Monomers - Definition, Examples, Quiz, FAQ, Trivia
Discover how small molecules come together to create the materials around us!
What is a Monomer?
A monomer is a small molecule that can join together with other similar molecules to form a larger structure called a polymer. The word "monomer" comes from Greek words meaning "one part."
Think of monomers like individual LEGO bricks. Each brick by itself is simple, but when you connect many bricks together, you can build amazing structures like castles, cars, or spaceships!
In chemistry, monomers are the basic building blocks that create many materials we use every day, from plastic bottles to rubber tires.
Science Fact!
The process of monomers joining together to form polymers is called polymerization - just like connecting building blocks!
Monomer Examples
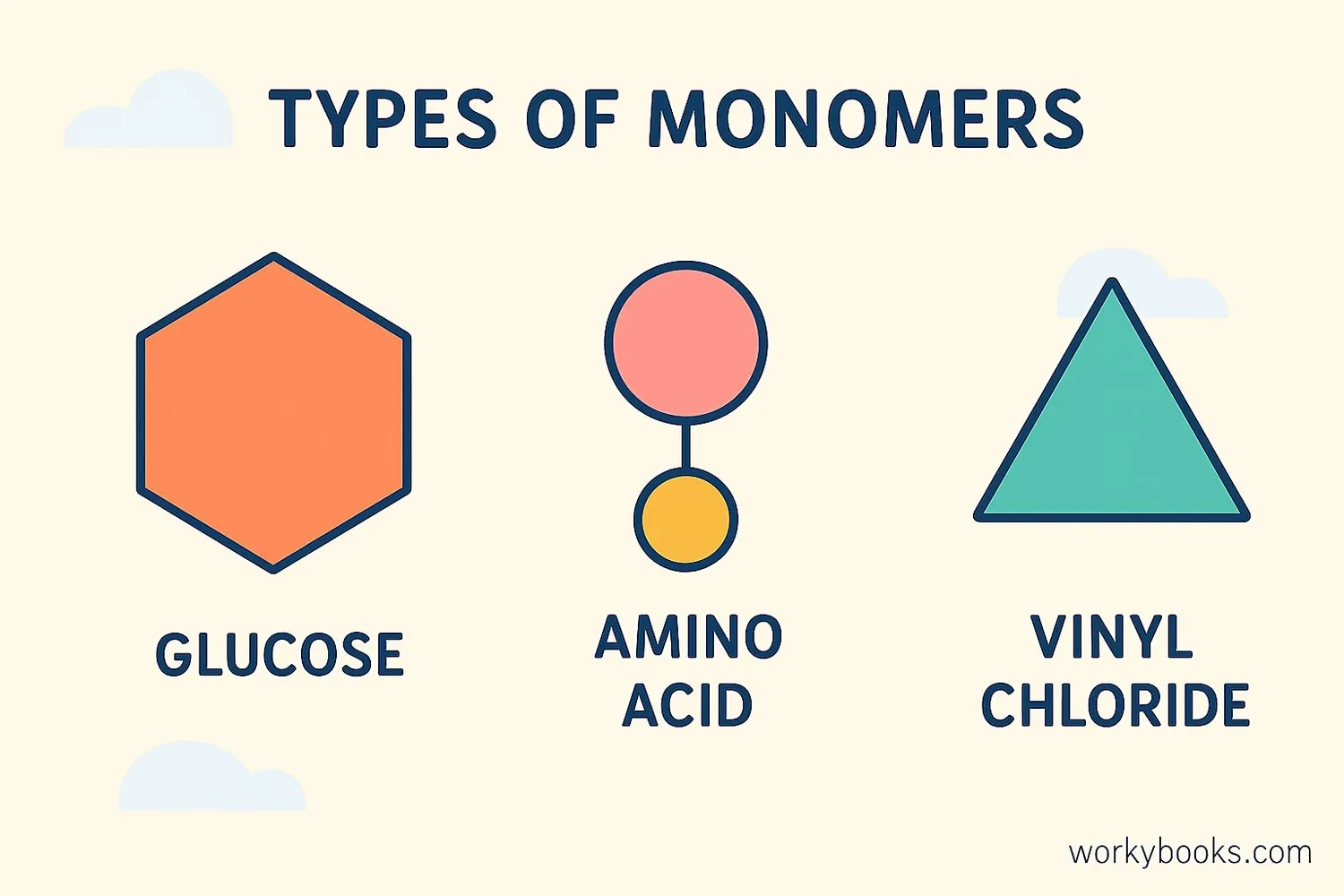
Monomers are all around us! Here are some common examples:
Glucose
A sugar molecule that is the monomer for starch and cellulose
Amino Acids
The monomers that join together to form proteins
Nucleotides
Monomers that form DNA and RNA, our genetic material
Vinyl Chloride
A monomer used to make PVC plastic for pipes and bottles
Ethylene
A gas that serves as the monomer for polyethylene plastic
These monomers join together in different ways to create the materials and substances that make up our world. Some occur naturally, while others are created in laboratories for specific purposes.
Monomer and Polymer Relationship
The relationship between monomers and polymers is like the relationship between letters and words:
Monomers are like individual letters. Each letter has its own identity, but when you combine them in specific ways, they form words with completely new meanings.
Polymers are like words formed from letters. They have properties and functions that are different from the individual letters (monomers) that make them up.
Connection Fact!
Just as different arrangements of letters create different words (cat vs. act), different arrangements of monomers create polymers with different properties!
When monomers join together to form a polymer, the process is called polymerization. This can happen in different ways:
• Addition polymerization: Monomers add to a growing chain without losing any atoms
• Condensation polymerization: Monomers join together while losing small molecules like water
Monomer vs Polymer
While monomers and polymers are related, they have important differences. Understanding these differences helps us understand how materials are formed and how they behave.
| Characteristic | Monomer | Polymer |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small, simple molecule | Large, complex molecule |
| Molecular Weight | Low | High |
| Structure | Single unit | Chain of repeating units |
| Physical State | Often gases or liquids | Often solids |
| Strength | Weak individually | Strong when connected |
| Example | Ethylene (a gas) | Polyethylene (plastic) |
This comparison shows how simple building blocks (monomers) can transform into completely different materials (polymers) with new properties when they connect together.
Transformation Fact!
Ethylene gas (a monomer) becomes solid polyethylene plastic (a polymer) through polymerization - quite a transformation!
Monomer Knowledge Check
Test your understanding of monomers with this quiz! Answer all 5 questions to see how much you've learned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about monomers:
Interesting Monomer Facts
Discover some amazing facts about monomers and polymers!
DNA Building Blocks
Your DNA is made from just 4 different types of nucleotide monomers! The sequence of these monomers determines your unique genetic code.
Plastic Revolution
The development of synthetic polymers (plastics) from simple monomers revolutionized manufacturing in the 20th century, creating lightweight, durable materials.
Protein Power
Your body can create over 50,000 different proteins from just 20 different amino acid monomers! The arrangement determines each protein's function.
Recycling Challenge
Different plastics are made from different monomers, which makes recycling complicated. That's why plastic products have recycling codes to identify what type of polymer they are.





