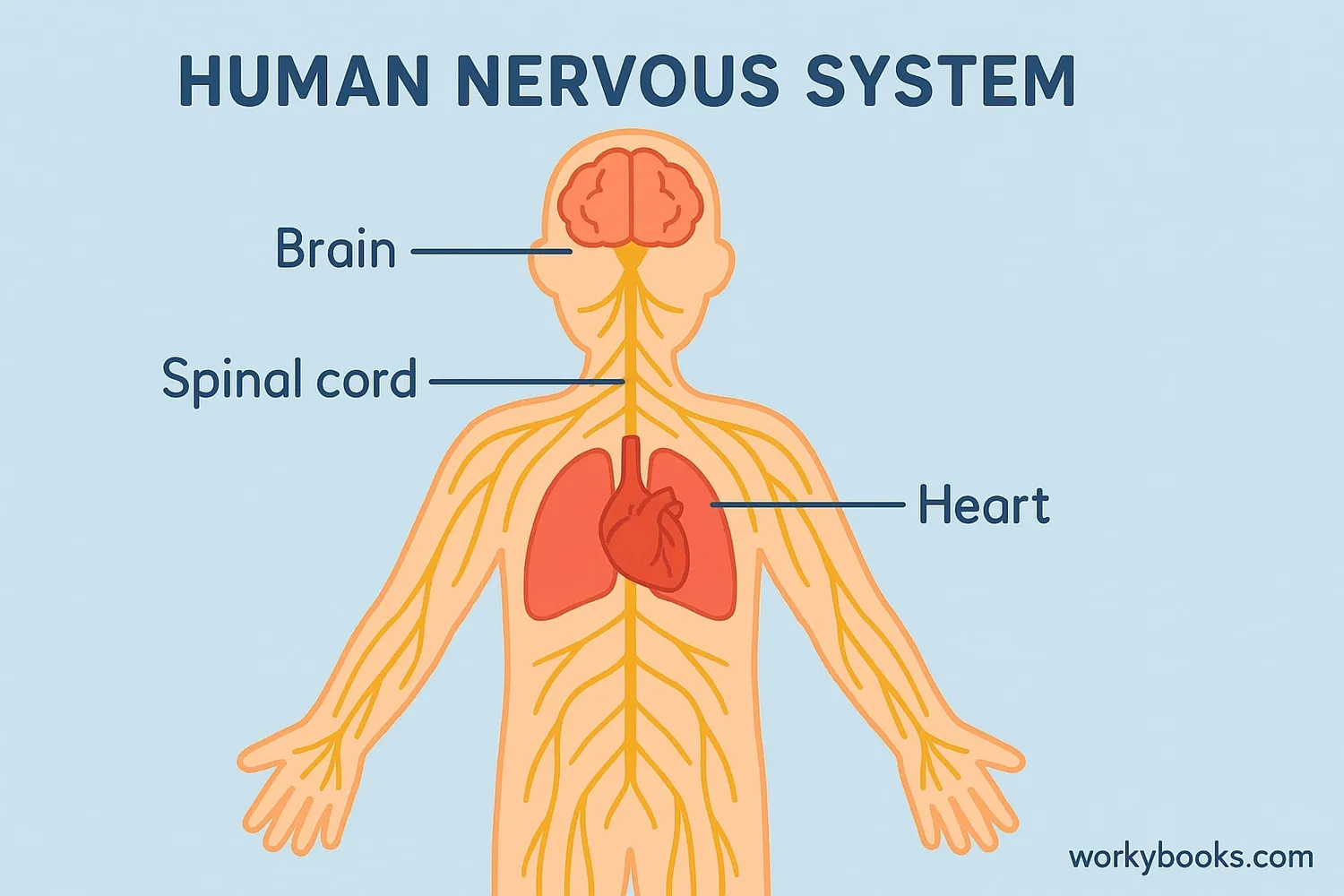
The sympathetic nervous system is part of your body's autonomic nervous system that works automatically without you thinking about it. It's often called your body's "emergency response system" because it prepares your body to handle dangerous or stressful situations.
Think of it like your body's personal alarm system! When you face something scary or exciting, this system activates to help you respond quickly. It controls many automatic functions like your heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
Did You Know?
The sympathetic nervous system is just one part of your autonomic nervous system. The other part is called the parasympathetic nervous system, which helps your body relax after the danger has passed.
How the Sympathetic Nervous System Works
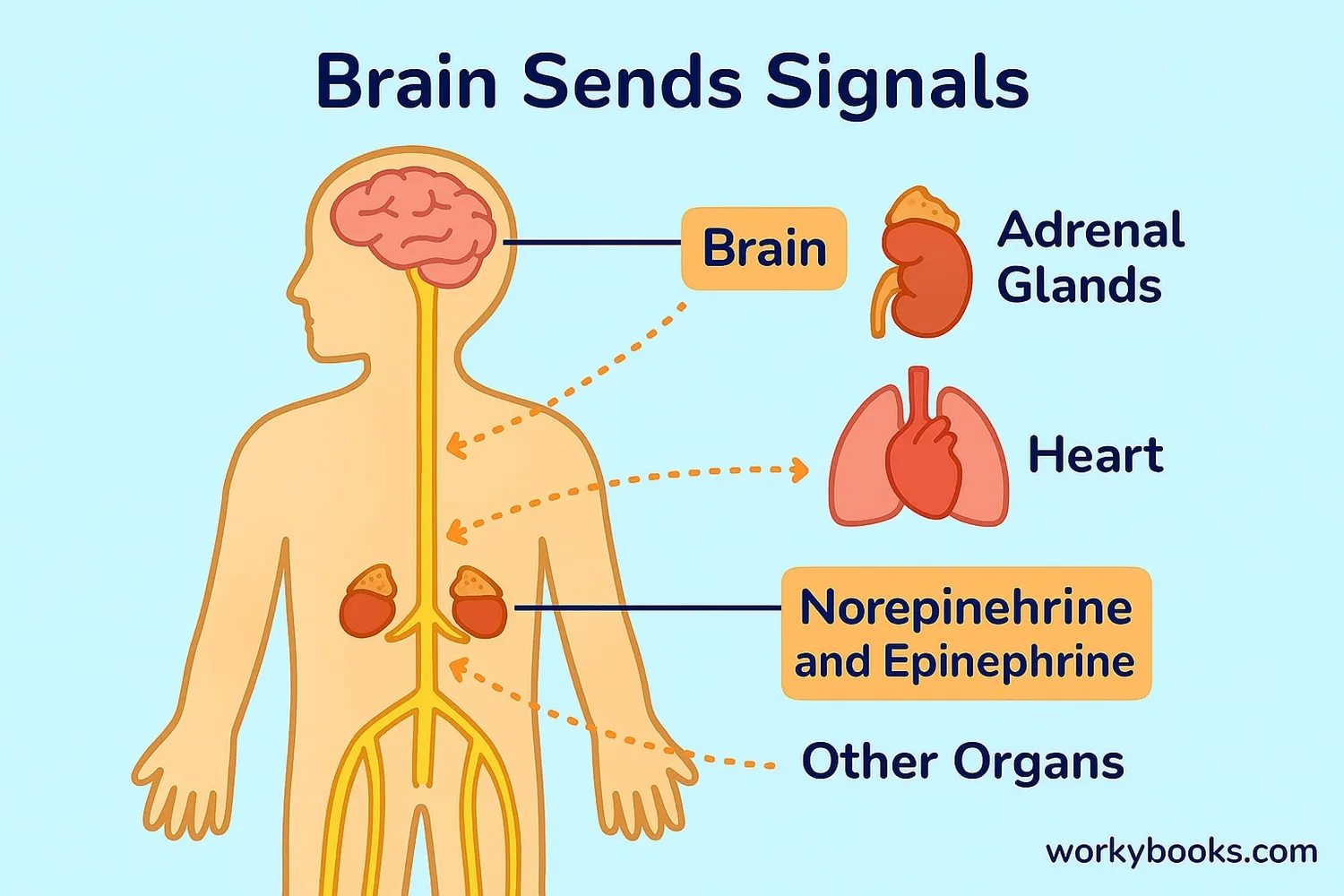
When your brain detects a threat or stress, it sends signals through your spinal cord to nerves throughout your body. These nerves release chemical messengers called neurotransmitters like norepinephrine that prepare your body for action.
The sympathetic nervous system also signals your adrenal glands to release hormones like epinephrine (also called adrenaline) into your bloodstream. These hormones travel throughout your body, creating widespread effects that prepare you to face challenges.
Brain Detection
Your brain perceives a threat or stressful situation
Signal Transmission
Nerves carry signals from brain to body organs
Neurotransmitter Release
Nerves release norepinephrine at organ sites
Hormone Production
Adrenal glands release epinephrine (adrenaline)
Body Response
Organs throughout body prepare for action
Chemical Messengers
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are chemically similar but work in different ways. Norepinephrine works locally at nerve endings, while epinephrine travels through blood to affect the whole body.
The Fight or Flight Response

The fight or flight response is your body's reaction to perceived danger, controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. It gets you ready to either face the threat ("fight") or run away from it ("flight").
This response causes many physical changes that help you survive dangerous situations. These changes happen automatically and very quickly—often within seconds!
Faster Heartbeat
Heart pumps more blood to deliver oxygen to muscles
Faster Breathing
Lungs take in more oxygen for energy production
Pupil Dilation
Eyes let in more light to see better in dim conditions
Reduced Digestion
Blood flow shifts from digestion to muscles
Energy Release
Liver releases stored sugar for quick energy
These physical changes helped our ancestors survive real physical threats like predators. Today, this same system activates for modern stresses like tests, public speaking, or near-misses in traffic.
Why the Sympathetic Nervous System is Important
The sympathetic nervous system is essential for survival and optimal functioning. While we often focus on its role in emergencies, it also has important everyday functions:
Protection
Prepares body to respond to immediate physical danger
Performance
Enhances physical and mental performance under pressure
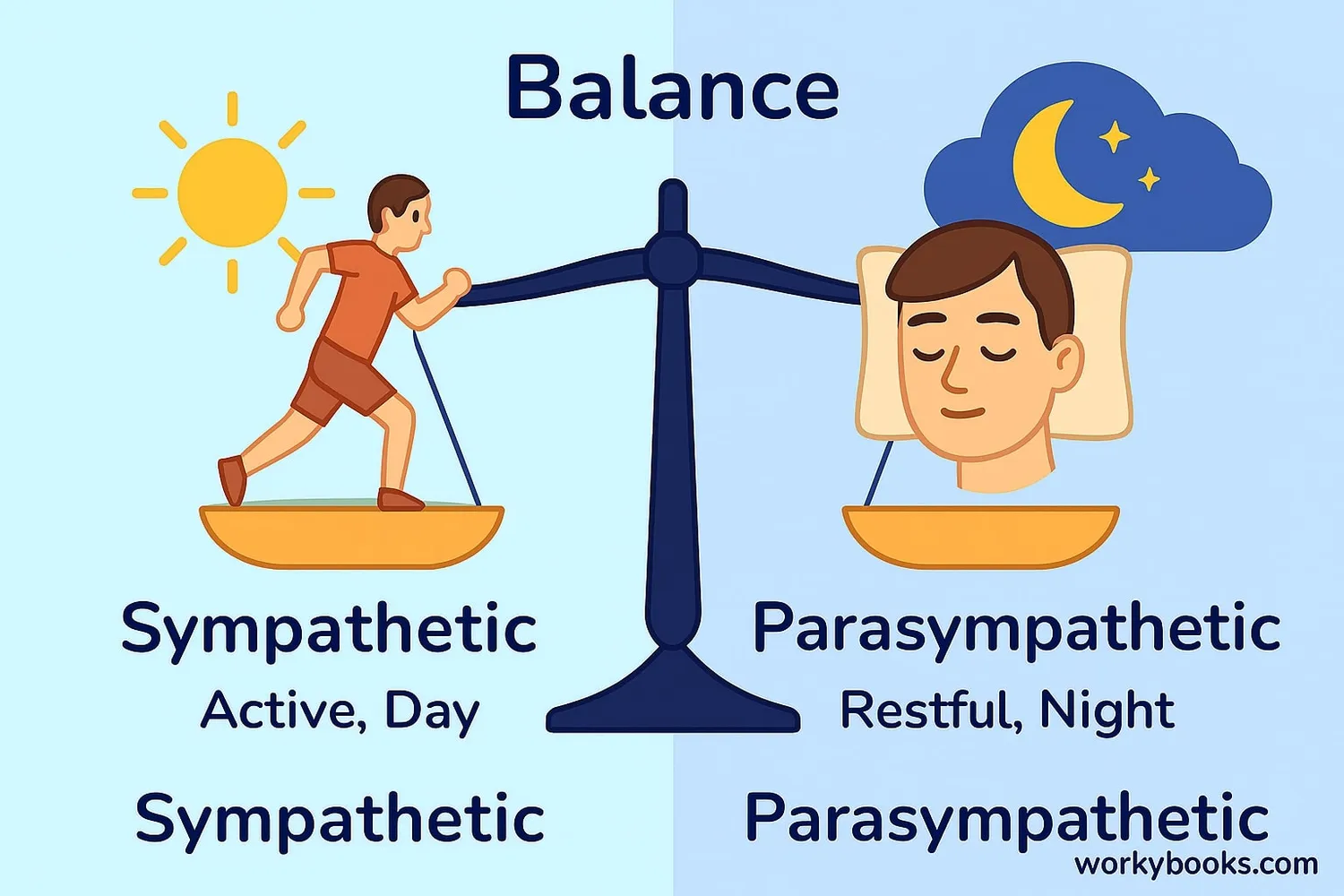
Balance
Works with parasympathetic system to maintain equilibrium
A healthy sympathetic nervous system helps with:
• Quick reactions to avoid danger
• Enhanced focus during important tasks
• Temporary boosts in strength and speed
• Readiness for physical challenges
The key is balance. While the sympathetic system prepares us for action, the parasympathetic nervous system helps us rest and recover. Both systems working together keep our bodies functioning properly.
Modern Life Consideration
In today's world, our sympathetic nervous system can activate too often for non-life-threatening stresses. Learning relaxation techniques helps maintain a healthy balance between active and rest states.
Sympathetic Nervous System Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz about the sympathetic nervous system. Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about the sympathetic nervous system:
Interesting Facts
Discover some fascinating facts about the sympathetic nervous system:
Ancient Survival System
The fight or flight response evolved over millions of years to help our ancestors survive physical threats like predators. This same system activates for modern stresses like tests or public speaking.
Adrenaline Power
During extreme stress, adrenaline can increase strength and pain tolerance dramatically. There are accounts of people performing incredible feats of strength in emergencies due to adrenaline surges.
Animal Responses
Different animals have variations of the fight or flight response. Some animals like opossums "play dead" (freeze response), while others like gazelles rely extremely on the flight response to escape predators.
Medical Importance
Doctors sometimes use medications that block sympathetic nervous system activity to treat conditions like high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and anxiety disorders.




