Electromagnetic Waves - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover the invisible waves that power our world, from radio signals to sunlight!
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
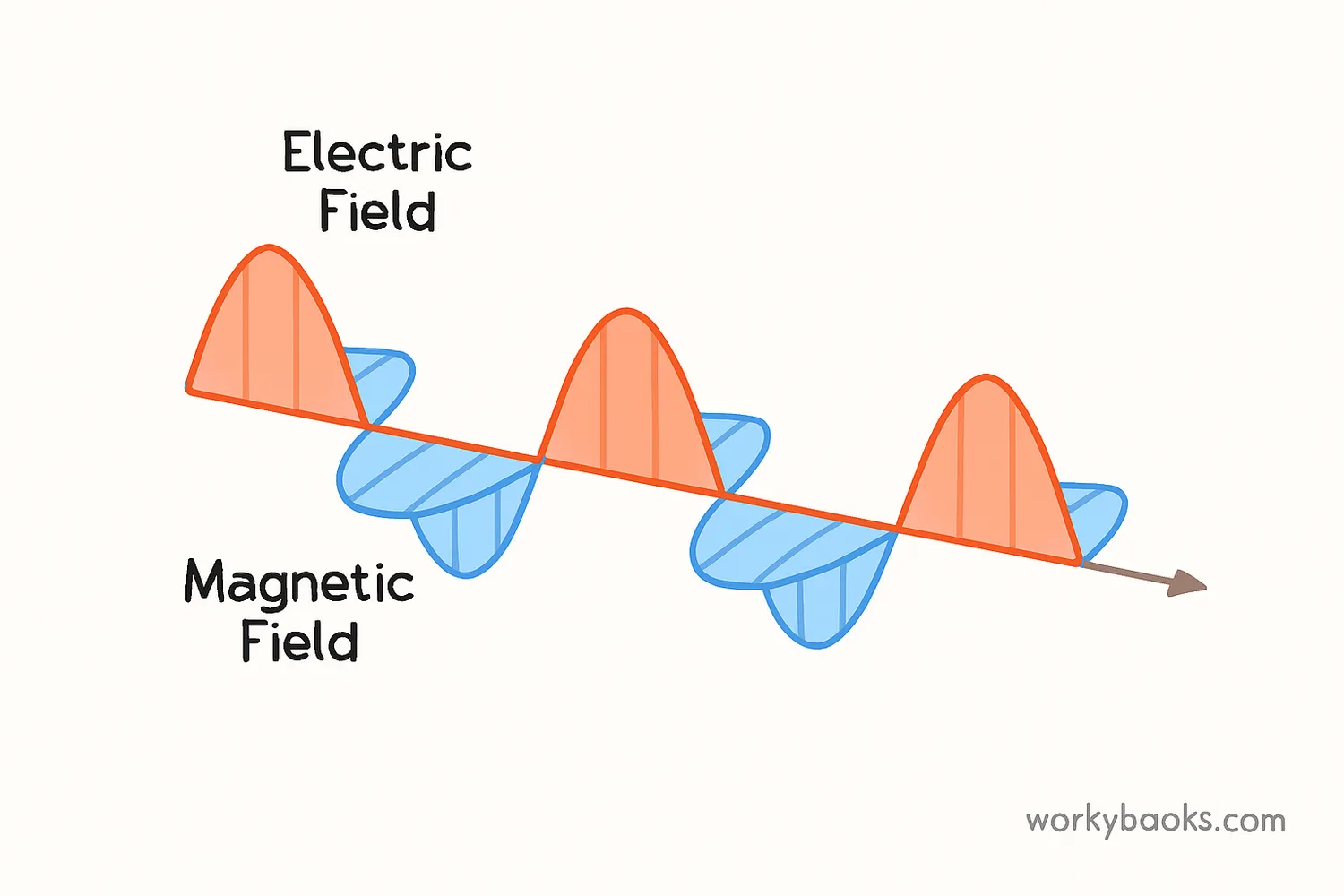
Imagine a wave, like a ripple on a pond. Now imagine a wave that doesn't need water to travel! That's what an electromagnetic (EM) wave is. These special waves are made of tiny, linked vibrations of electric and magnetic energy. They can travel through anything—air, glass, even the empty space of the cosmos!
Key Concept
An electromagnetic wave is a form of energy that travels as a wave of both electric and magnetic fields. They do not require a medium (like air or water) to travel, which is why they can move through the vacuum of space.
Properties of EM Waves
All electromagnetic waves have some important properties in common.
- The Speed of Light: All EM waves travel at the same incredible speed in a vacuum: the speed of light! This is about 300,000,000 meters per second. Nothing travels faster!
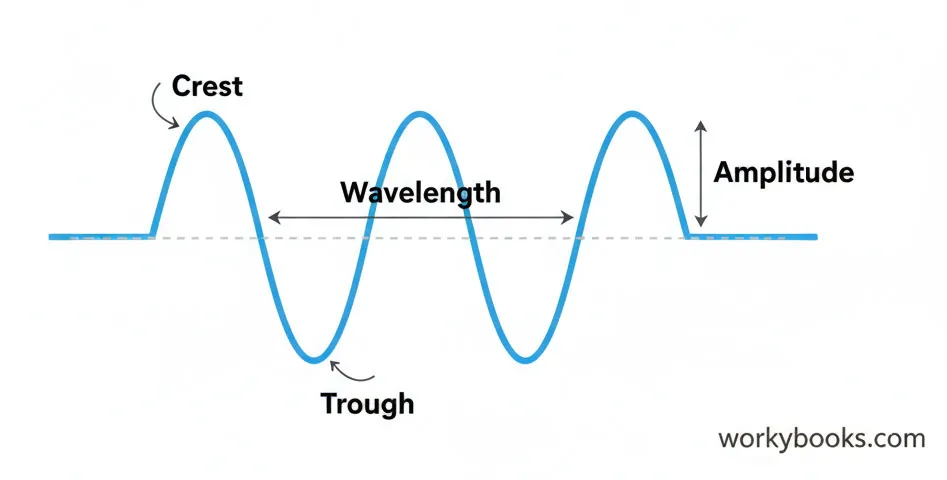
- Frequency and Wavelength: Think of a rope you are shaking. You can shake it fast or slow. The speed of your shaking is the frequency (how many waves pass a point each second). The distance between the waves is the wavelength. Waves with a high frequency have a short wavelength, and waves with a low frequency have a long wavelength.
- Energy: The energy of an EM wave depends on its frequency. Waves with a higher frequency (shorter wavelength) carry more energy. This is why some EM waves are more powerful than others.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a big "family" of all the different types of EM waves, arranged by their frequency and wavelength. From the lowest energy waves to the highest, the order is always the same.
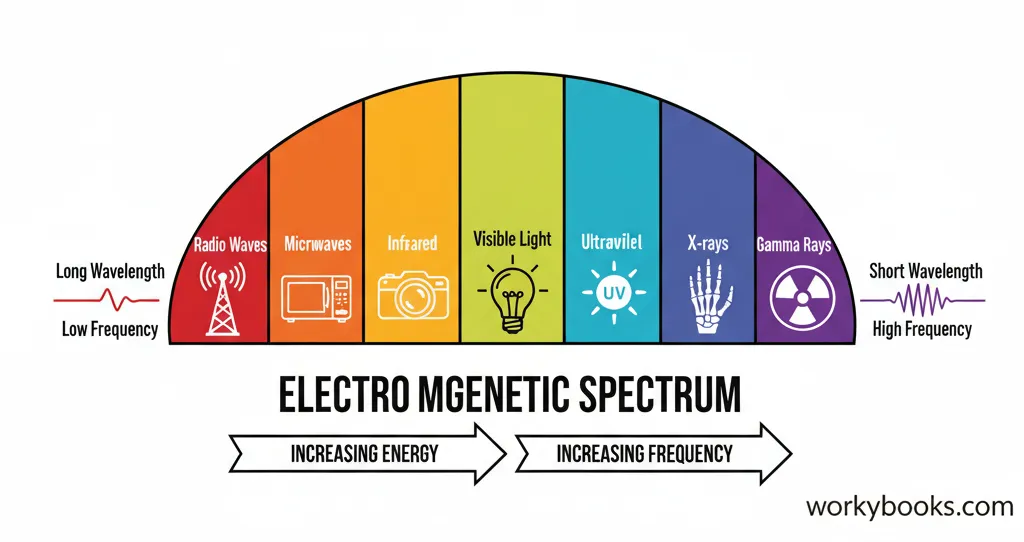
Radio Waves
These have the longest wavelengths and the least energy. We use them for radio, TV, and Wi-Fi signals.
Microwaves
Shorter than radio waves. They are used in microwave ovens to heat food and by cell phones to send signals.
Infrared Waves
These are the heat waves we feel from a fireplace or the sun. Night-vision goggles also use them to see in the dark.
Visible Light
This is the only part of the spectrum our eyes can see! It includes all the colors of the rainbow: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Ultraviolet (UV) Rays
Shorter than visible light. The sun gives off UV rays, which can cause sunburns. They are also used to sterilize objects.
X-rays
These powerful waves have a lot of energy and can pass through soft tissues, which is why doctors use them to see our bones.
Gamma Rays
The most energetic of all! Gamma rays are created by very powerful events in space and can be used in medicine to treat certain illnesses.
EM Waves Quiz
Test your knowledge about electromagnetic waves with this short quiz. Choose the best answer for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about electromagnetic waves:
Science Trivia
Here are some interesting facts about electromagnetic waves:
The Sun's Power
It takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds for visible light from the sun to travel 93 million miles and reach Earth!
Faster than a Blink
A single electromagnetic wave can travel around the entire Earth more than seven times in just one second!
Seeing the Invisible
Visible light is only a tiny part of the entire electromagnetic spectrum. We can only see this small portion of all the EM waves that exist around us!





