Gravitational Lensing - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how gravity bends light and helps us see distant galaxies!
What is Gravitational Lensing?

Gravitational lensing is a fascinating phenomenon where gravity bends light! Just like a magnifying glass can bend light to make things look bigger, massive objects in space like galaxies and black holes can bend the light from objects behind them.
Think of space as a stretchy rubber sheet. When you place a heavy object on it, it creates a dip. If you roll a marble near this dip, its path will curve. Similarly, when light passes near a massive object in space, its path curves because of gravity's pull.
This amazing effect was predicted by Albert Einstein over 100 years ago! His theory of general relativity taught us that gravity isn't just a force—it actually warps space and time itself.
Space Fact!
Gravitational lensing acts like a natural telescope, allowing us to see galaxies that would otherwise be too far away to observe!
How Gravitational Lensing Works
Gravitational lensing works because massive objects warp the fabric of space-time around them. Light always follows the straightest possible path through space, but if space itself is curved, light's path will curve too!
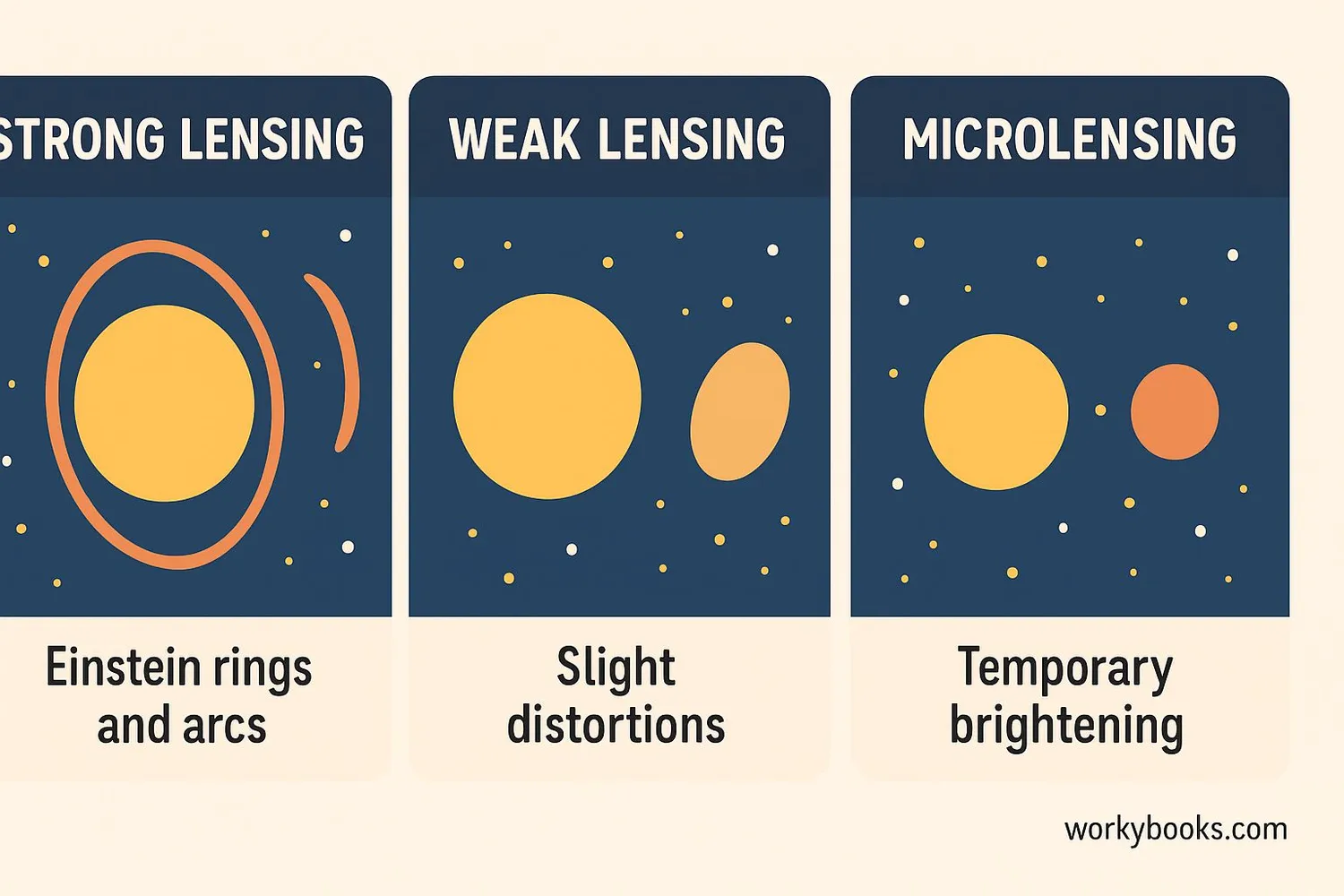
There are three main types of gravitational lensing:
Strong Lensing
When the alignment is perfect, it creates amazing patterns like Einstein rings or multiple images of the same galaxy
Weak Lensing
Small distortions in the shapes of many background galaxies that help us map dark matter
Microlensing
Temporary brightening of a star when a smaller object passes in front of it, used to find planets and other objects
The amount of bending depends on two things:
1. How massive the object is - More mass means more bending
2. How close the light passes - Closer passage means more bending
This is why huge galaxy clusters make the best gravitational lenses—they have enormous mass that can significantly bend light from galaxies behind them.
Einstein Rings
When a distant galaxy is directly behind a massive object, the light bends in a circle around it, creating a beautiful pattern called an Einstein ring!
Why Gravitational Lensing is Important

Gravitational lensing is incredibly important for astronomy and helps scientists make amazing discoveries about our universe! Here's why it matters:
Cosmic Magnifying Glass
It lets us see galaxies that are too far away to observe with regular telescopes
Dark Matter Detective
Helps scientists map invisible dark matter by how it bends light
Testing Einstein
Allows us to test Einstein's theory of general relativity on cosmic scales
Thanks to gravitational lensing, astronomers have:
• Discovered some of the most distant galaxies ever observed
• Created maps of dark matter distribution throughout the universe
• Found planets orbiting other stars
• Confirmed that Einstein's predictions were correct
The Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories use gravitational lensing to peer deeper into space than ever before, helping us understand the history and structure of our universe.
Gravitational Lensing Quiz
Test your knowledge about gravitational lensing with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about gravitational lensing:
Space Trivia: Gravitational Lensing
Discover some amazing facts about gravitational lensing!
Einstein's Prediction
Albert Einstein first calculated gravitational lensing in 1912, but didn't publish until 1936 because he thought we'd never be able to observe it!
Natural Telescope
The galaxy cluster Abell 370 acts as such a powerful gravitational lens that it magnifies galaxies behind it by up to 30 times!
First Discovery
The first gravitational lens was discovered in 1979—two quasars that looked like separate objects but were actually multiple images of the same quasar lensed by a galaxy.
Dark Matter Mapper
Gravitational lensing has helped create the most detailed maps of dark matter distribution in our universe, revealing the invisible scaffolding that holds galaxies together.





