Electric vs Magnetic Forces - Definition, Facts, Example, Quiz, Trivia
Discover the invisible forces that power our world and make modern technology possible!
What are Electric and Magnetic Forces?
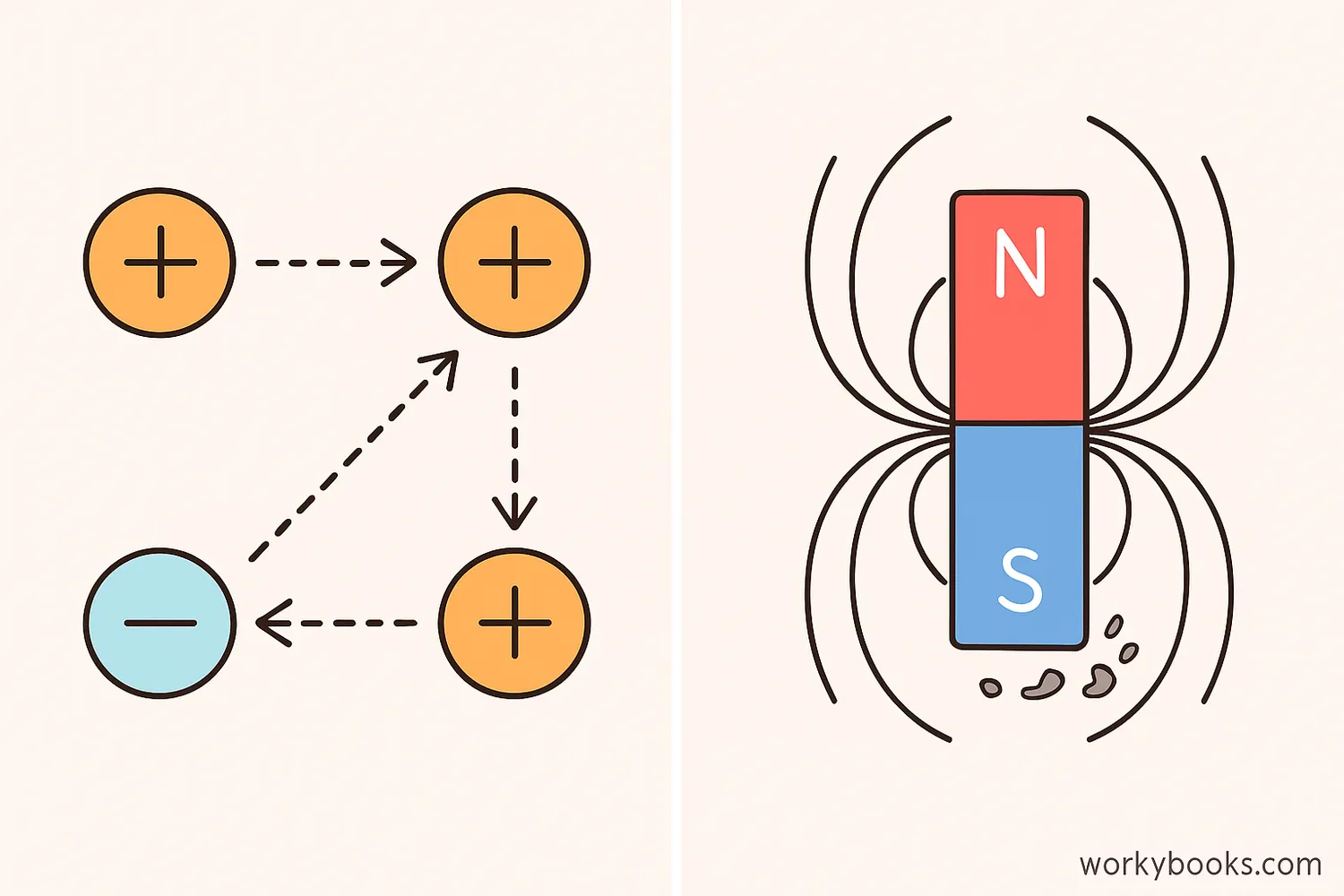
Electric and magnetic forces are fundamental forces in nature that affect our everyday lives. They are part of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces in the universe.
These invisible forces power our technology, from the electricity in our homes to the magnets on our refrigerators. Understanding how they work helps us understand the world around us!
Science Fact!
Electric and magnetic forces are actually two aspects of the same fundamental force called electromagnetism!
Electric Forces
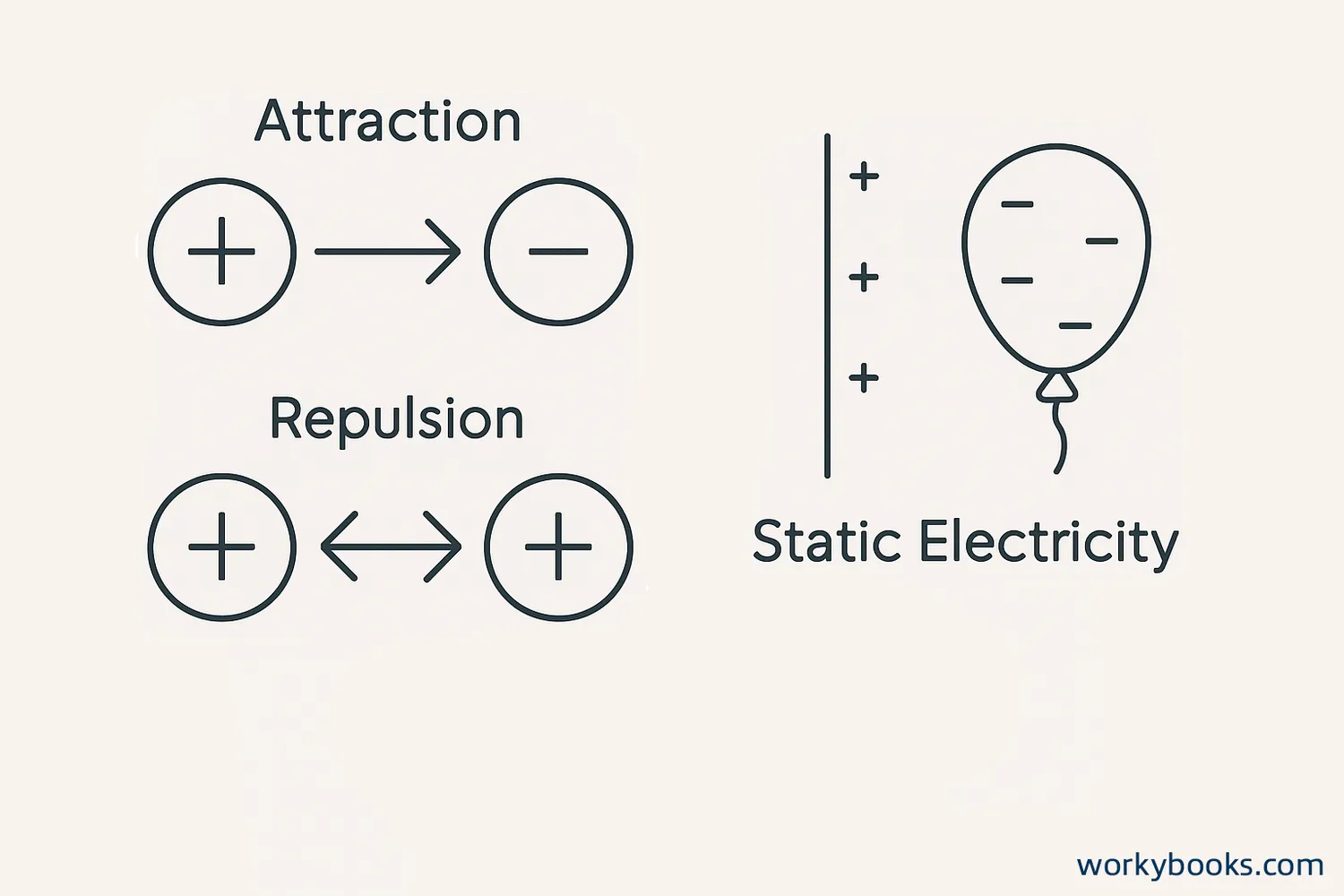
Electric forces are caused by electric charges. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract.
Opposite Charges
Attract each other
Like Charges
Repel each other
Like Charges
Repel each other
The strength of the electric force depends on the amount of charge and the distance between charges. Electric forces can act through empty space, even when objects aren't touching!
Real World Example
When you rub a balloon on your hair, electrons transfer from your hair to the balloon, creating static electricity that makes the balloon stick to walls!
Magnetic Forces
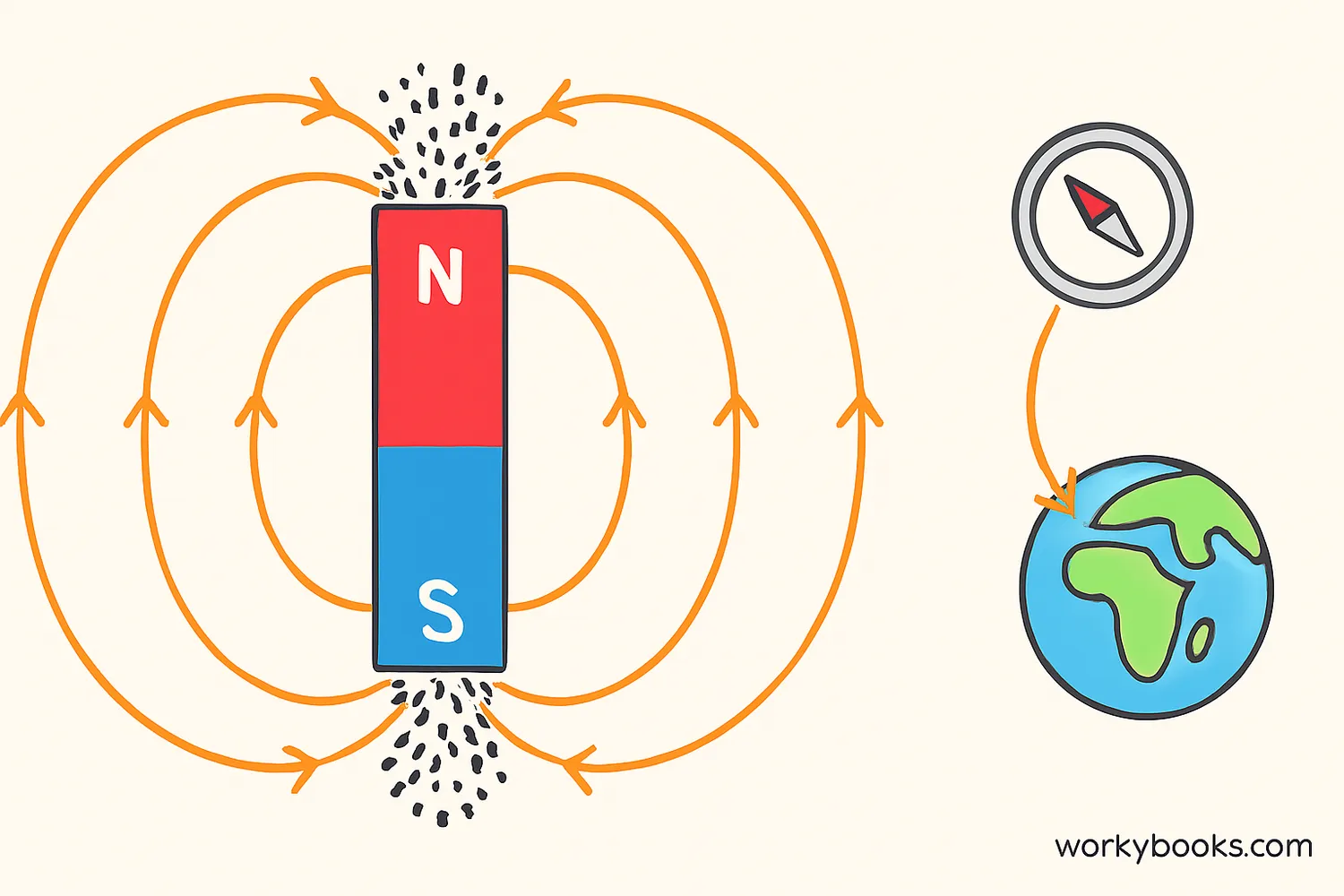
Magnetic forces are caused by magnets or moving electric charges. All magnets have two poles: north and south. Like poles repel each other, while opposite poles attract.
Opposite Poles
Attract each other
Like Poles
Repel each other
Like Poles
Repel each other
Magnetic forces act on certain materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt. They also act on moving electric charges. The Earth itself is a giant magnet with a magnetic field that protects us from solar radiation!
Real World Example
Compass needles point north because they align with Earth's magnetic field, helping people navigate for centuries!
Key Differences
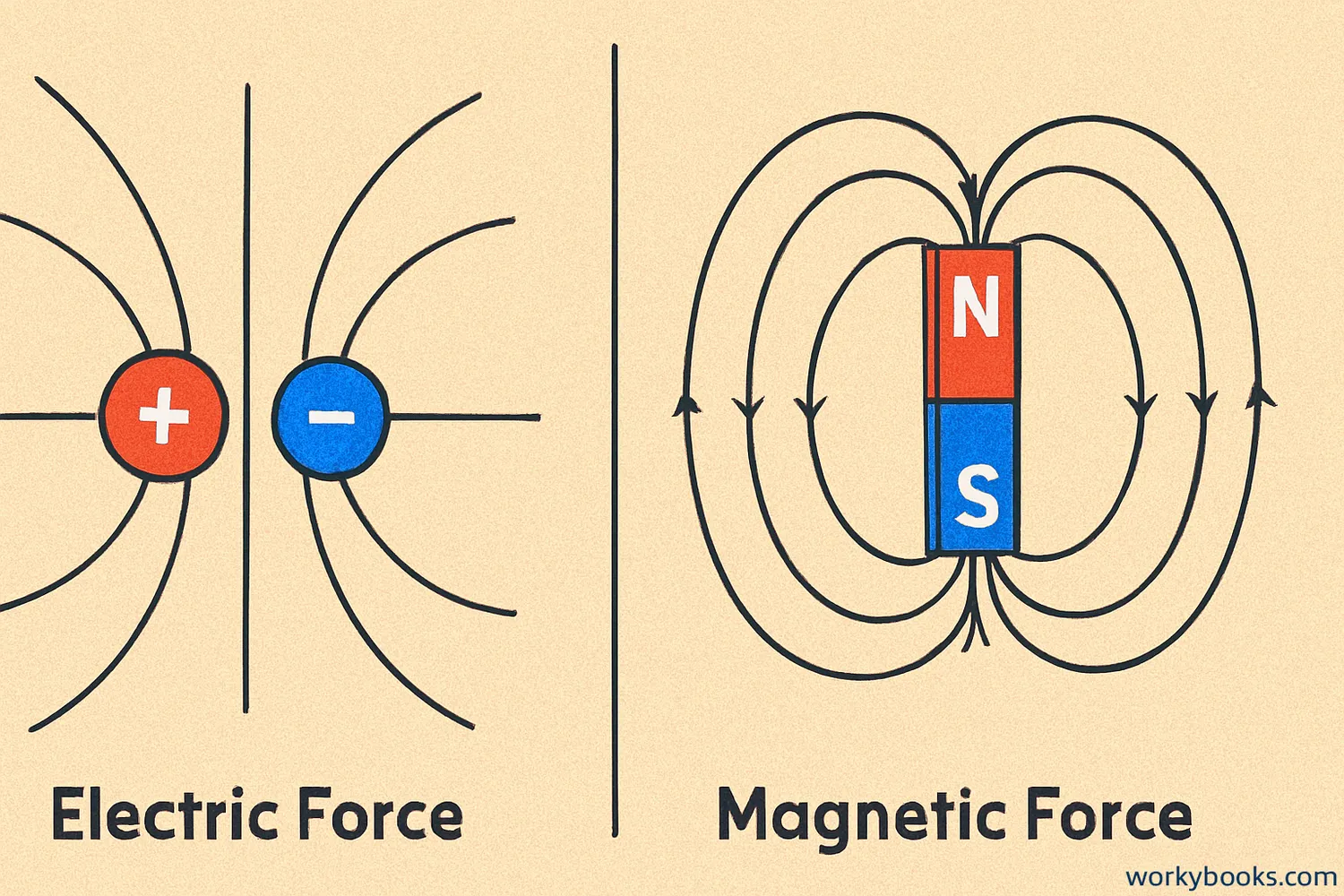
While electric and magnetic forces are related, they have important differences. Understanding these differences helps us understand how they work in our world.
| Aspect | Electric Force | Magnetic Force |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Electric charges | Moving charges or magnets |
| Acts on | Charged particles | Magnetic materials & moving charges |
| Field lines | Start and end on charges | Form closed loops |
| Monopoles | Exist (positive/negative) | Don't exist (always dipoles) |
| Strength | Can be strong or weak | Generally weaker than electric |
One key difference is that electric monopoles (single positive or negative charges) exist, but magnetic monopoles have never been found. Magnets always have both north and south poles.
Working Together: Electromagnetism
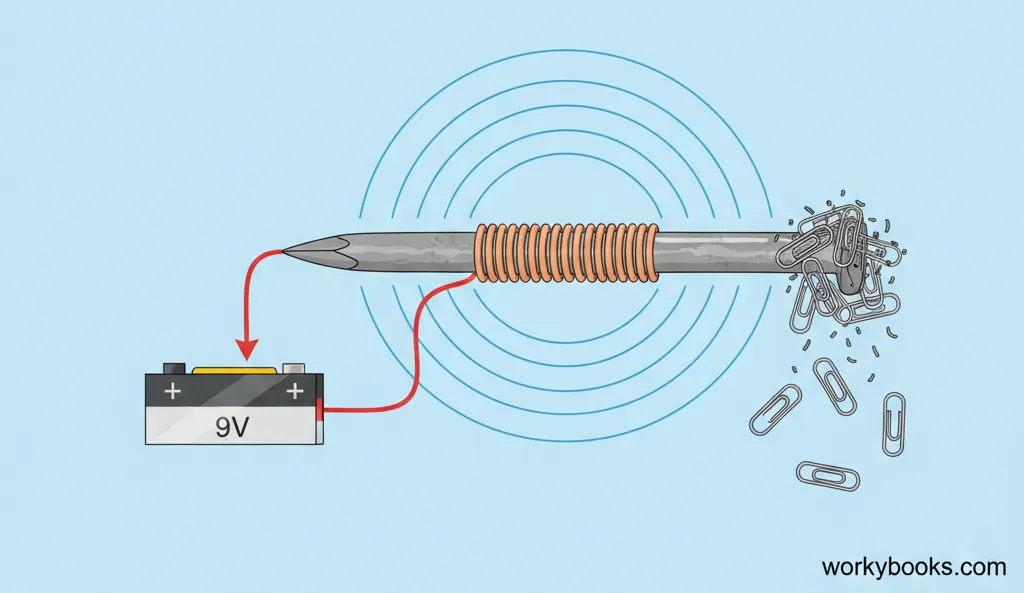
Electric and magnetic forces are closely related and often work together. This relationship is called electromagnetism. When electric charges move, they create magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields can create electric currents.
Electric Currents Create Magnetic Fields
When electricity flows through a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire.
Example: Electromagnets
Changing Magnetic Fields Create Electric Currents
When a magnet moves near a wire, it can create an electric current in the wire.
Example: Electric generators
This connection between electricity and magnetism is why we can generate electricity from moving magnets (in generators) and why we can create powerful electromagnets with electric currents.
Modern Application
MRI machines in hospitals use powerful electromagnets to create detailed images of the inside of our bodies!
Forces Quiz
Test your knowledge about electric and magnetic forces with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about electric and magnetic forces:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about electric and magnetic forces!
Animal Navigation
Some animals, like birds, turtles, and bees, can sense Earth's magnetic field and use it for navigation during migration!
Powerful Forces
Electromagnetism is about 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 times stronger than gravity! But we don't usually notice because most objects have balanced positive and negative charges.
Medical Marvel
Your heart produces electrical signals that can be measured by an ECG (electrocardiogram) machine. Doctors use these signals to check if your heart is working properly!
Solar Flares
Solar flares are enormous explosions on the Sun that release massive amounts of energy and charged particles. When these particles interact with Earth's magnetic field, they can create spectacular auroras but also disrupt power grids and communications!





