Law of Conservation of Mass - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how matter can change form but never disappear!
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?

The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental scientific principle discovered by French chemist Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century. It states that:
Mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction or physical change.
This means that the total mass of substances before any change (called reactants) must equal the total mass of substances after the change (called products). Matter simply changes form but never disappears!
Important Fact!
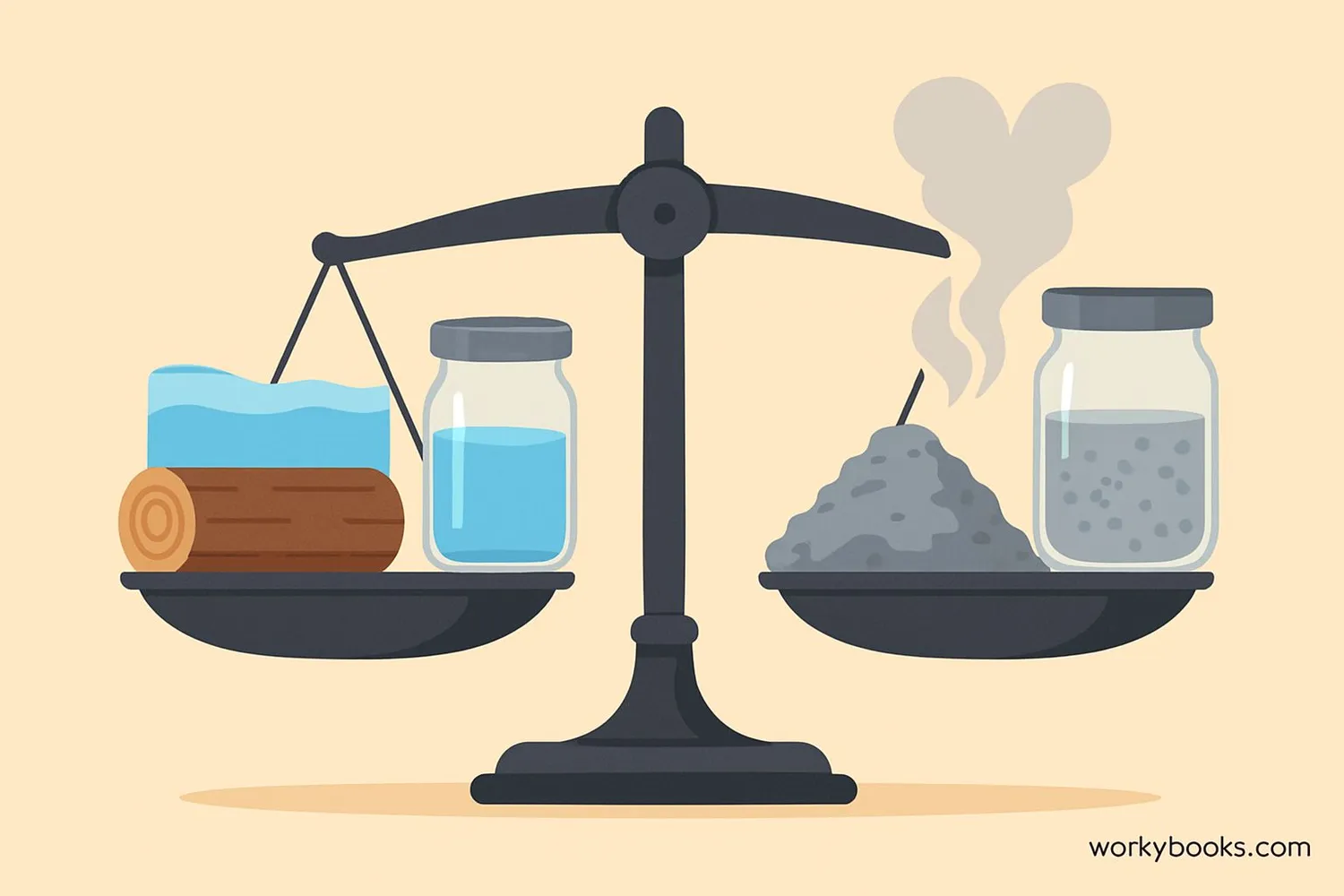
This law applies to both chemical reactions (like burning wood) and physical changes (like melting ice).
How the Law Works
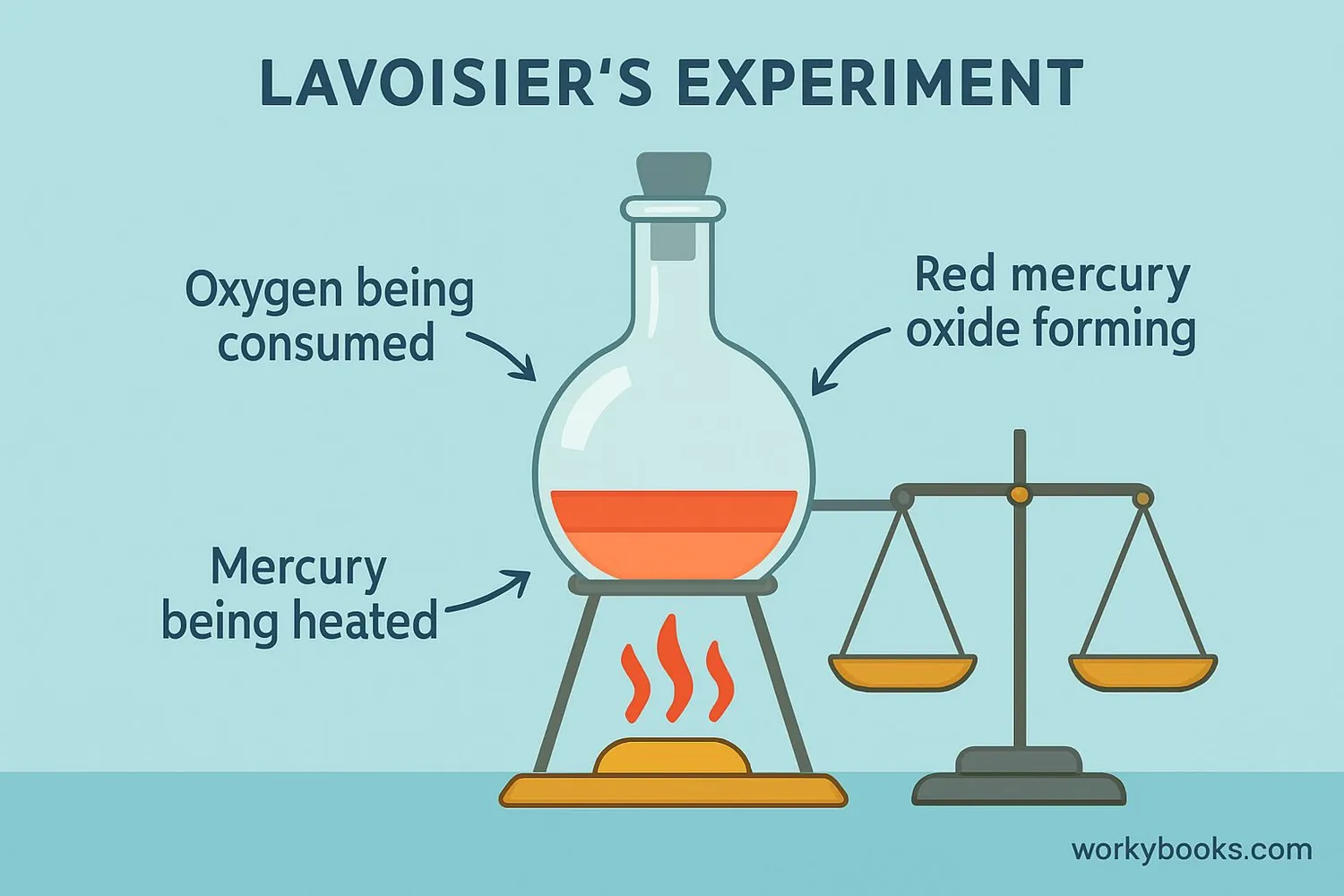
Antoine Lavoisier proved this law with careful experiments. He showed that when mercury was heated in a sealed container, the mass before heating equaled the mass after heating, even though the mercury had changed into a different substance (mercury oxide).
Let's look at some examples:
Physical Change
Melting ice: 100g ice = 100g water
Chemical Reaction
Burning wood: Mass of wood + oxygen = mass of ash + gases
Dissolving
Salt in water: Mass of salt + water = mass of saltwater
Isolated Systems
For the law to hold true, the system must be "isolated" - meaning no matter enters or leaves during the change.
Importance & Applications
The Law of Conservation of Mass is crucial in science and everyday life:
Chemical Engineering
Used to balance chemical equations and design industrial processes
Rocket Science
Calculates fuel requirements for space missions
Environmental Science
Tracks pollutants and materials in ecosystems
This law also connects to Einstein's famous equation E=mc², showing that mass and energy are related. But in everyday chemical reactions, the mass change from energy conversion is too small to measure!
Conservation of Mass Quiz
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to common questions about conservation of mass:
Science Trivia
Discover amazing facts about conservation of mass:
Lavoisier's Precision
Antoine Lavoisier used balances that could detect mass differences as small as 0.0005 grams - about the weight of a snowflake!
Space Travel
Rocket scientists must account for conservation of mass precisely. For a trip to Mars, about 90% of a rocket's initial mass is fuel!
Earth's Constant Mass
Earth gains about 40,000 tons of space dust each year but loses atmosphere to space. The net mass change is less than 0.000000000001% per year!
Mass-Energy Connection
In nuclear reactions, converting just 1 gram of mass to energy could power a 100-watt lightbulb for about 30,000 years!





