Direct Proportion - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Learn about proportional relationships with simple explanations, visual examples, and interactive activities
What is Direct Proportion?
Direct proportion means that two quantities change at the same rate. When one quantity increases, the other increases at the same rate. When one decreases, the other decreases at the same rate.
Imagine you're buying apples. If 1 apple costs $1, then 2 apples cost $2, and 3 apples cost $3. The cost is directly proportional to the number of apples. This relationship stays the same no matter how many apples you buy.
We say that the cost of apples is directly proportional to the number of apples. This is also called direct variation or a proportional relationship.
Key Concept
In direct proportion, the ratio between the two quantities always remains constant.
| Number of Apples | Cost (in dollars) | Ratio (Cost ÷ Apples) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 5 | 1 |
Understanding y = kx
In mathematics, we write direct proportion using a simple formula:
The Direct Proportion Formula
Where:
- y is the dependent variable
- x is the independent variable
- k is the constant of proportionality
Here's how we find k:
Once we know k, we can find y for any x using y = kx, or find x for any y using x = y ÷ k.
Remember
The constant of proportionality (k) always stays the same in a proportional relationship.
Example 1: Driving
If a car travels at a constant speed of 60 miles per hour:
- After 1 hour: 60 miles
- After 2 hours: 120 miles
- After 3 hours: 180 miles
Here, distance = 60 × time. k = 60 (miles per hour).
Example 2: Baking
To make 12 cookies, you need:
- 2 cups of flour
- 24 cookies: 4 cups of flour
- 36 cookies: 6 cups of flour
Flour = (1/6) × cookies. k = 1/6 (cups per cookie).
Real-World Examples
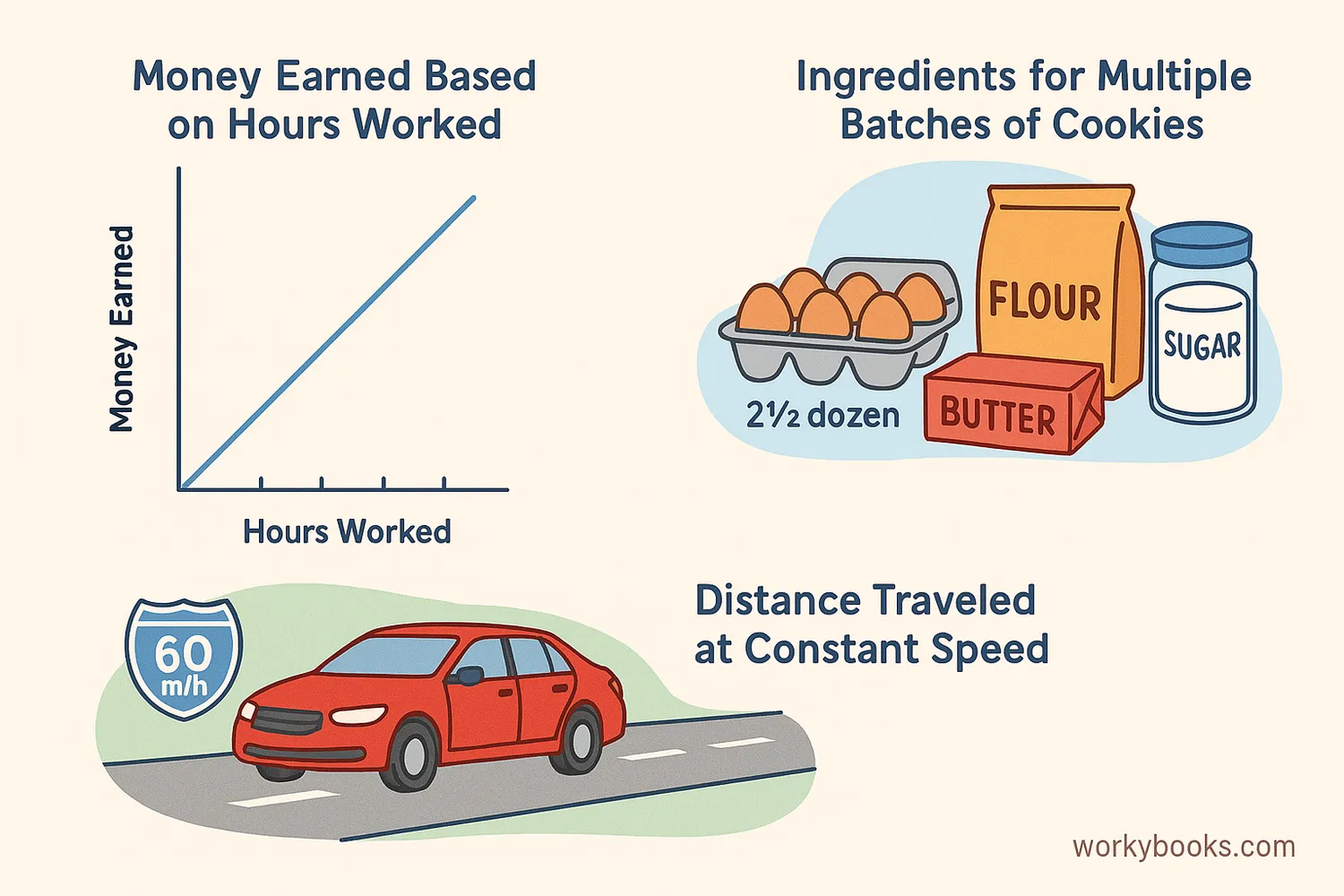
Direct proportion is all around us! Here are some common examples:
Money and Hours
If you earn $10 per hour:
- 2 hours = $20
- 5 hours = $50
- 8 hours = $80
Money = 10 × hours. k = 10 (dollars per hour).
Fuel Consumption
A car uses 1 gallon of gas every 25 miles:
- 50 miles = 2 gallons
- 100 miles = 4 gallons
- 200 miles = 8 gallons
Gas used = (1/25) × miles. k = 1/25 (gallons per mile).
Pencils and Boxes
Each box contains 12 pencils:
- 1 box = 12 pencils
- 3 boxes = 36 pencils
- 5 boxes = 60 pencils
Pencils = 12 × boxes. k = 12 (pencils per box).
Check Understanding
If it takes 3 eggs to make 12 pancakes, how many eggs are needed for 36 pancakes?
Answer: Since 12 pancakes require 3 eggs, the ratio is 3:12 or 1:4. For 36 pancakes (3 times more), you'll need 3 × 3 = 9 eggs.
Practice Quiz
Test your understanding of direct proportion with these practice questions:
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about direct proportion:
Math Trivia
Discover interesting facts about proportional relationships:
Ancient Origins
The concept of proportion dates back to ancient Egypt and Babylon, where it was used for construction and trade. The Greek mathematician Eudoxus formalized the theory of proportions around 350 BCE.
Proportional in Nature
Many patterns in nature follow proportional relationships, like the spiral of a nautilus shell which grows at a constant rate, maintaining the same proportions throughout its life.
Space Exploration
Direct proportion is essential in space travel. The amount of fuel needed to launch a rocket is directly proportional to its weight. Every extra kilogram requires more fuel to escape Earth's gravity.
Art and Proportion
Famous artists like Leonardo da Vinci used proportional relationships to create realistic human figures. His "Vitruvian Man" illustrates ideal human proportions based on ratios.





