Beryllium - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the unique properties and uses of this remarkable element
What is Beryllium?
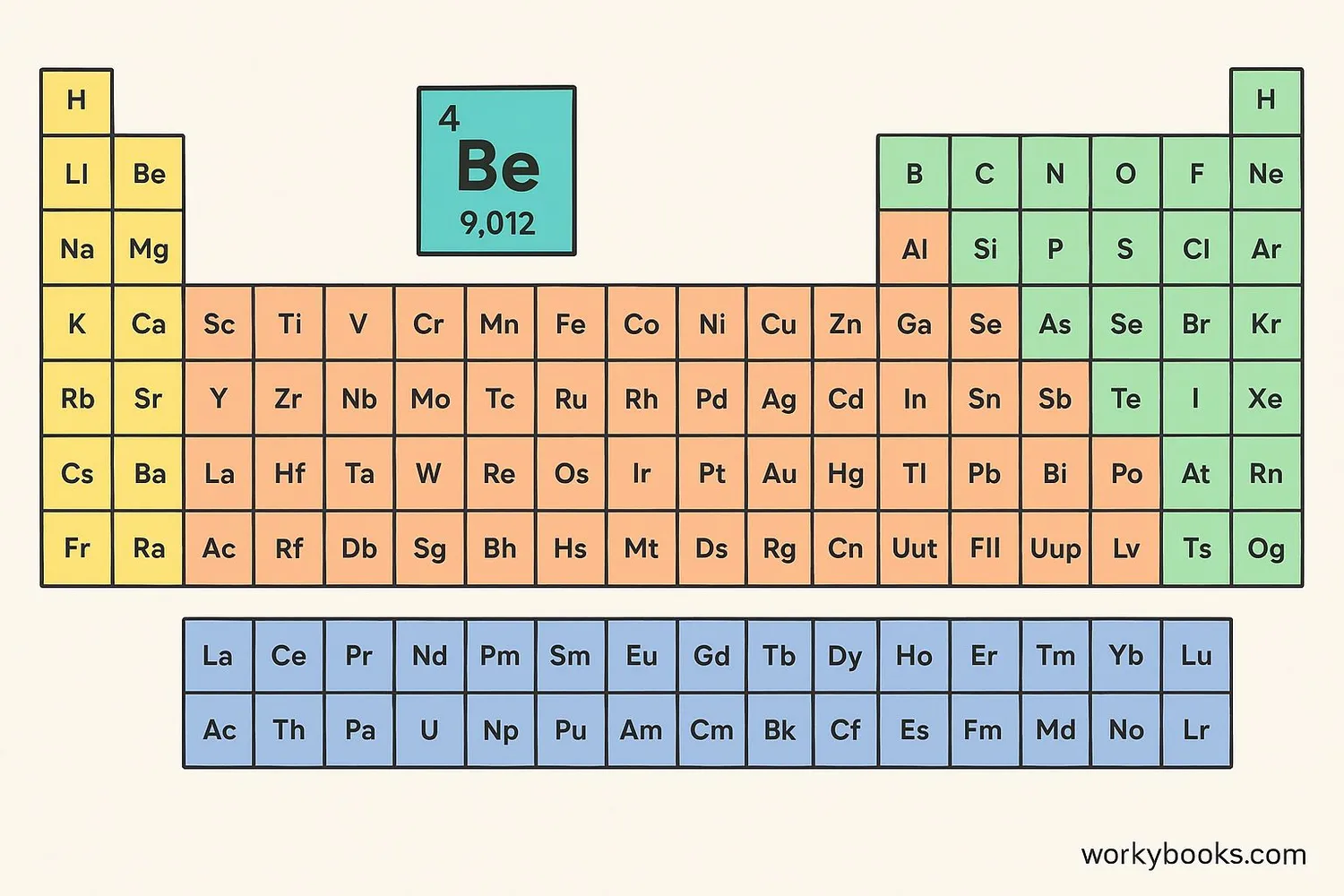
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a lightweight, steel-gray metal that belongs to the alkaline earth metals group. Despite its simple atomic structure, beryllium has some remarkable properties that make it valuable in many industries.
Beryllium is relatively rare in the universe and in the Earth's crust. It wasn't until the early 19th century that scientists were able to isolate pure beryllium metal. The name "beryllium" comes from the Greek word "beryllos," which refers to the mineral beryl, where beryllium is commonly found.
Beryllium in the Periodic Table
Beryllium is element number 4, located in period 2 and group 2 of the periodic table.
Element Fact!
Beryllium is one of the lightest metals and has one of the highest melting points of all light metals.
Properties of Beryllium
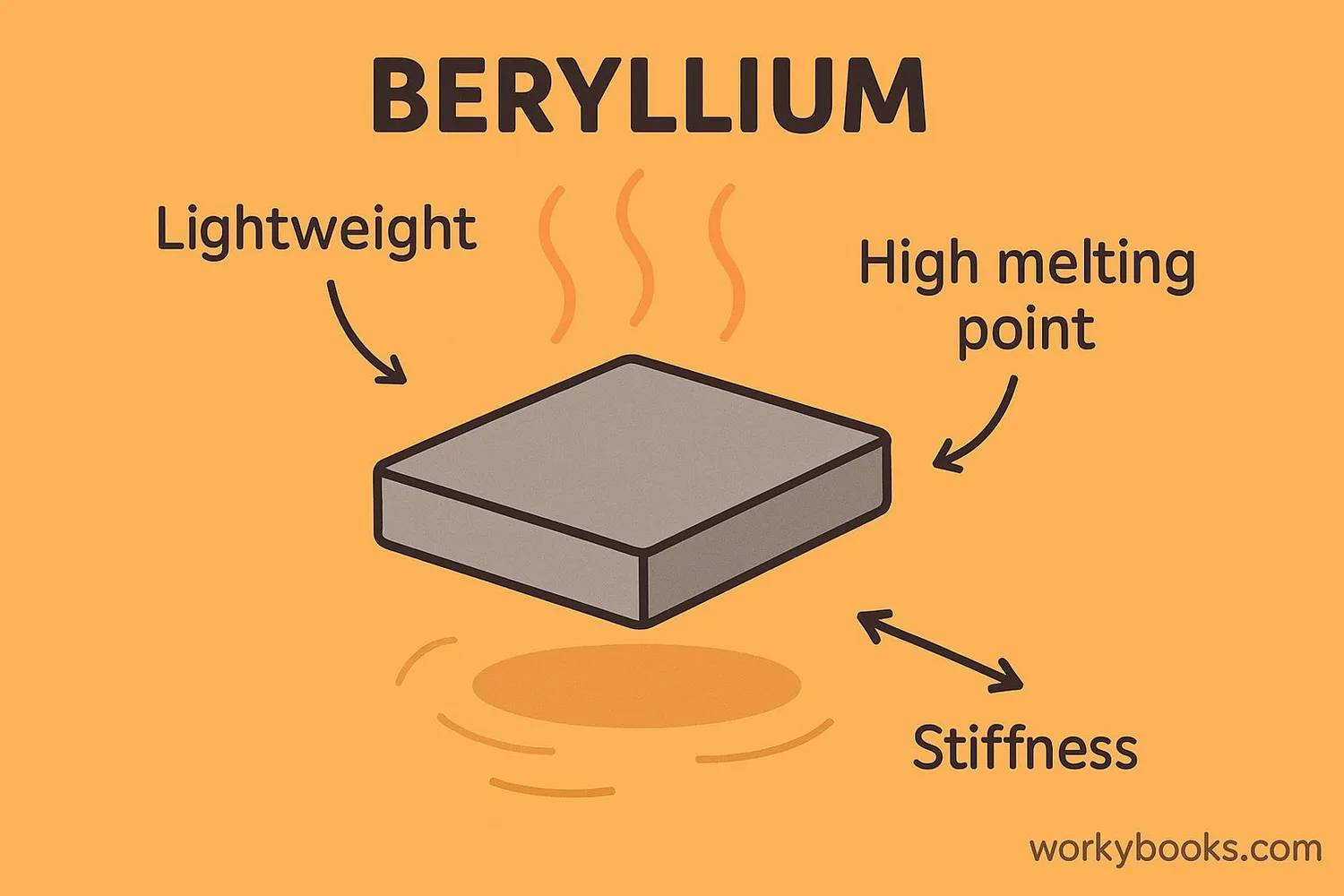
Beryllium has several unique physical and chemical properties that make it valuable for specialized applications:
Lightweight
Beryllium is about two-thirds as dense as aluminum
Stiffness
It is six times stiffer than steel
High Melting Point
Melts at 1,287°C (2,349°F)
Thermal Properties
Excellent heat absorption and dissipation
Transparency
Beryllium is transparent to X-rays
These properties make beryllium particularly useful in applications where weight, stiffness, and thermal stability are critical. However, beryllium is also brittle at room temperature, which can make it challenging to work with.
Did You Know?
Beryllium has a very high thermal conductivity—about 50% higher than aluminum!
Uses & Applications
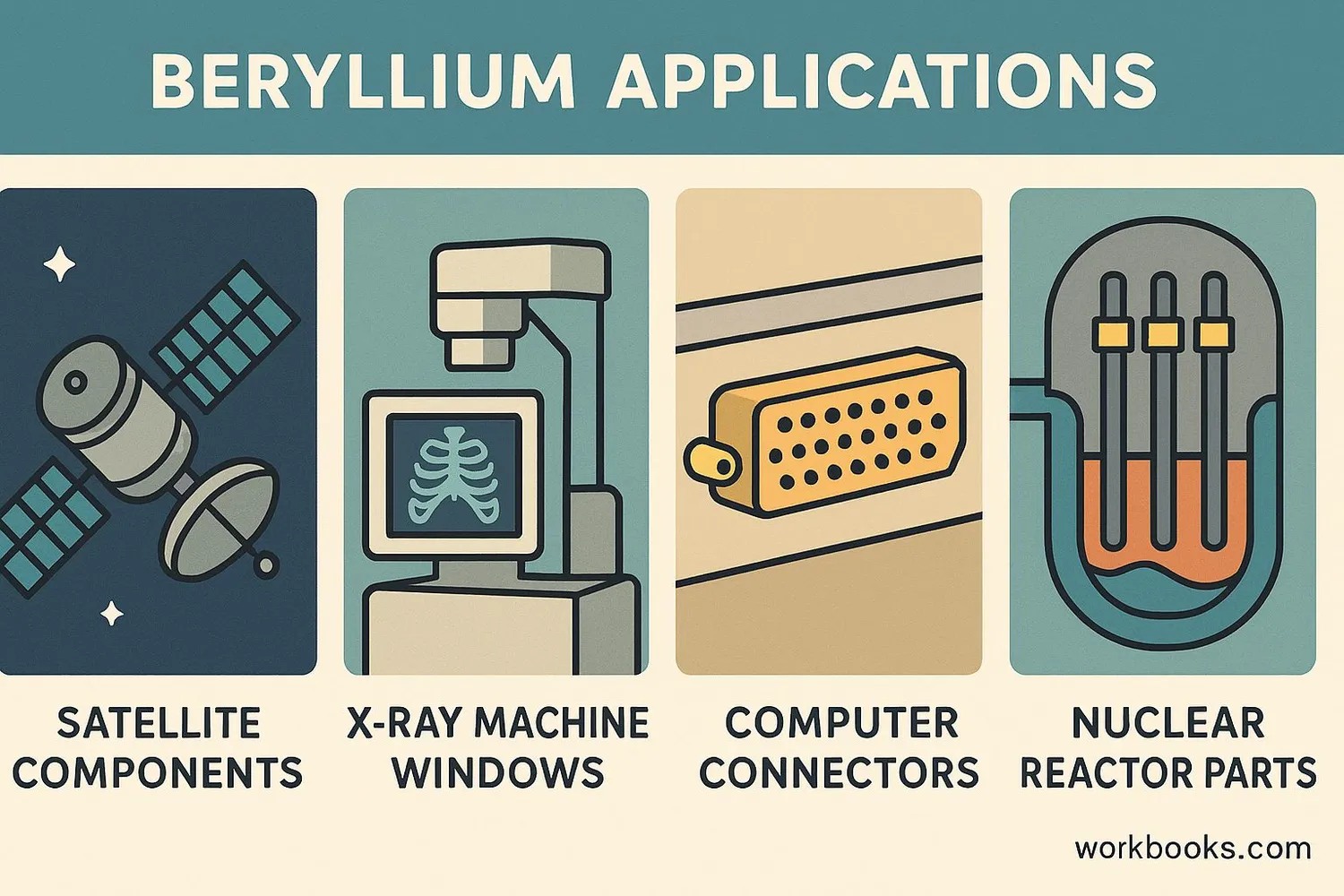
Because of its unique properties, beryllium is used in many specialized applications:
Aerospace
Used in satellites, spacecraft, and high-speed aircraft
Electronics
Used in computer components and telecommunications equipment
Medical
Used in X-ray equipment and medical imaging devices
Nuclear
Used as a reflector and moderator in nuclear reactors
Alloys
Beryllium copper alloys are strong, non-sparking, and non-magnetic
Beryllium-copper alloys are particularly valuable because they combine high strength with excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. These alloys are used in many applications where non-sparking tools are needed, such as in explosive environments.
Safety Considerations

While beryllium has many useful applications, it's important to understand that it can be toxic if not handled properly. Beryllium dust or fumes can cause a serious lung condition called chronic beryllium disease (CBD) in susceptible individuals.
Safety measures for working with beryllium include:
• Using proper ventilation systems
• Wearing personal protective equipment
• Implementing strict hygiene practices
• Regular medical monitoring for workers
These precautions are especially important in industries where beryllium is machined or processed, as these activities can create airborne particles.
Important Safety Note
While learning about beryllium is educational and important, students should never handle beryllium or its compounds without proper supervision and safety equipment.
Beryllium Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of beryllium with this interactive quiz. Select the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about beryllium:
Beryllium Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about beryllium:
Precious Forms
Some of the world's most famous gemstones contain beryllium! Emeralds and aquamarines are both varieties of the mineral beryl, which contains beryllium.
Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope uses beryllium for its primary mirror segments because beryllium maintains its shape extremely well at the cold temperatures of space.
Ancient Knowledge
Although beryllium wasn't isolated until the 19th century, ancient Egyptians were mining beryl (which contains beryllium) as early as 2,000 BCE for gemstones.
Limited Production
The United States is the world's leading producer of beryllium, with only one mine in Utah supplying most of the world's beryllium ore.





