Cathodes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how cathodes work in batteries, electronics, and chemistry!
What is a Cathode?
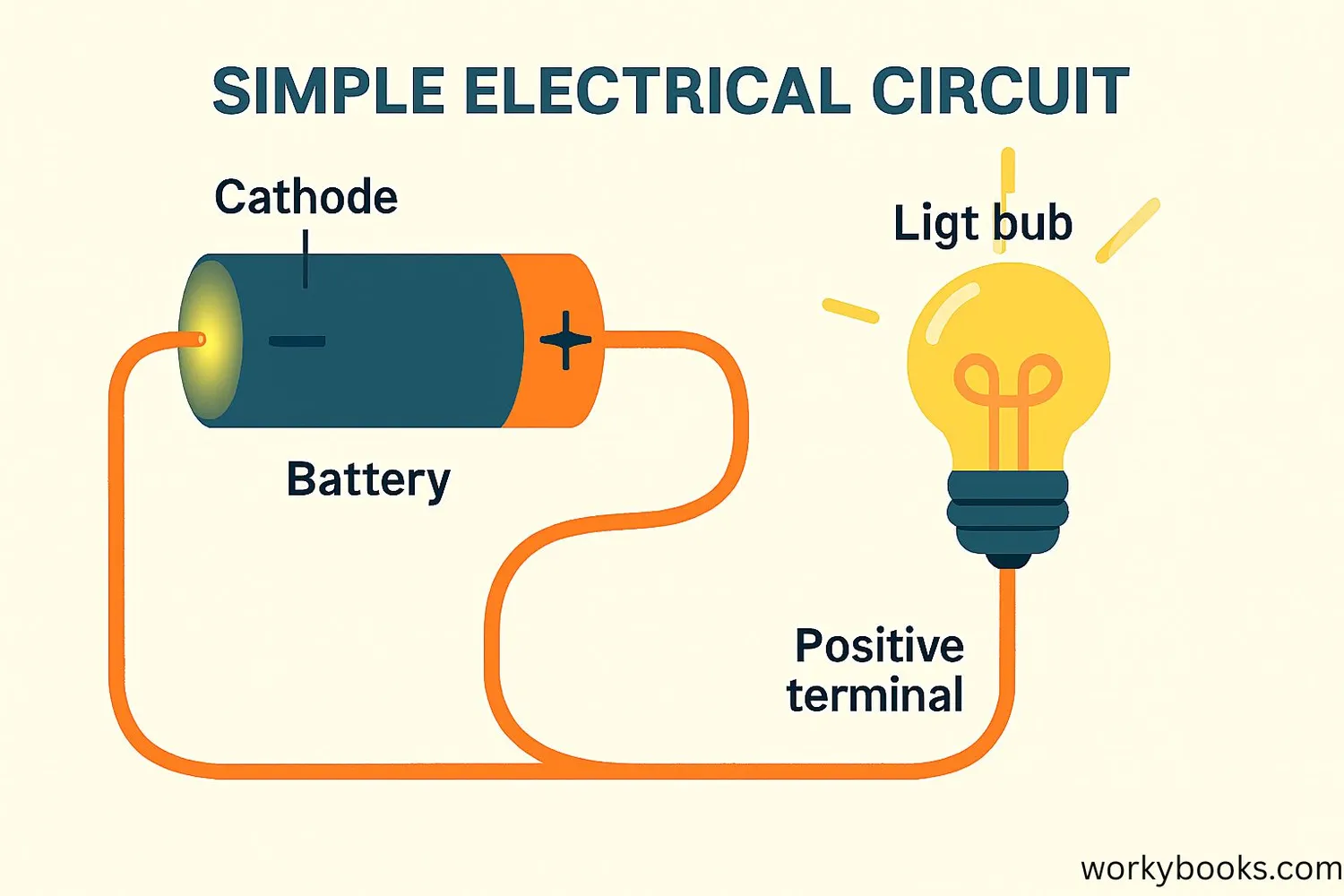
A cathode is the electrode in an electrical device where electricity flows out. Think of it as the "exit door" for electrons in a circuit.
In batteries, the cathode is the positive terminal where electrons leave the battery to power devices. In electronics, cathodes play important roles in devices like cathode ray tubes (old TVs and monitors) and electroplating.
The word "cathode" comes from Greek words meaning "down" and "way" - it's the path where electric current flows out of a device. Remember: Cathode = Current Out.
Science Fact!
In a battery that's being used (discharging), the cathode is positive. But in a battery that's charging, the cathode becomes negative! It depends on whether the device is providing or receiving electricity.
Anode vs Cathode
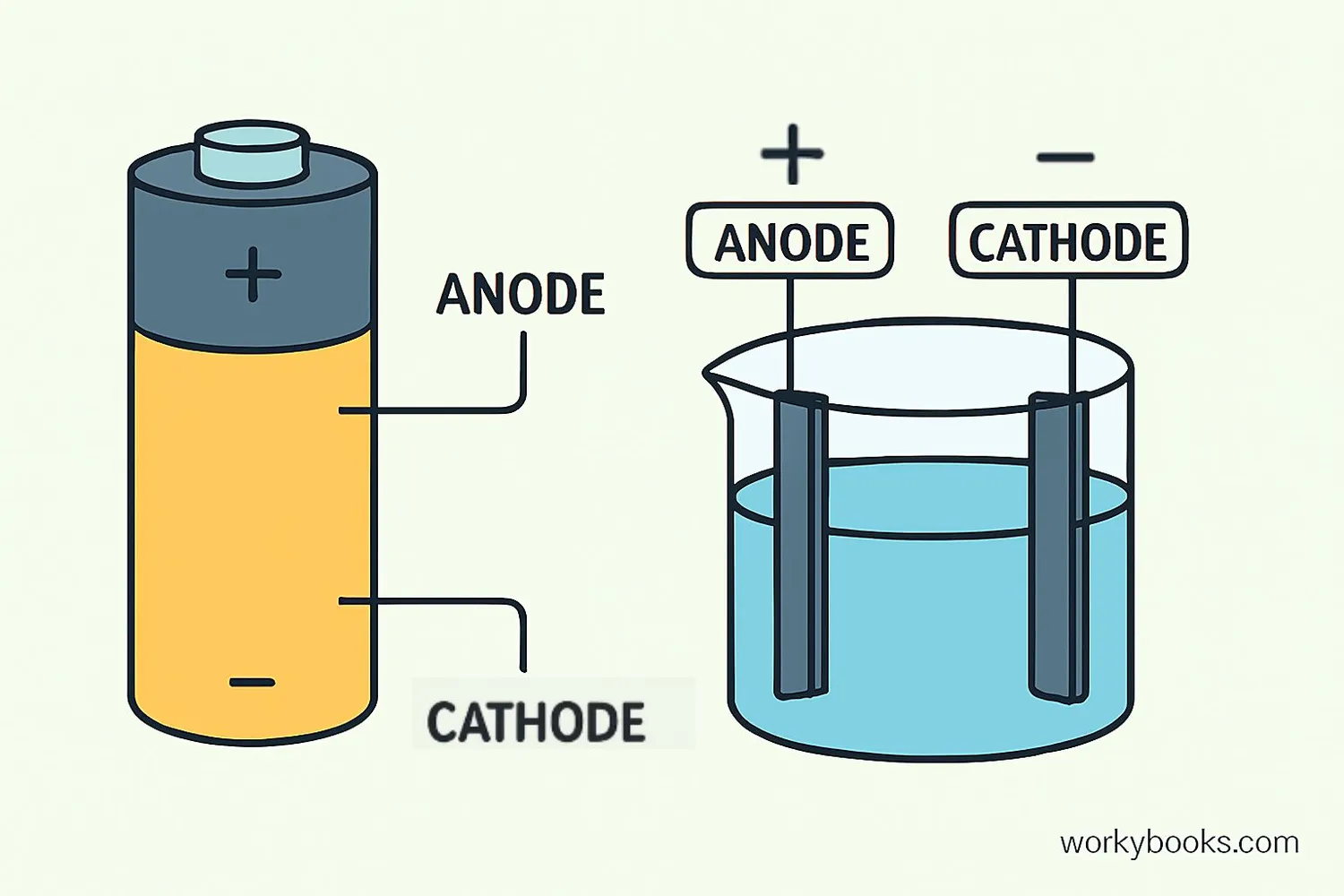
Understanding the difference between anode and cathode is important in electricity and chemistry. Here's a simple way to remember:
| Feature | Anode | Cathode |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Charge | Negative (in discharging devices) | Positive (in discharging devices) |
| Electron Flow | Electrons enter the device here | Electrons exit the device here |
| Chemical Reaction | Oxidation occurs (loss of electrons) | Reduction occurs (gain of electrons) |
| In Batteries | Where current enters during discharge | Where current exits during discharge |
| Memory Trick | A for Anode, A for Arrival (electrons arrive) | C for Cathode, C for Current leaving |
Here's a simple rhyme to remember:
"Anode attracts anions (negative ions),
Cathode attracts cations (positive ions).
Electrons flow from anode to cathode,
Through the circuit on their route!"
Cathode in Batteries
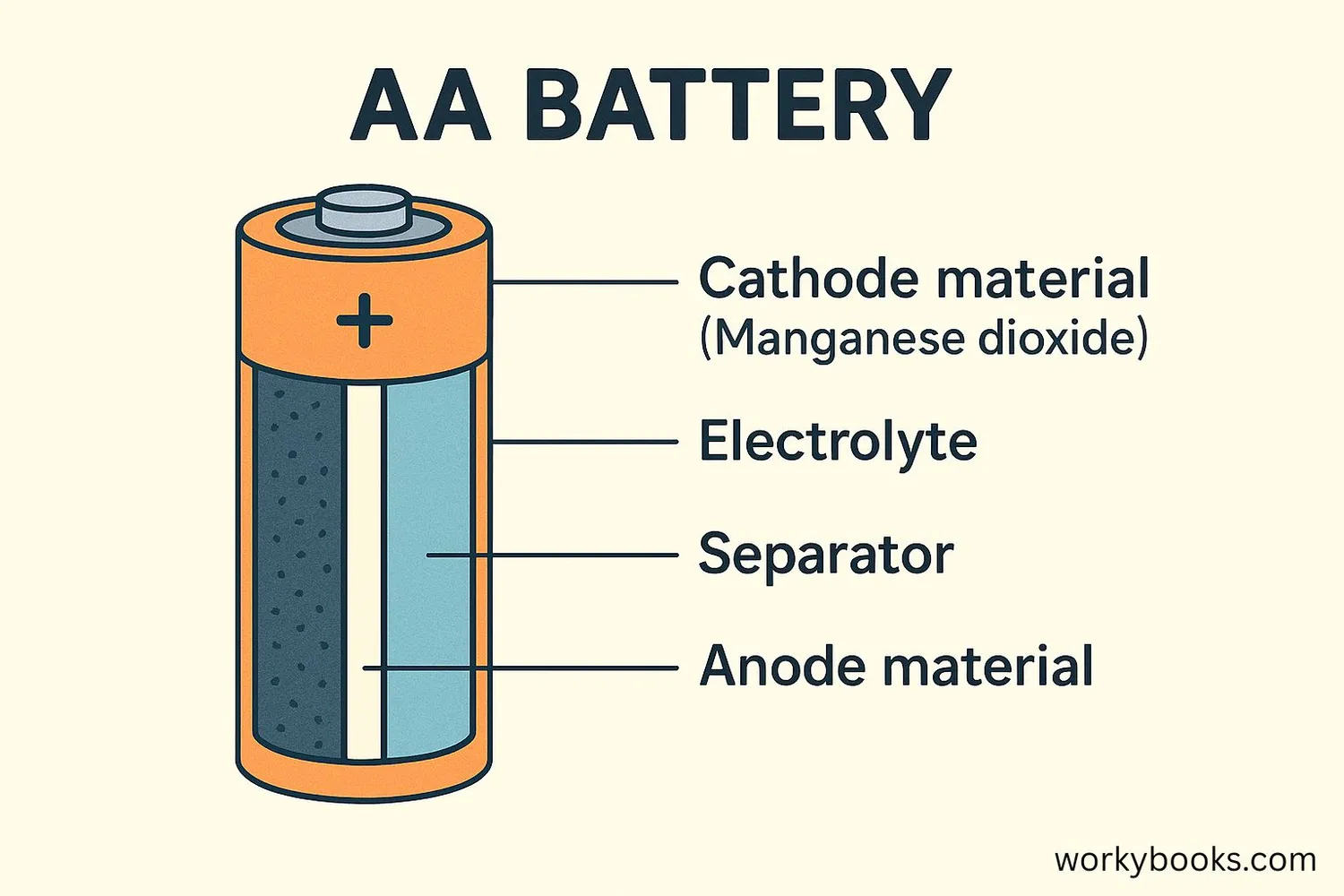
In batteries, the cathode is one of the most important parts! It's where the chemical reactions happen that produce electricity.
How it works in a typical battery:
Chemical Reaction
Chemical reactions occur at the cathode and anode
Electron Release
Electrons are released at the anode
Electron Travel
Electrons travel through the circuit
Cathode Reaction
Electrons enter the battery at the cathode
Ion Movement
Ions move through electrolyte to balance charge
Different types of batteries use different cathode materials:
• Alkaline batteries: Manganese dioxide
• Lithium-ion batteries: Lithium cobalt oxide
• Lead-acid batteries: Lead dioxide
• Nickel-metal hydride: Nickel oxyhydroxide
The cathode material determines many properties of the battery, including its voltage, capacity, and how long it lasts.
Cathode Ray Tubes
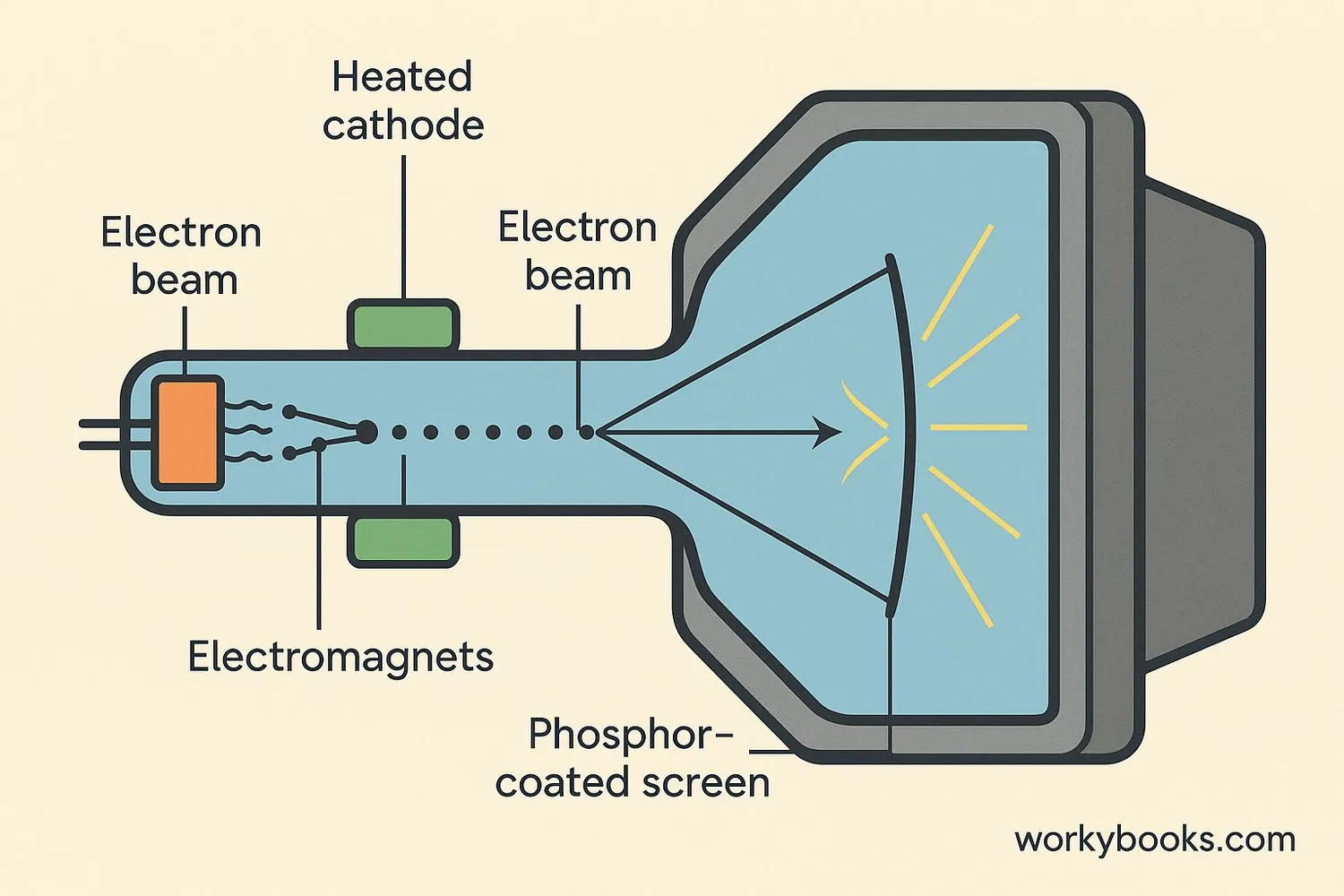
Before flat-screen TVs, most televisions and computer monitors used Cathode Ray Tubes (CRTs). These devices used cathodes in a special way:
Heated Cathode
A heated cathode releases electrons
Electron Beam
High voltage creates a beam of electrons
Beam Steering
Electromagnets steer the electron beam
The electron beam scans rapidly across the screen, hitting phosphor coating that glows red, green, or blue. By controlling where the beam hits, the CRT creates images on the screen.
Although CRT technology is mostly replaced by LCD and OLED screens today, understanding how they worked helped scientists develop modern display technologies.
Did You Know?
The first cathode ray tube was invented in 1897 by Karl Ferdinand Braun. This invention led to the development of television and computer monitors!
Cathode Knowledge Quiz
Test your knowledge about cathodes with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about cathodes:
Cathode Science Trivia
Discover some fascinating facts about cathodes:
Historical Discovery
The term "cathode" was coined by scientist William Whewell in 1837 at the request of Michael Faraday, who needed names for the electrodes in his electrolysis experiments.
Electron Microscope Connection
Electron microscopes use a heated cathode to produce a beam of electrons that can magnify objects up to 10 million times - much more powerful than light microscopes!
Space Exploration
Cathodes are used in ion thrusters for spacecraft! These thrusters use electric fields to accelerate ions (usually xenon) out of a cathode to generate thrust more efficiently than chemical rockets.
Battery Evolution
The development of new cathode materials is the main reason batteries keep improving. Modern lithium-ion batteries can store 3 times more energy than batteries from 20 years ago thanks to cathode innovations.





