The Science of Combustion - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how things burn and release energy
What is Combustion?
Combustion is a scientific word for burning. It's a chemical reaction that happens when a fuel combines with oxygen and produces heat and light. This process is happening all around us - when you light a candle, start a campfire, or even when your body uses food for energy!
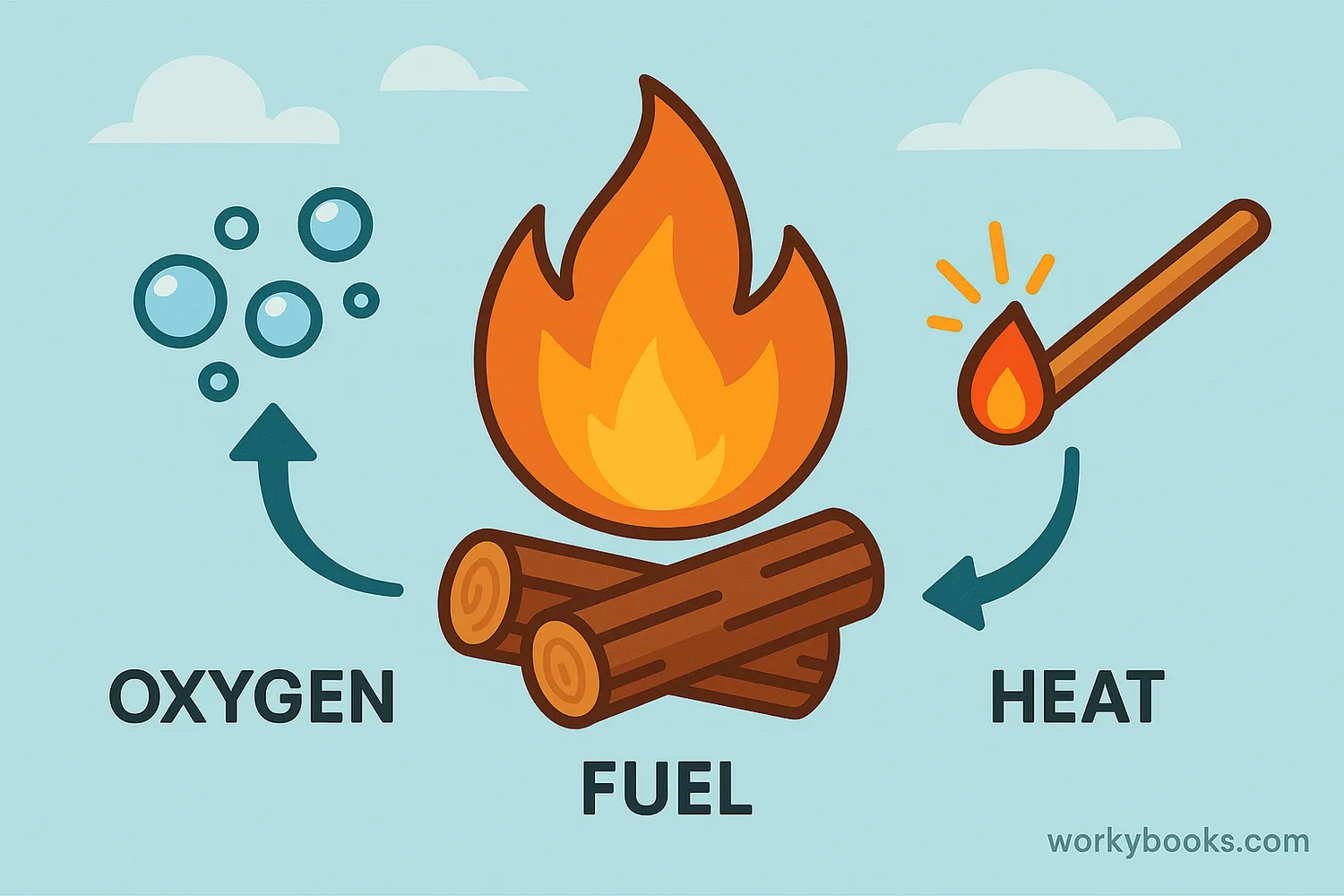
For combustion to happen, we need three things:
• Fuel - something that can burn (like wood, gas, or paper)
• Oxygen - from the air around us
• Heat - enough energy to start the reaction
This combination is often called the Fire Triangle. If you remove any one of these three elements, the fire will go out!
Science Fact!
The visible flame in combustion is actually hot gas that's glowing. Different fuels produce different colored flames!
Types of Combustion

Not all burning is the same! Scientists recognize two main types of combustion:
Complete Combustion
Happens when there's plenty of oxygen. The fuel burns completely, producing mainly carbon dioxide and water. This creates a blue flame and is more efficient.
Incomplete Combustion
Happens when there's not enough oxygen. The fuel doesn't burn completely, producing carbon monoxide, soot, and other pollutants. This creates a yellow or orange flame.
Complete combustion is what we want in engines and heaters because it produces the most energy and fewer pollutants. Incomplete combustion can be dangerous because carbon monoxide is poisonous and soot can dirty the air.
Safety First!
Carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion is called the "silent killer" because you can't see or smell it. Always have carbon monoxide detectors in your home!
Combustion Reaction
Combustion is a chemical reaction where a fuel combines with oxygen to produce new substances and release energy. The general equation for combustion is:
Fuel + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (heat and light)
Here's an example with methane (the main component of natural gas):
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + Energy
This means: One molecule of methane combines with two molecules of oxygen to produce one molecule of carbon dioxide, two molecules of water, and energy.
Energy Measurement
The amount of energy released during combustion is called the "heat of combustion." Scientists measure this to compare different fuels.
Combustion Examples
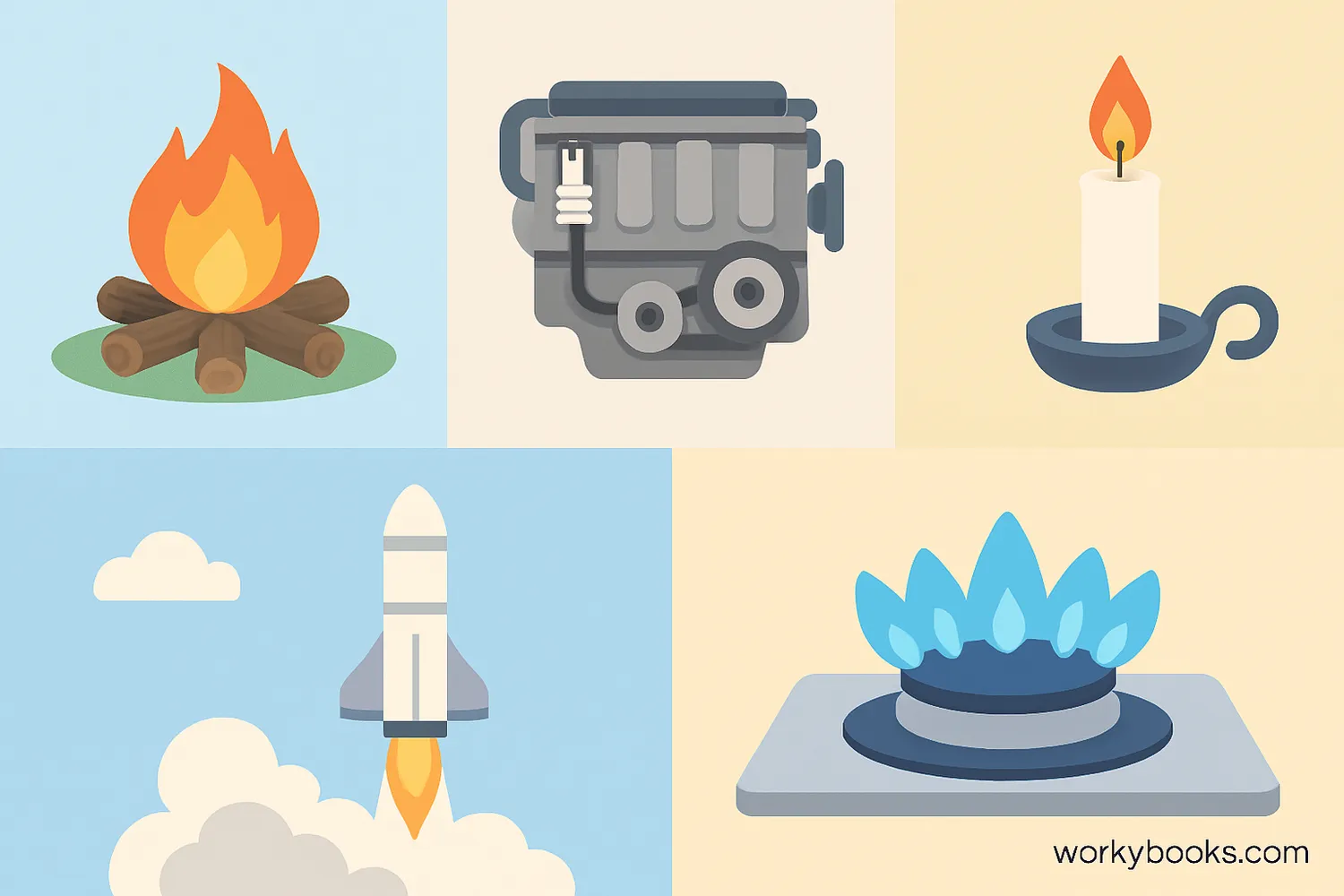

Combustion is happening all around us! Here are some common examples:
Campfires
Wood burns with oxygen from the air, producing heat, light, and the cozy feeling we all enjoy
Car Engines
Gasoline mixes with air and ignites to power your vehicle and make it move
Candles
Wax vapor burns with oxygen to create a steady flame and pleasant light
Rockets
Special fuels burn rapidly to produce thrust that pushes rockets into space
Gas Stoves
Natural gas burns to provide heat for cooking our favorite meals
Combustion also happens inside our bodies! When we "burn" food for energy through cellular respiration, it's a slow, controlled form of combustion that doesn't produce flames but still releases the energy we need to live.
Combustion Quiz
Test your combustion knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about combustion:
Combustion Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about combustion!
Extreme Heat
The hottest flame ever produced was 4,990°C (9,000°F) using carbon subnitride! That's hotter than the surface of most stars.
Ancient Discovery
Humans have been using controlled combustion for at least 400,000 years! Evidence of fire use dates back to early human ancestors.
Energy Power
Combustion reactions power about 80% of the world's energy production, from cars and planes to electricity generation.
Space Flames
In microgravity, flames form spheres instead of teardrops! Without gravity pulling cooler air down, flames burn in all directions equally.





