Halogens - Definition, Facts, Examples, Quiz, Trivia
Discover the reactive elements that make up Group 17 of the periodic table!
What Are Halogens?
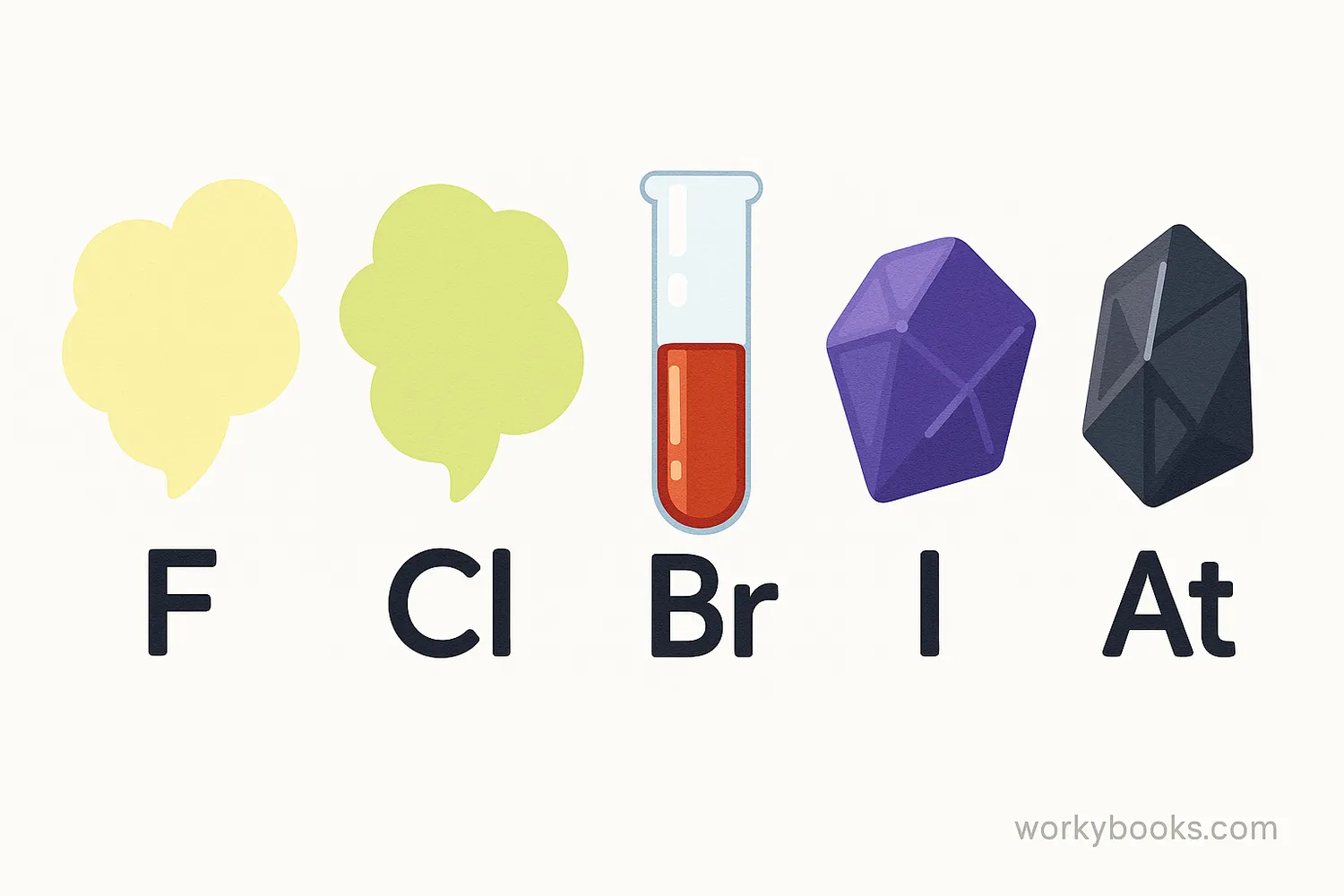
Halogens are a special group of elements on the periodic table that are known for being highly reactive. The word "halogen" comes from Greek words meaning "salt former" because these elements easily form salts when they react with metals.
There are five halogens: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). These elements are never found alone in nature because they're so reactive—they're always combined with other elements in compounds.
Science Fact!
Halogens are the only group in the periodic table that contains elements in all three states of matter at room temperature: gas (fluorine, chlorine), liquid (bromine), and solid (iodine, astatine).
Halogens in the Periodic Table
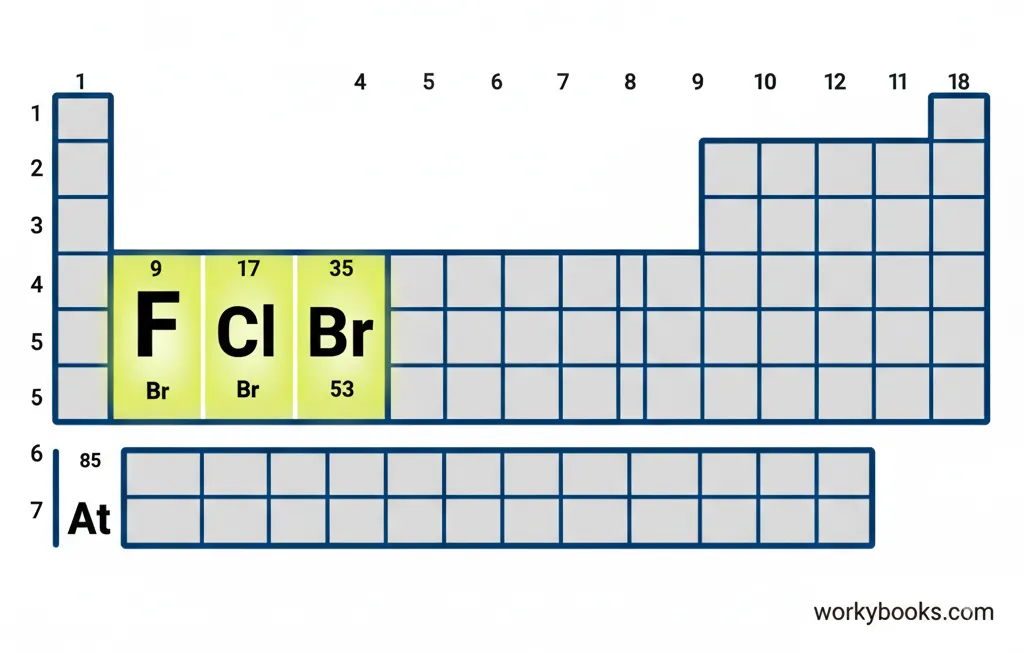
In the periodic table, elements are arranged in columns called groups and rows called periods. The halogens are found in Group 17, which is the second column from the right.
All halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell, which makes them highly likely to gain one more electron to become stable. This is why they're so reactive!
As we move down the group from fluorine to astatine, the elements become less reactive. Fluorine is the most reactive halogen, while astatine is the least reactive.
Properties of Halogens
Halogens share several important properties because they all have seven electrons in their outer shell:
Common Properties of Halogens:
- They are highly reactive nonmetals
- They have seven valence electrons
- They form diatomic molecules (two atoms bonded together)
- They form salts when combined with metals
- They become less reactive as you move down the group
- Their melting and boiling points increase down the group
Halogens also show interesting trends in their physical appearance. Fluorine is a pale yellow gas, chlorine is a greenish-yellow gas, bromine is a reddish-brown liquid, iodine is a dark purple solid, and astatine is a black solid.
Did You Know?
Halogens are so reactive that they can even form compounds with noble gases, which were once thought to be completely unreactive!
Halogen Examples
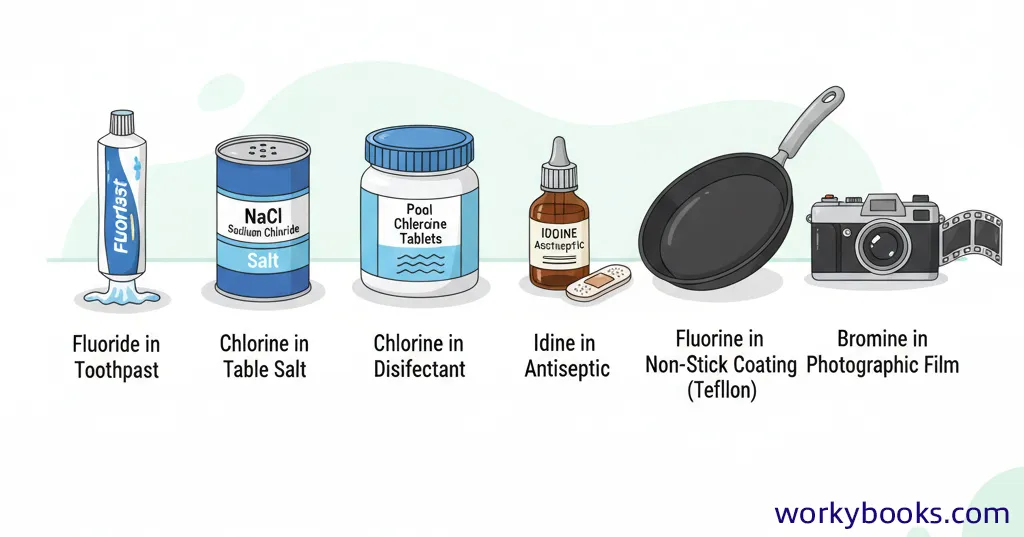
While we rarely encounter pure halogens in daily life (they're too reactive!), we use many compounds containing halogens every day:
Fluorine Compounds
Toothpaste (fluoride), non-stick pans (Teflon)
Chlorine Compounds
Table salt (sodium chloride), swimming pool disinfectants
Bromine Compounds
Flame retardants, photographic film
Iodine Compounds
Disinfectants (iodine solution), table salt (iodized salt)
These compounds are much safer and more stable than the pure halogen elements. For example, while chlorine gas is poisonous, sodium chloride (table salt) is essential for our bodies!
Uses of Halogens
Halogens and their compounds have countless uses in industry, medicine, and everyday life:
Important Uses of Halogens:
- Water purification: Chlorine kills harmful bacteria in drinking water and swimming pools
- Medicine: Fluoride prevents tooth decay, iodine is used as disinfectant
- Agriculture: Chlorine compounds are used in pesticides
- Technology: Halogens are used in lighting and electronics
- Manufacturing: Used in plastics, solvents, and refrigerants
While halogens are incredibly useful, some halogen compounds can be harmful to the environment. For example, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were once used in refrigerators and aerosol sprays but were found to damage the ozone layer. Today, safer alternatives are used instead.
Halogen Quiz
Test your knowledge about halogens with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about halogens:
Science Trivia
Discover some amazing facts about halogens!
Fluorine's Special Power
Fluorine is the most reactive of all elements—it can form compounds with almost every other element, including some noble gases which were once thought to be completely unreactive!
Life-Saving Chlorine
Chlorination of drinking water (adding chlorine to kill germs) is considered one of the greatest public health achievements of the 20th century, dramatically reducing diseases like cholera and typhoid.
Bromine's Bright History
Before digital photography, bromine compounds were essential for photographic film. Silver bromide is sensitive to light, making it perfect for capturing images.
Iodine for Health
Iodine is essential for thyroid function. Iodine deficiency used to cause goiter (swelling of the thyroid gland), which is why iodine is now added to table salt in many countries.





