Boyle's Law - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how gas pressure and volume are related in this science learning resource
What is Boyle's Law?
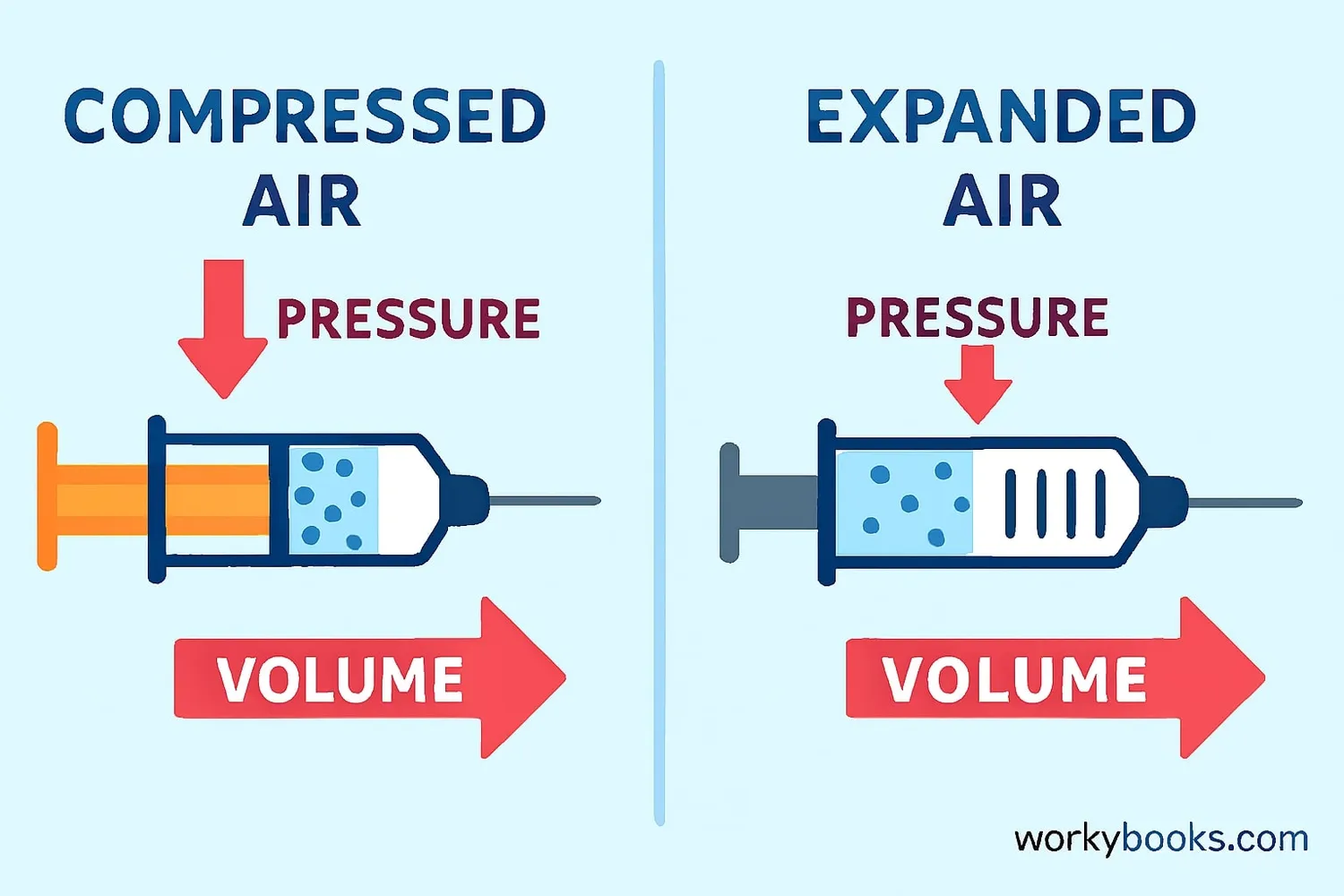
Boyle's Law is a scientific principle that describes how the pressure and volume of a gas are related when the temperature stays the same.
Discovered by Robert Boyle in 1662, this law states that:
When you increase the pressure on a gas, its volume decreases
When you decrease the pressure on a gas, its volume increases
Imagine a balloon filled with air. If you squeeze the balloon (increase pressure), it gets smaller (volume decreases). If you let go, it expands again! That's Boyle's Law in action.
Key Fact!
Boyle's Law only works when the temperature doesn't change. It's one of the fundamental gas laws in science!
Boyle's Law Formula
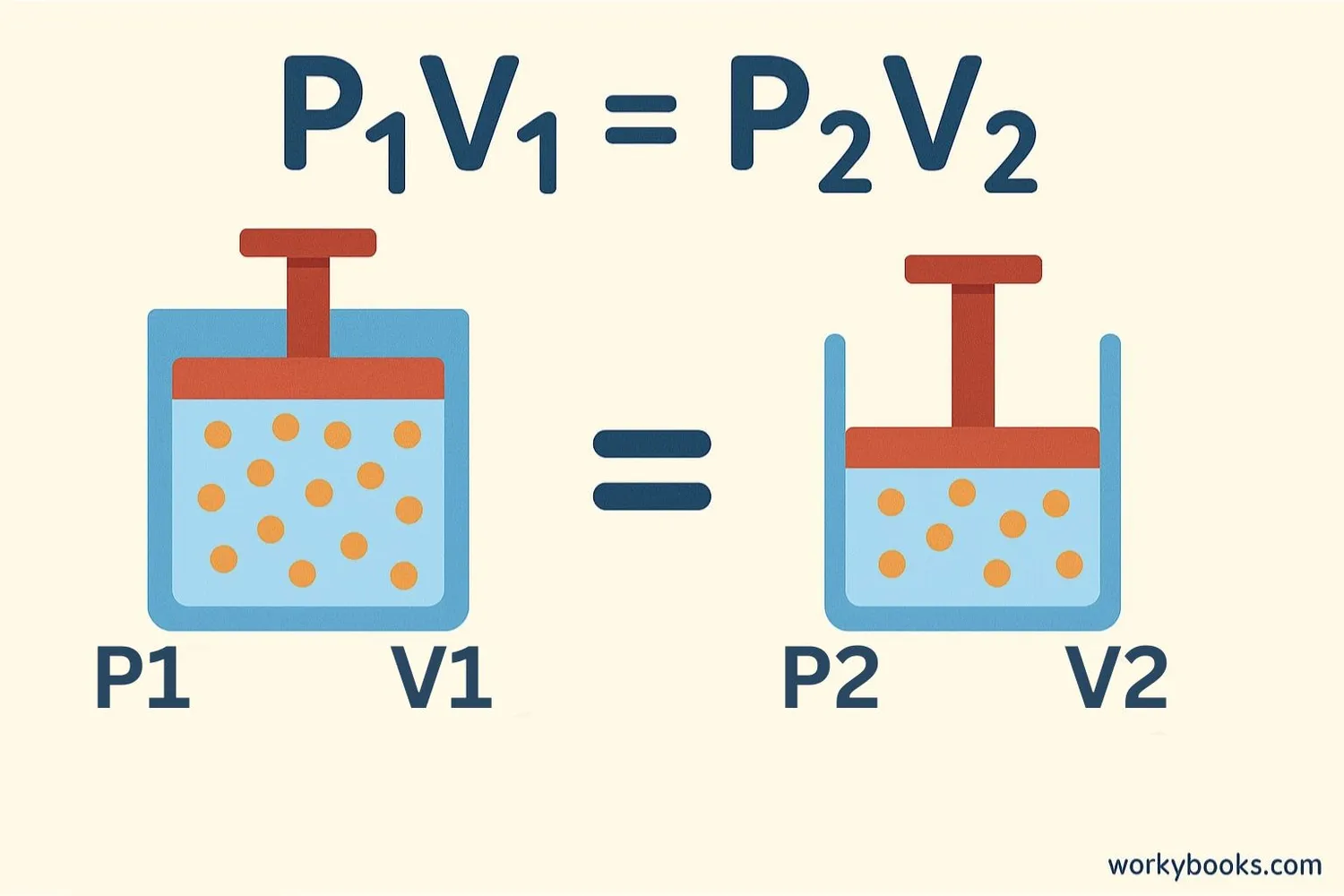
The mathematical relationship in Boyle's Law can be expressed with this simple formula:
Where:
• P₁ = Initial pressure
• V₁ = Initial volume
• P₂ = Final pressure
• V₂ = Final volume
This formula tells us that the product of pressure and volume remains constant as long as the temperature doesn't change. If you know three of these values, you can calculate the fourth!
Pressure Increases
Volume decreases proportionally
Pressure Decreases
Volume increases proportionally
Constant Temperature
Essential for Boyle's Law to apply
Remember!
Boyle's Law only applies to gases, not liquids or solids. And temperature must remain constant!
Examples of Boyle's Law
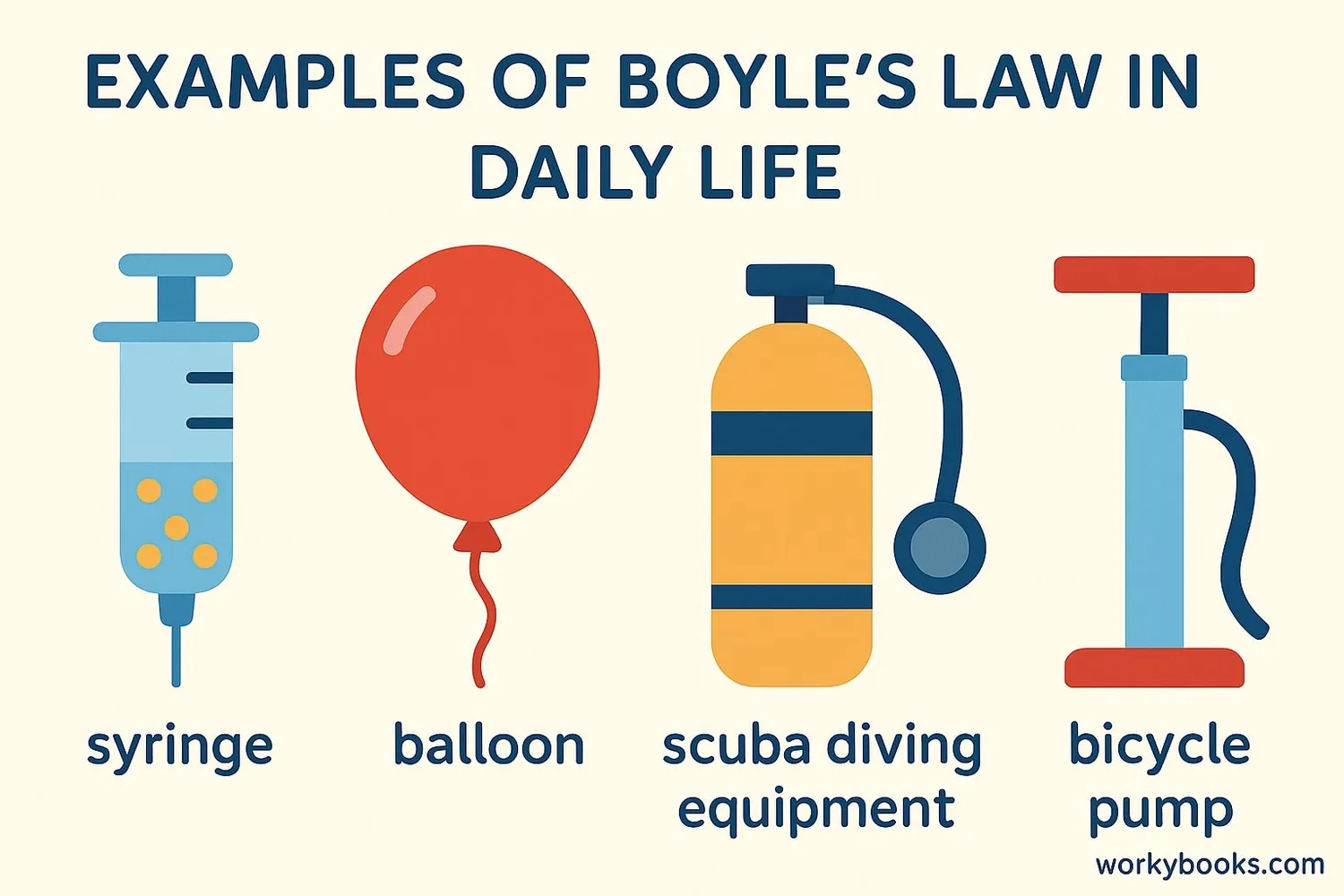
Boyle's Law isn't just a science concept - it's at work all around us! Here are some real-world examples:
Syringes
When you pull the plunger, volume increases and pressure decreases, drawing liquid in
Scuba Diving
As divers go deeper, pressure increases, decreasing the volume of air in their tanks
Breathing
When you inhale, your diaphragm expands, decreasing pressure and drawing air in
More examples:
• Balloons: When you squeeze a balloon, pressure increases and volume decreases
• Soda bottles: When you open a bottle, pressure decreases and gas volume increases (fizz!)
• Bicycle pumps: When you push down, pressure increases, forcing air into the tire
• Ears popping: When ascending or descending in altitude, pressure changes affect air volume in your ears
Applications of Boyle's Law
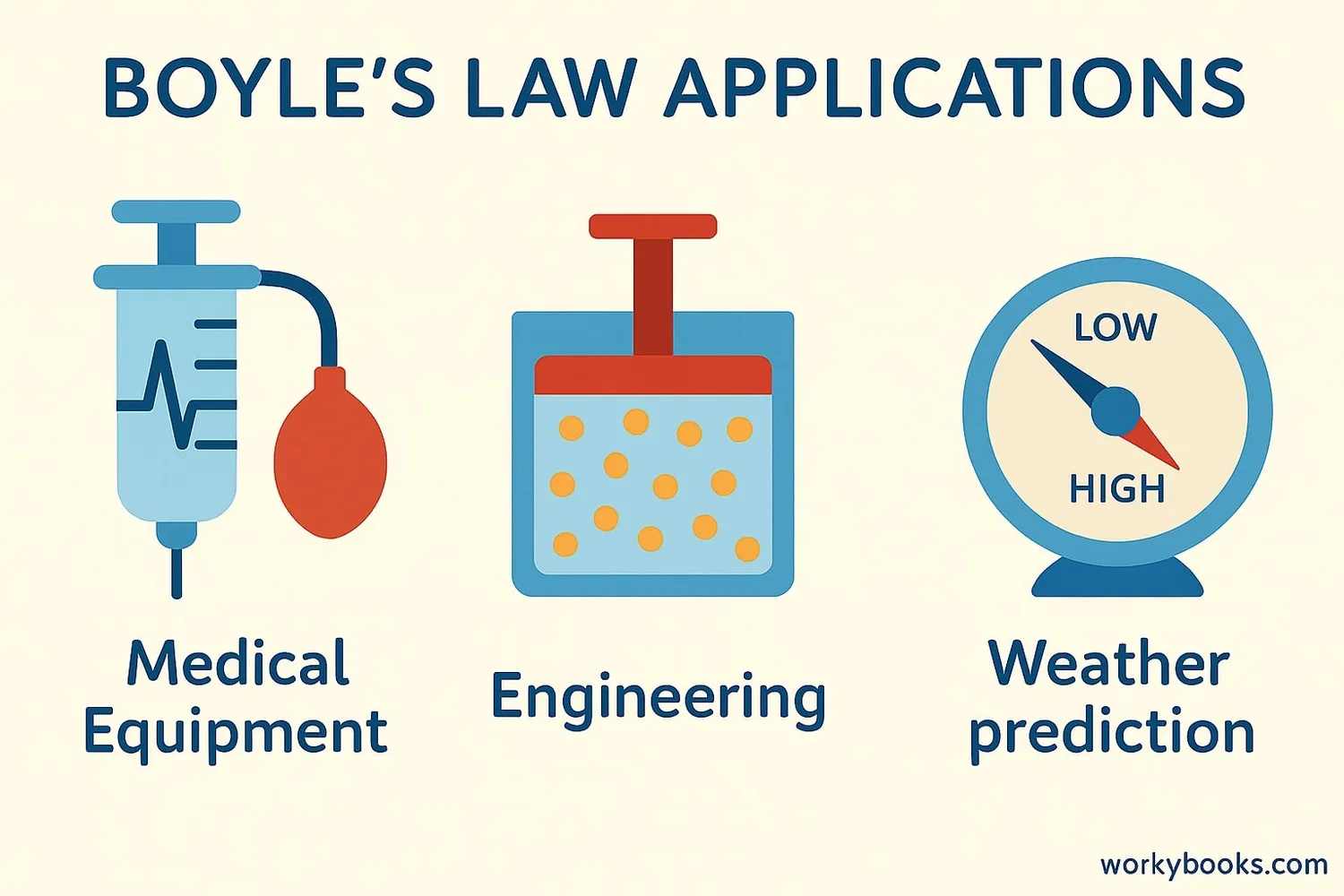
Boyle's Law has many important applications in science, medicine, and technology:
Medical Equipment
Used in ventilators, syringes, and anesthesia machines to control gas flow
Engineering
Helps design compressed air systems, engines, and refrigeration units
Weather Prediction
Explains how air pressure affects weather patterns and balloon measurements
Other important applications:
• Space exploration: Understanding gas behavior in spacecraft and spacesuits
• Deep-sea exploration: Calculating pressure effects on submarines
• Food packaging: Creating vacuum-sealed containers that preserve food
• Chemistry research: Studying gas reactions under different pressures
Boyle's Law Quiz
Test your understanding with this Boyle's Law quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about Boyle's Law:
Boyle's Law Trivia
Discover fascinating facts about Boyle's Law and gases:
Historical Discovery
Robert Boyle discovered his law using a J-shaped glass tube sealed at one end. He poured mercury into the tube, trapping air in the sealed end, and observed how volume changed with pressure.
Space Applications
NASA engineers use Boyle's Law when designing spacesuits. The suits must maintain proper pressure to keep astronauts safe in the vacuum of space.
Deep-Sea Creatures
Deep-sea fish have special adaptations to handle Boyle's Law effects. Their bodies don't have air spaces that could collapse under extreme pressure.
Sports Equipment
Soccer balls and basketballs are designed with Boyle's Law in mind. The air pressure inside affects how the ball bounces and moves through the air.





