Electrodes - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how electricity flows through materials and powers our world!
What is an Electrode?
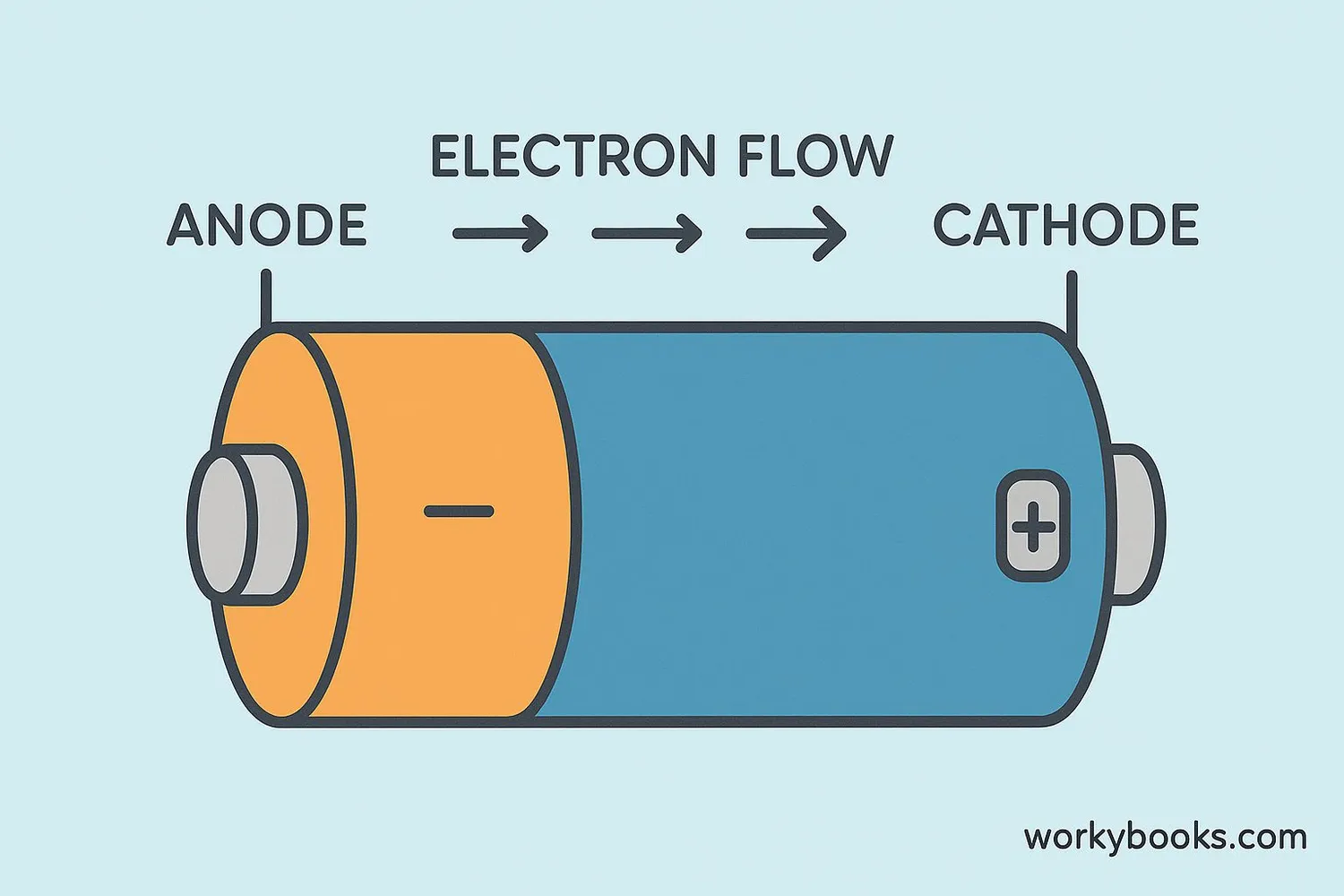
An electrode is a special conductor that helps electricity flow into or out of something. Think of it like a doorway for electricity!
Electrodes are made of materials that can conduct electricity, like metals (copper, zinc) or graphite. Every battery has two electrodes: a positive end (cathode) and a negative end (anode). When you connect these with a wire, electricity flows between them!
Simple definition: Electrodes are electrical conductors that connect non-metallic parts of a circuit to the metallic parts where electricity flows.
Real-World Example
When you put batteries in a flashlight, the metal ends that touch the spring are electrodes!
How Electrodes Work
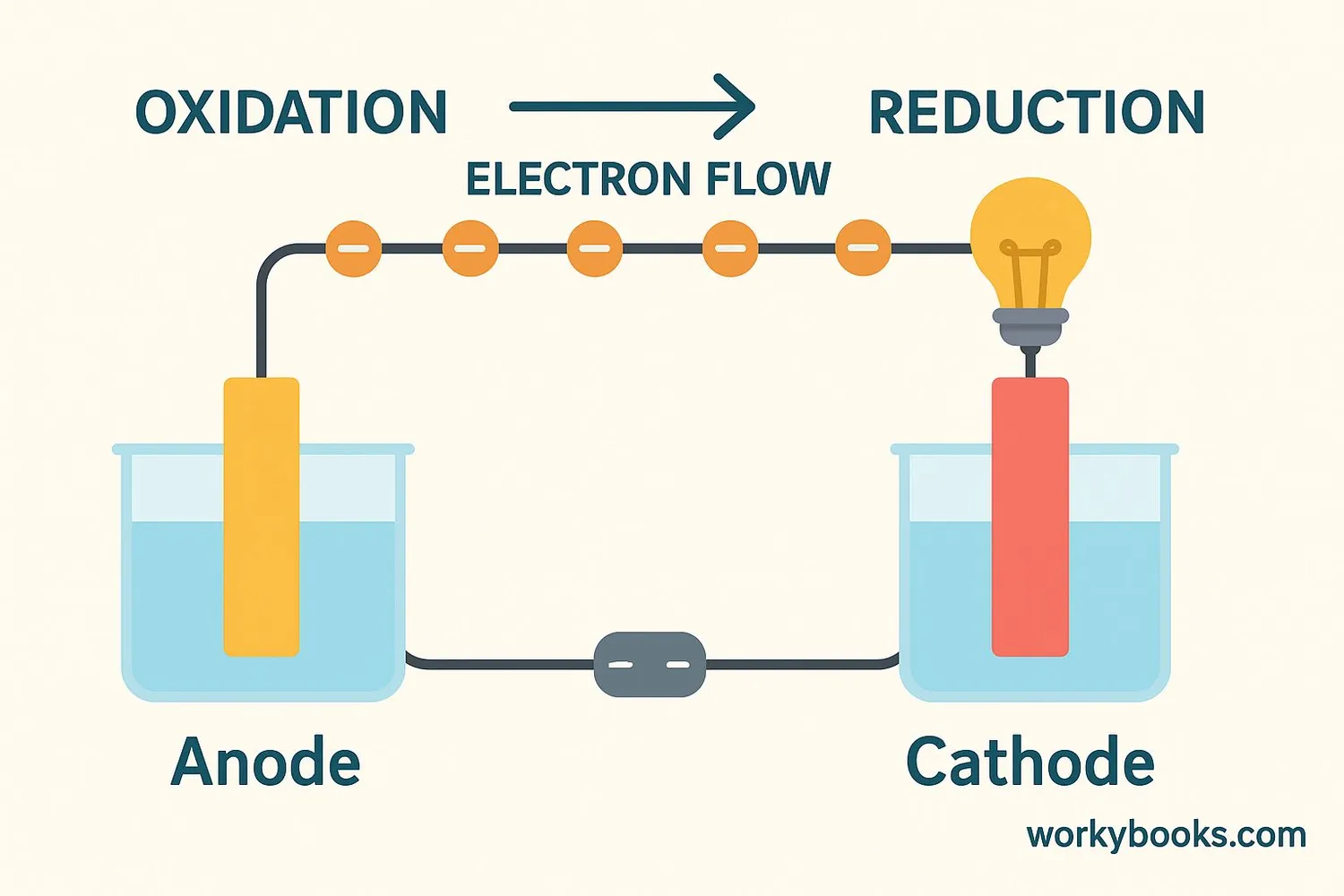
Electrodes work in pairs: the anode and the cathode. Here's how electricity flows between them:
Anode
Where oxidation happens - electrons leave from here
Cathode
Where reduction happens - electrons arrive here
Electron Flow
Electrons travel from anode to cathode through a circuit
Ion Flow
Ions move through electrolyte to balance the charge
Remember this: At the anode, oxidation occurs (loss of electrons). At the cathode, reduction occurs (gain of electrons).
This flow of electrons is what we call electricity! In batteries, chemical reactions create this electron flow. In electrolysis, electricity causes chemical reactions.
Memory Trick
AN-OX: Anode is where OXidation happens. RED-CAT: Reduction happens at the Cathode.
Types of Electrodes
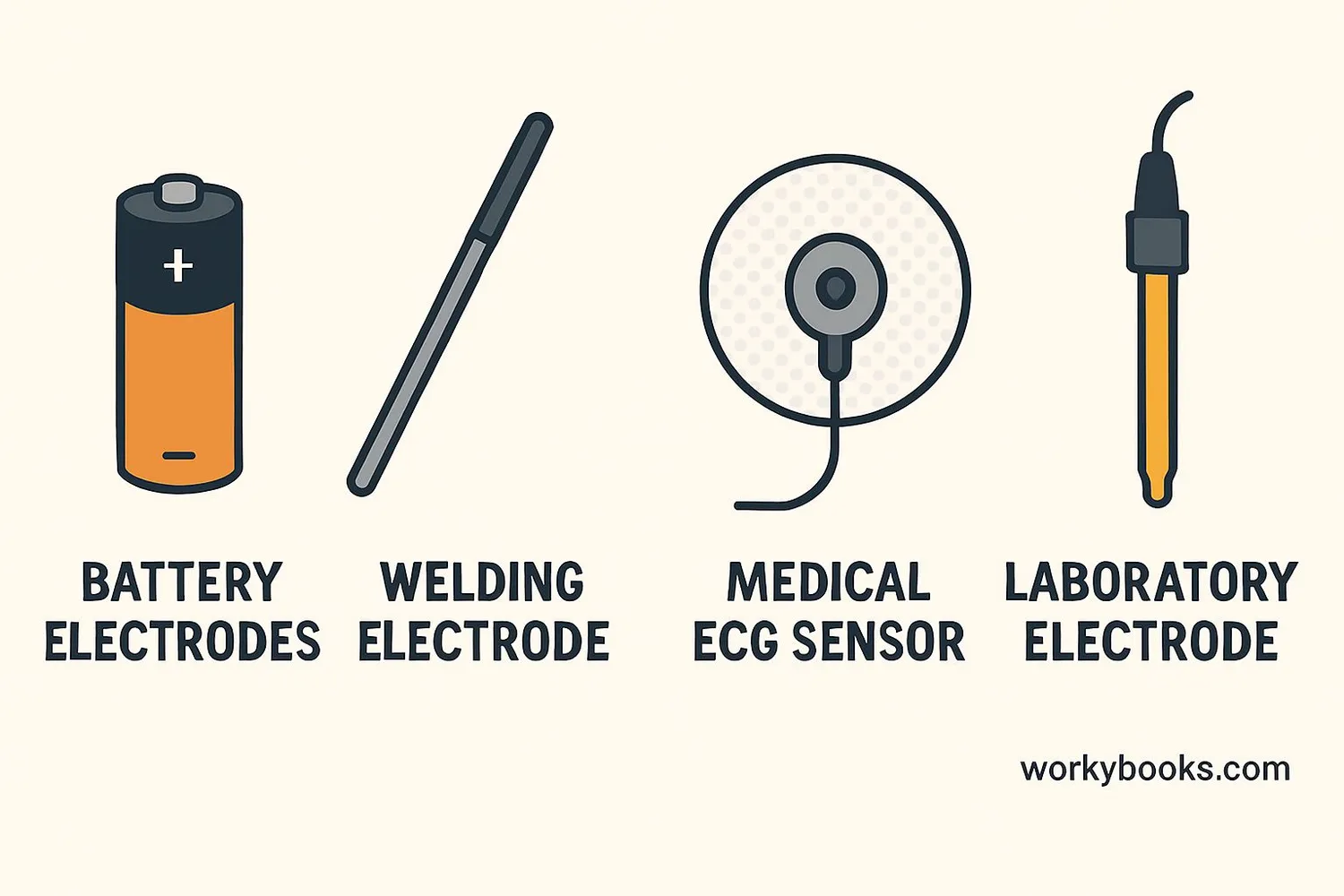
Electrodes come in different forms depending on their job:
Battery Electrodes
Positive (cathode) and negative (anode) terminals in batteries
Welding Electrodes
Metal rods that conduct electricity to create welding arcs
Medical Electrodes
Used in ECGs to measure heart electrical activity
Laboratory Electrodes
Used in experiments like electroplating or electrolysis
There are also two main types of electrochemical cells that use electrodes:
Galvanic Cells (like batteries): Convert chemical energy to electrical energy
Electrolytic Cells: Use electrical energy to cause chemical reactions (like electroplating)
Why Electrodes Matter
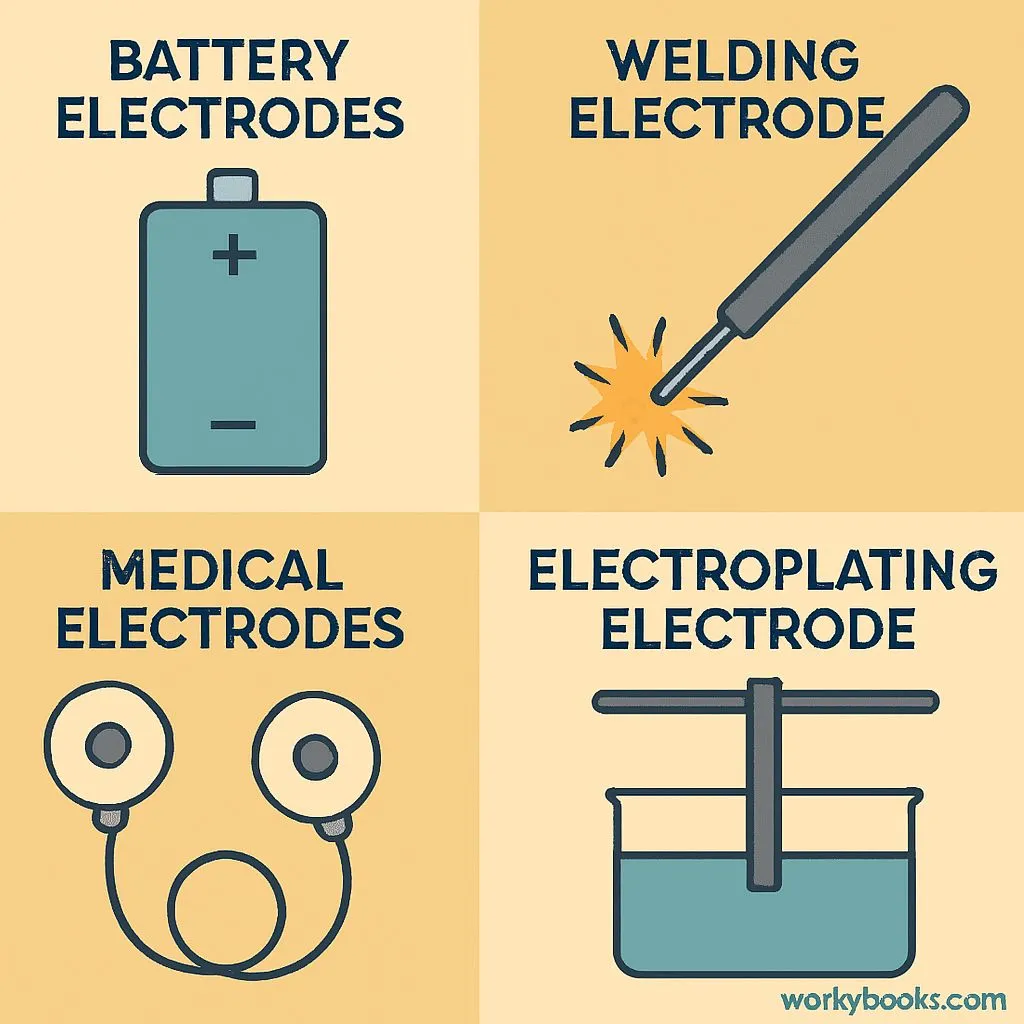
Electrodes are essential in our modern world. Here's why they're important:
Power Sources
All batteries need electrodes to store and release electricity
Manufacturing
Welding electrodes join metal parts in cars, buildings, and more
Medicine
Electrodes monitor heart activity (ECG) and brain waves (EEG)
Electroplating
Electrodes coat objects with thin layers of metal like gold or chrome
Without electrodes, we wouldn't have:
• Portable electronic devices
• Modern medical diagnostics
• Electric vehicles
• Many manufacturing processes
Next time you use your phone or see a skyscraper, remember the tiny electrodes making it all possible!
Electrodes Knowledge Check
Test what you've learned about electrodes with this quiz!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about electrodes:
Cool Electrode Facts
Discover some amazing facts about electrodes!
Historical Discovery
The term "electrode" was coined in 1834 by scientist Michael Faraday, combining the Greek words "elektron" (amber) and "hodos" (way or path).
Space Electrodes
NASA uses special electrodes in spacecraft to measure electrical activity in Earth's ionosphere during missions.
Brain Interfaces
Scientists are developing electrodes small enough to connect to individual brain cells, which could help people control computers with their thoughts!
Environmental Cleanup
Special electrodes can remove pollutants from water through a process called electrochemical treatment, helping clean our environment.





