Celsius to Fahrenheit (°C to °F) - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature measurements with easy explanations and practice activities
What is Temperature Conversion?
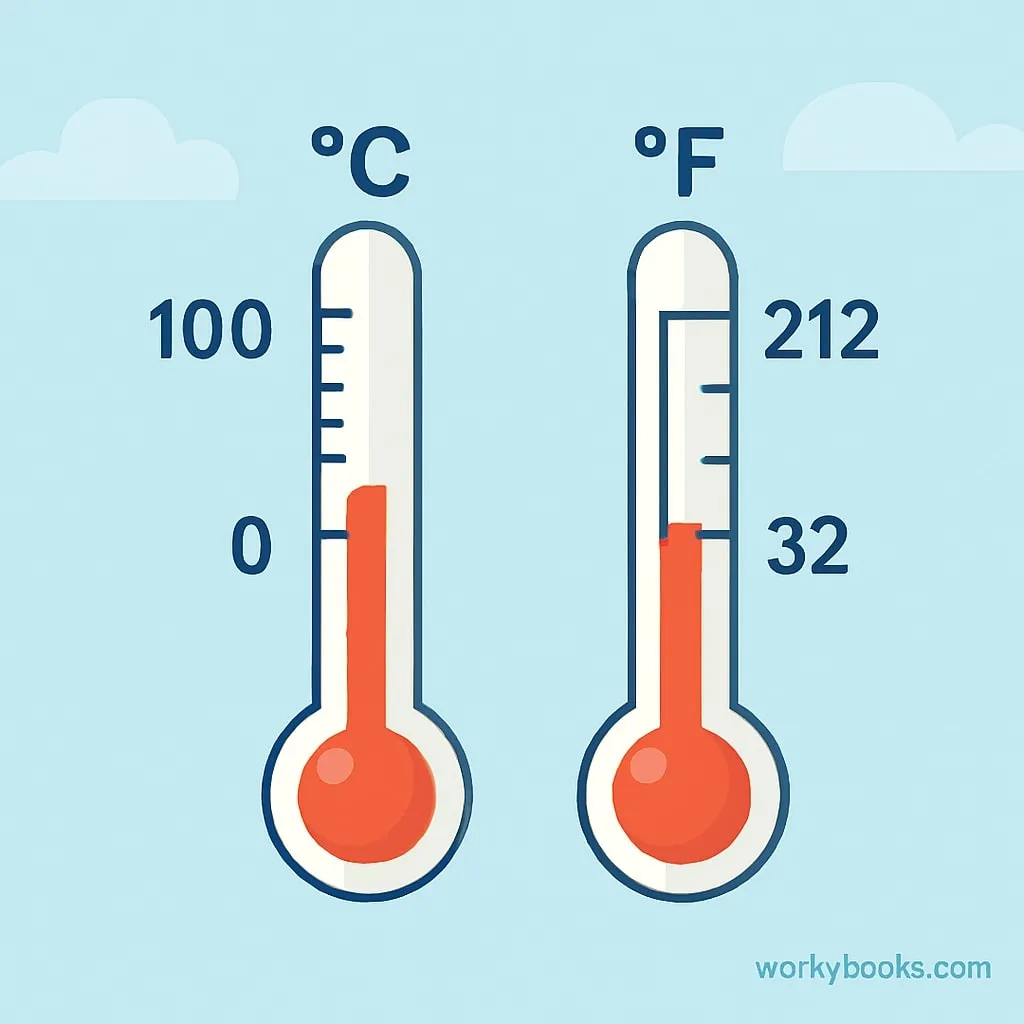
Temperature conversion means changing a temperature measurement from one scale to another. In this lesson, we're learning how to convert between Celsius (used in most countries) and Fahrenheit (used primarily in the United States).
Why do we need to convert? Different countries use different temperature scales. Scientists use Celsius for consistency, while weather forecasts in the US use Fahrenheit. Understanding both helps us communicate globally.
Celsius (°C)
- Water freezes at 0°C
- Water boils at 100°C
- Used in science worldwide
- Standard in most countries
Fahrenheit (°F)
- Water freezes at 32°F
- Water boils at 212°F
- Used primarily in the US
- Common in weather reports
Key Concept
Temperature scales have different starting points and different sized degrees. This is why we need conversion formulas.
How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
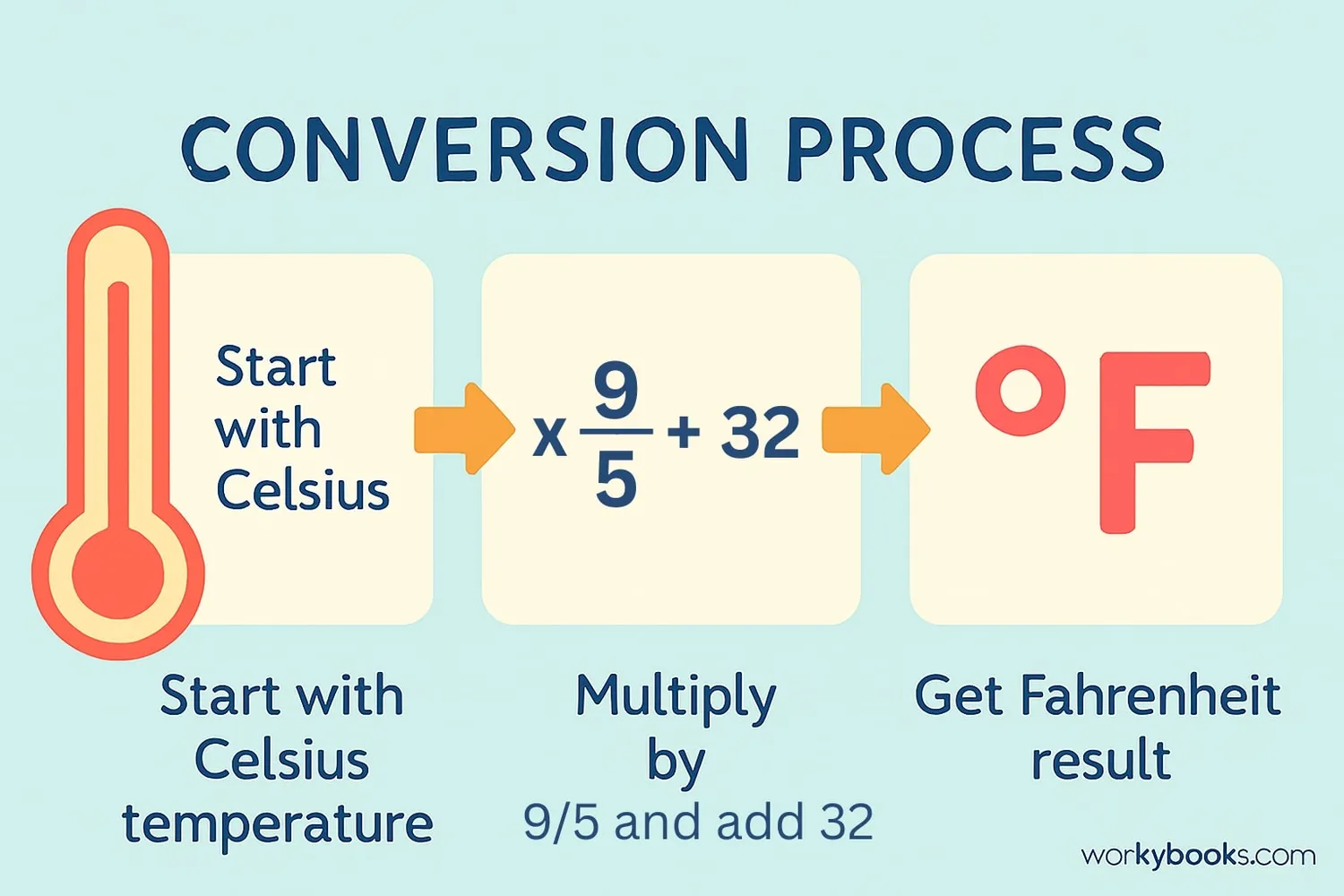
Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is simple with this formula:
Conversion Formula
To convert any Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit, multiply by 9/5 (or 1.8) and then add 32.
Example: Convert 20°C to Fahrenheit
Step 1: Multiply by 9/5 → 20 × 9/5 = 36
Step 2: Add 32 → 36 + 32 = 68
Step 3: Result → 68°F
So 20°C equals 68°F. You can remember that room temperature is about 20°C or 68°F.
Remember
Fahrenheit degrees are smaller than Celsius degrees. That's why the same temperature has a higher number in Fahrenheit.
Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion Charts
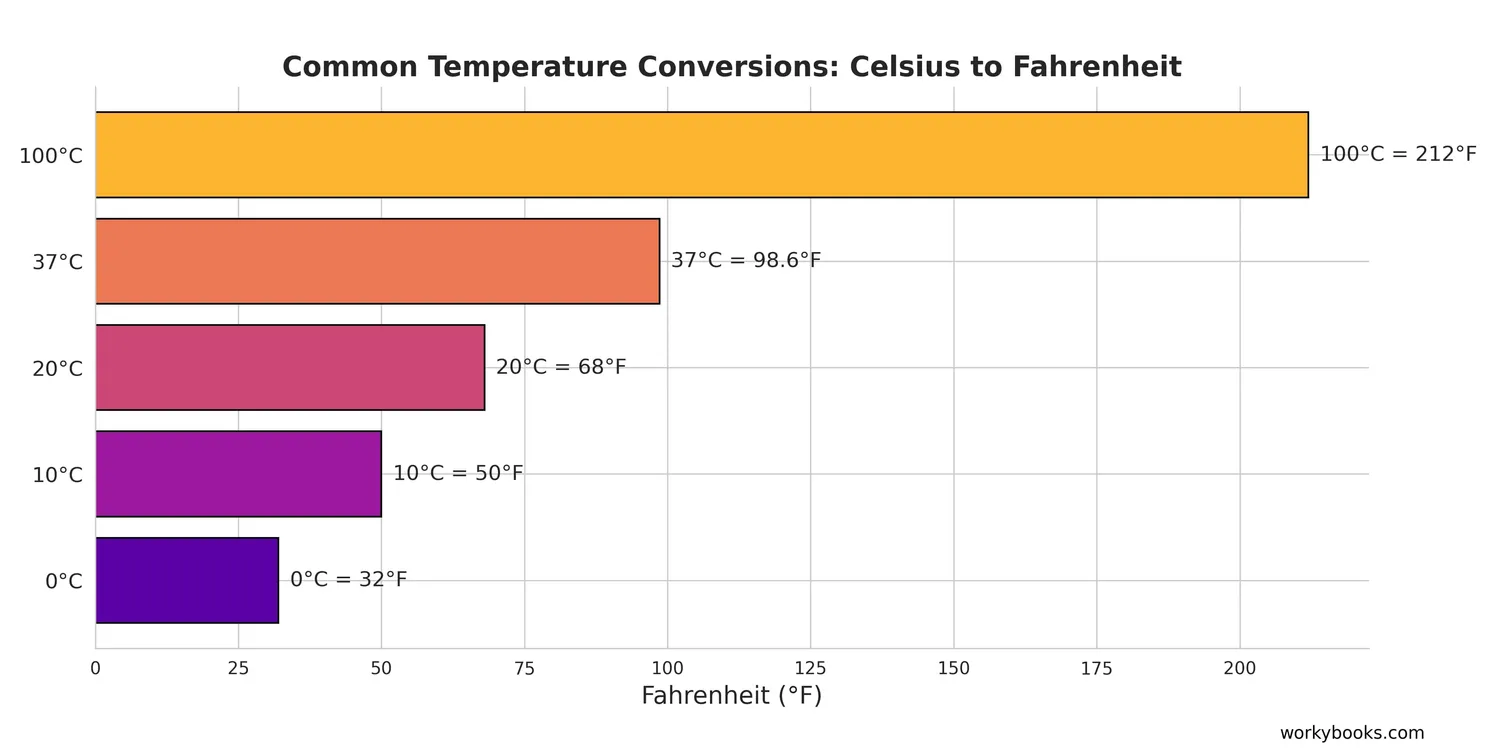
Conversion charts help us quickly find equivalent temperatures without calculating each time. Here are two useful charts:
Common Temperature Conversion Chart
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
|---|---|
| -40°C | -40°F |
| -20°C | -4°F |
| 0°C | 32°F |
| 10°C | 50°F |
| 20°C | 68°F |
| 30°C | 86°F |
| 37°C | 98.6°F |
| 40°C | 104°F |
| 100°C | 212°F |
Weather Temperature Conversion Chart
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -10°C | 14°F | Very Cold |
| 0°C | 32°F | Freezing |
| 10°C | 50°F | Cool |
| 20°C | 68°F | Room Temperature |
| 30°C | 86°F | Warm |
| 40°C | 104°F | Hot |
Chart Tip
Notice that -40° is the same in both scales! This is the only temperature where Celsius and Fahrenheit meet.
Real-World Examples
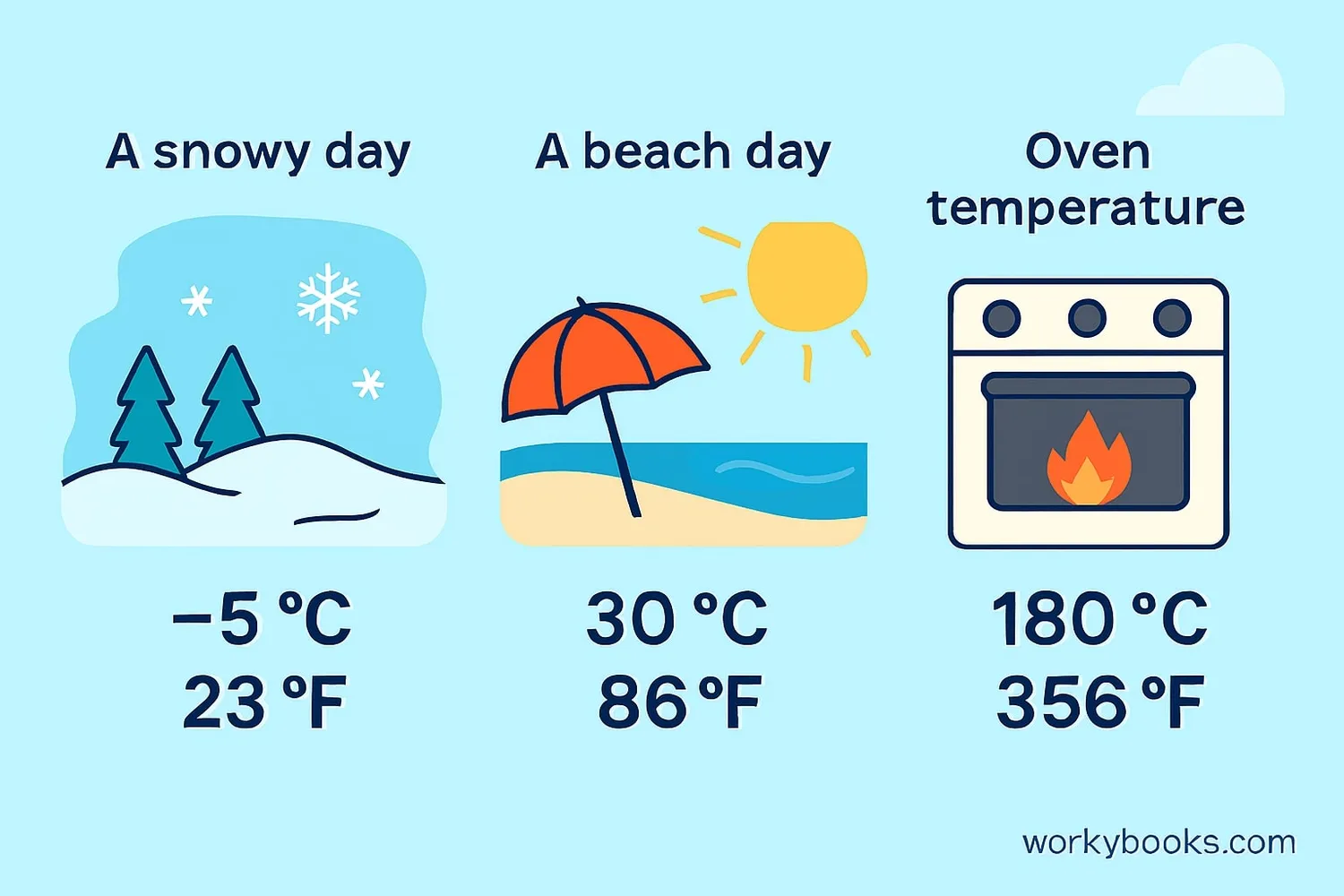
Let's practice conversion with some real-world examples:
Example 1: Water freezes at 0°C. What is this in Fahrenheit?
Solution: (0 × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F
Example 2: Normal body temperature is 37°C. Convert to Fahrenheit.
Solution: (37 × 9/5) + 32 = (66.6) + 32 = 98.6°F
Example 3: A hot summer day is 95°F. What is this in Celsius?
Solution: To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius: (°F - 32) × 5/9
(95 - 32) × 5/9 = 63 × 5/9 ≈ 35°C
Example 4: Oven temperature for baking cookies is 350°F. Convert to Celsius.
Solution: (350 - 32) × 5/9 = 318 × 5/9 ≈ 176.7°C (about 180°C)
Practice converting temperatures you encounter - weather forecasts, cooking instructions, or science experiments!
Conversion Tip
To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, subtract 32 and then multiply by 5/9.
Conversion Practice Quiz
Test your conversion skills with this 5-question quiz. Choose the correct answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Celsius and Fahrenheit conversion:
Temperature Trivia
Discover interesting facts about temperature measurement:
Origin of Celsius Scale
Anders Celsius originally defined his scale backwards! In 1742, he set 0° as boiling water and 100° as freezing. It was reversed after his death to the system we use today.
Absolute Zero
The coldest possible temperature is -273.15°C (-459.67°F). At this temperature, atoms stop moving entirely. Scientists have gotten within billionths of a degree above absolute zero!
Space Temperatures
In space, temperatures vary wildly. In sunlight, objects can reach 120°C (248°F), while in shadow they can drop to -157°C (-250°F). Space suits must protect astronauts from both extremes.
Extreme Temperatures
The highest natural temperature ever recorded on Earth was 56.7°C (134°F) in Death Valley, California. The coldest was -89.2°C (-128.6°F) in Antarctica.





